The calculation of implied volatility can be done in the following steps:
- Gathered the inputs of the Black and Scholes model, such as the Market Price of the underlying, which could be stock,...
- Now, one has to input the above data in the Black and Scholes Model.
- Once the above steps are completed, one needs to start doing an iterative search by trial and error.
How do you calculate implied volatility?
The factors are as follows:
- The market price of the option
- The underlying stock price
- The strike price
- The time to expiration
- The risk-free interest rate
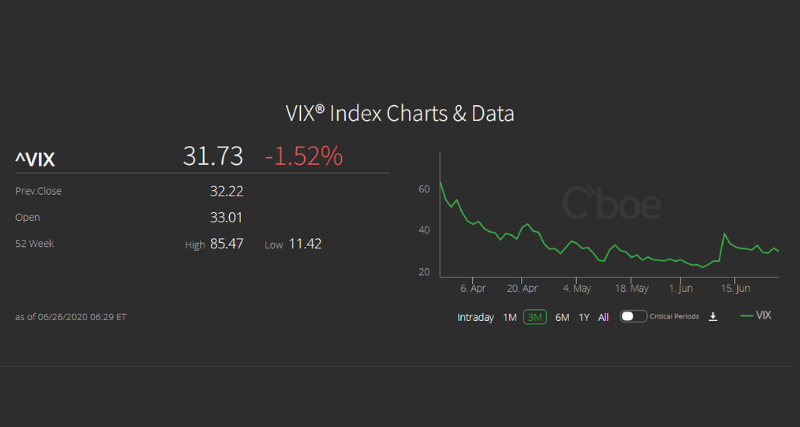
How implied volatility (VIX) can impact a trade?
How Implied Volatility (VIX) Can Impact a Trade. Implied Volatility (IV) is a measure of how much the “market place” expects the price of an underlying stock or index to move; i.e. the volatility that the market itself is implying for the underlying stock or index. The VIX index represents the Implied Volatility for the S&P 500 index (SPX ...
What exactly does implied volatility mean?
The term implied volatility refers to a metric that captures the market's view of the likelihood of changes in a given security's price. Investors can use implied volatility to project future moves and supply and demand, and often employ it to price options contracts.
What determines the volatility of a stock?
TL;DR
- Market volatility is a measure of the variance of returns on a market index over a given period.
- High volatility is associated with high risk and unpredictability.
- Historical market volatility represents the current market volatility based on historical returns. ...
- A market is considered volatile if it rises or falls more than 1% over a given period.

Is 80% implied volatility high?
Put simply, IVP tells you the percentage of time that the IV in the past has been lower than current IV. It is a percentile number, so it varies between 0 and 100. A high IVP number, typically above 80, says that IV is high, and a low IVP, typically below 20, says that IV is low.
How do you calculate implied volatility in Excel?
First, you must set all the parameters that enter option price calculation:Enter 53.20 in cell C4 (Underlying Price)Enter 55 in cell C6 (Strike Price)Cell C8 contains volatility, which you don't know. ... Enter 1% in cell C10 (Interest Rate)Enter 2% in cell C12 (Dividend Yield) ?More items...
How do you calculate stock volatility in NSE?
Volatility is found by calculating the annualized standard deviation of daily change in price. If the price of a stock moves up and down rapidly over short time periods, it has high volatility. If the price almost never changes, it has low volatility. Stock with High Volatility are also knows as High Beta stocks.
How does R calculate implied volatility?
Implied Volatility is generally calculated by solving the inverse pricing formula of an option pricing model. This means that instead of using the pricing model to calculate the price of an option, the price that is observed in the market is used as an input and the output is the volatility.
How do you find implied volatility from Black-Scholes?
Calculating Implied Volatility Plugging the option's price into the Black-Scholes equation, along with the price of the underlying asset, the strike price of the option, the time until expiration of the option, and the risk-free interest rate allow one to solve for volatility.
What is the best volatility indicator?
Top 5 Volatility Indicators:Bollinger Bands:Keltner Channel:Donchian Channel:Average True Range (ATR):India VIX:
How do I find volatile stocks for intraday?
Monitoring Intraday Volatility You can do this by using volatility and top gainers/top losers filters on stock screeners such as FINVIZ or TradingView. Most brokers and trading platforms will also provide this information in real time. Watch for changes in the list throughout the day.
Which indicator is used for volatility?
Some of the most commonly used tools to gauge relative levels of volatility are the Cboe Volatility Index (VIX), the average true range (ATR), and Bollinger Bands®.
What is implied volatility?
Implied volatility is one of the important parameters and a vital component of the Black-Scholes model which is an option pricing model that shall give the option’s market price or market value. Implied volatility formula shall depict where the volatility of the underlying in question should be in the future and how the marketplace sees them. ...
Which method is used to calculate implied volatility?
Now we can use the interpolation method, to calculate the implied volatility at which it shall exist:
What inputs are used in Black and Scholes model?
Gathered the inputs of the Black and Scholes model, such as the Market Price of the underlying, which could be stock, the market price of the option, the strike price of the underlying, the time to expire, and the risk-free rate.
Can interpolation be near implied volatility?
One can also do interpolation , which could be near to the implied volatility, and by doing this, one can get approximate nearby implied volatility. This is not simple to calculate as it requires care at every stage to compute the same.
Can implied volatility be forecast?
However, it has to be not ed that the implied volatility will not forecast in which the direction an option is leaning towards. This implied volatility can be used to compare with historical volatility, and hence decisions can be made based on those cases. This could be the measure of risk that the trader is putting into.
What is iterative search?
The iterative search is one method using the Black-Scholes formula to calculate implied volatility.
How to calculate implied volatility?
Implied volatility is calculated by taking the market price of the option, entering it into the Black-Scholes formula, and back-solving for the value of the volatility. But there are various approaches to calculating implied volatility. One simple approach is to use an iterative search, or trial and error, to find the value of implied volatility.
What is implied volatility?
Implied volatility shows how the marketplace views where volatility should be in the future. Since implied volatility is forward-looking, it helps us gauge the sentiment about the volatility of a stock or the market. However, implied volatility does not forecast the direction in which an option is headed.
What is the Black Scholes model?
It is a mathematical model that projects the pricing variation over time of financial instruments, such as stocks, futures, or options contracts.
Why is the Black Scholes formula important?
The Black-Scholes formula has been proven to result in prices very close to the observed market prices. And, as we've seen, the formula provides an important basis for calculating other inputs, such as implied volatility. While this makes the formula quite valuable to traders, it does require complex mathematics.
Is implied volatility forward looking?
Since implied volatility is forward-looking, it helps us gauge the sentiment about the volatility of a stock or the market. However, implied volatility does not forecast the direction in which an option is headed. In this article, we'll review an example of how implied volatility is calculated using the Black-Scholes model and we'll discuss two different approaches to calculate implied volatility.
Who is Steven Nickolas?
Steven Nickolas is a freelance writer and has 10+ years of experience working as a consultant to retail and institutional investors. Implied volatility is the parameter component of an option pricing model, such as the Black-Scholes model, which gives the market price of an option.
How to find implied volatility?
While these models are handy to know about, the easier way to determine implied volatility is to use an online implied volatility calculator or choose an online brokerage that offers advanced stock screeners . A stock screener that filters for implied volatility can save you time and effort when trying to determine which stocks or options to invest in. This is something you don’t get at every brokerage, so it’s important to compare online trading platforms carefully.
What are the indicators used to track the price of a stock?
When trading stocks or stock options, there are certain indicators you may use to track price momentum. Implied volatility, which measures how likely a security’s price is to change, can be useful for determining whether the market is set for bearish or bullish movements. It can also be important when pricing options contracts.
What is a stock screener?
A stock screener that filters for implied volatility can save you time and effort when trying to determine which stocks or options to invest in. This is something you don’t get at every brokerage, so it’s important to compare online trading platforms carefully.
What does it mean when implied volatility is high?
When implied volatility is high that can signal that a large price swing is ahead, but it won’t tell you which way the swing will move. Similarly, low implied volatility can be a sign that a security’s price is set to remain relatively stable, without any rapid up or down movements.
How does implied volatility affect stock price?
For example, the release of a quarterly earnings report or the announcement of a merger can affect volatility levels and in turn, stock prices. When trading options, using implied volatility can help you identify a range from the high to low point of a stock’s price before the option expires. Specifically, it can tell you whether your beliefs about which way a stock’s price is headed are supported by the general market consensus.
What is the binomial model?
There’s also the binomial model, which uses a tree-style diagram to illustrate volatility at varying levels. With this model, you get lots of possibilities for which way a stock or option’s price could go. You might use this pricing model if you’re trading American options, which are options that can be exercised at any time prior to the expiration date.
How to get a quick overview of your investment?
One way you can get a quick and relatively accurate overview of your investing is by taking advantage of a free, easy-to-use investment calculator.
How to find the change in stock price?
First, divide the number of days until the stock price forecast by 365, and then find the square root of that number. Then, multiply the square root with the implied volatility percentage and the current stock price. The result is the change in price.
How is implied volatility calculated?
It is calculated through a formula using several variables in market and stock price.
Why use implied volatility?
Investors can use implied volatility to help judge market sentiment of a company stock, but it doesn't always take into account certain market factors. Because implied volatility considers historical data and certain market conditions, it doesn't forecast larger market swings based on investor emotions.
What is volatility in stocks?
Volatility is a measurement of how much a company's stock price rises and falls over time. Stocks with high volatility see relatively large spikes and dips in their prices, and low-volatility stocks show more consistent gains and losses.
How long do you have to know when an option expires?
When calculating for options trading, investors need the number of days until the option expires.
Can volatility be realized?
Once volatility is no longer "implied" -- it becomes "realized" -- an investor can look at historical volatility. Over a given period, a security's movement regarding its price offers a comparison from its historical volatility to its implied volatility. This comparison may help investors make investing decisions.
Who is Terry Lane?
Terry Lane has been a journalist and writer since 1997. He has both covered, and worked for, members of Congress and has helped legislators and executives publish op-eds in the “Wall Street Journal,” “National Journal” and “Politico.". He earned a Bachelor of Science in journalism from the University of Florida.
Why do stock traders use options alerts?
Therefore, most serious stock traders use a leading options alert service to deliver them implied volatility data or they use a charting tool to get their information . While these tools help professional brokers gain insight into the market, anyone who pays for the services can get information just as quickly as a professional day trader.
Why is risk limited?
Why is risk limited? Well, this is where implied volatility comes into play. As mentioned above, implied volatility is a number that is calculated based on certain market conditions. Then this number is used to derive the price of the options contract.
Why are options more volatile?
This is why options stocks with a longer period until expiration are more volatile—because there is more time left for them to change.
Why are options contracts cheaper?
Therefore an options contract with low volatility will likely be cheaper—because it is less risky— while an option for a stock with higher volatility will be more expensive. This enables a trader to evaluate risk before they buy, and if they do purchase the option, and the stock goes south, they can choose not to execute the contract, therefore having explored the market without damaging their portfolio.
What factors affect implied volatility?
Besides just supply and demand , another factor that affects implied volatility is the amount of time an option has remaining before it expires. Options that have only a few days left, or are only given a few days to begin with, tend to have a lower volatility, while options with more days left have a higher volatility. This is because the more days left on the option, the more chances a security has to drastically change in price.
What is the determining factor when it comes to calculating implied volatility?
But the major determining factor when it comes to calculating implied volatility is the law of supply and demand. This is because supply and demand have a huge effect on the prices of securities. When there is a higher demand the price will rise, and when the supply rises, the price will drop.
What is implied volatility?
Implied volatility is a term that refers to a certain measurement that establishes the likelihood a particular market is to change over time. So a security with a high volatility will be one that has a price that is going up and down quite frequently, while a stock with low volatility will have a price that is fluctuating much more slowly.
How to find the annualized standard deviation of the S&P 500?
Find the annualized standard deviation — annual volatility — of the the S&P 500 by multiplying the daily volatility by square root of the number of trading days in a year, which is 252. In cell D14, type "=SQRT (252)*D13" to determine that the annual volatility of the index is 11.72%.
How to calculate weekly volatility?
You can also calculate weekly volatility by multiplying the daily volatility by square root of the number of trading days in a week , which is 5. Using the formula "=SQRT (5)*D13" indicates that the weekly volatility is 1.65%.
How to find daily volatility of S&P 500?
Find the daily standard deviation — daily volatility — of the sample by using the STDEV.S function. Type "=STDEV.S (D4:D12)" in cell D13 to find the daily volatility of the S&P 500 within the sample data.
What is the biggest shortcoming of standard deviation?
The biggest shortcoming to using standard deviation to calculate volatility is that standard deviation measurements are based on the assumption that returns are normally distributed. With normal distribution, also known as a bell curve, more results cluster near the center and fewer results are significantly above or below average.
What is portfolio volatility?
Portfolio volatility is a measure of portfolio risk, meaning a portfolio's tendency to deviate from its mean return. Remember that a portfolio is made up of individual positions, each with their own volatility measures. These individual variations, when combined, create a single measure of portfolio volatility.
How to calculate the interday change in the value of the index?
Starting with cell D4, the formula is simply the current day's closing value divided by the previous day's closing value minus 1, or (C4/C3) - 1.
What is standard deviation in stock?
The standard deviation (volatility) of stock 1. The standard deviation of stock 2. The covariance, or relational movement, between the stock prices of stock 1 and stock 2. To calculate portfolio volatility, the logic underlying the equation is complicated, but the formula takes into account the weight of each stock in the portfolio, ...
Why do stock prices fluctuate?
Stock prices constantly fluctuate. This is because the demand for the stock changes. As more stocks change hands, greater is the change in its share price. This is called stock volatility. Even the amount of volatility in the market changes on a daily basis. To measure this volatility, the National Stock Exchange introduced the VIX India index, also called the fear gauge. VIX is often used as an indicator of stock price trends. This is because, VIX rises when there is more fear and uncertainty in the market.
How many inputs are there in an option model?
Now we know there are five inputs to the model. And we know the result of those five inputs is the options price. But what if you knew the options price and only four (strike, stock price, time to expiration, rates and dividends) of the models inputs? You could solve for X, that missing input, volatility. That’s how implied volatility is calculated. It’s the volatility implied by the market.
What is the European call option?
As you can see, the European Call option is equal to a probability of an event occurring, times the stock price, minus a probability of an event occurring, times the present value of the exercise price. Without going through the whole equation (I'll come back to edit this post and do just that) the only thing that traders need to be aware of is volatility σ² in d1 and d2.
What are the inputs for options pricing?
There are 5 inputs to an options pricing model: strike, stock price, time to expiration, interest rates and dividends, and volatility. The first three inputs are standardized and the same for everyone that trades an option on US markets (ignoring FLEX trades). For argument sake let’s say all traders use the same interest rates and dividends. The last input, volatility, is different for everyone and where people disagree.
Does implied volatility move constantly?
If only it were that easy . Options implied volatility moves constantly in response to a million different factors. What I gave you above is the basics, but it should give you a general understanding of how market makers and traders (people who price options) calculate the price of an option without an implied volatility.
Is implied volatility a closed form?
That value is considered implied volatility. Unfortunately, there's no Closed-form expression to do this, so most implementations rely on some sort of Bisection method to actually arrive at a value.
Can you use the current price of an option to calculate volatility?
Since all factors are known other than volatility, we can use the current trading price of an option to calculate what value for volatility would give the current price
Implied Volatility (IV): What Is It?
Implied volatility is a measure that shows how the market perceives price changes in a specific investment.
How to Understand Implied Volatility?
The implied volatility of an option is the predicted volatility of a stock over the option’s life. Option premiums adjust in response to changing expectations. The supply and demand of the underlying options, as well as the market’s estimate of the share price’s movement, have a direct impact on implied volatility.
How does Implied Volatility work?
The direction in which the price movement will progress is not predicted by implied volatility. High volatility, for example, signifies a huge price swing, yet the price could swing in opposite directions or bounce between them. Low volatility indicates that the price is unlikely to fluctuate dramatically and unexpectedly.
What factors affect Implied Volatility and How it works in the Market?
Supply and Demand are two of the most important factors that influence Implied Volatility. Prices rise as a result of high demand for certain assets. Also, when assets aren’t in high demand, prices tend to fall.
Implied Volatility: What are the risks involved?
An option’s implied volatility is not constant. It rises and falls in height. It evolves with time. However, there are a few instances where the price of an option changes dramatically. If the market falls sharply, rises sharply, or news regarding a particular stock breaks as expected, implied volatility can change suddenly.
Strategies to consider in the stock market with Implied volatility
Make sure you can tell whether implied volatility is rising or dropping and whether it is high or low. Remember that as implied volatility rises, option premiums rise as well.
Implied Volatility: Pros & Cons
Market sentiment can be measured using implied volatility. It calculates the size of a potential asset transfer. However, it does not reveal the movement’s direction. To price options contracts, option writers will utilize calculations that include implied volatility. Below are its pros and cons:
The Black-Scholes Formula
Implied Volatility Inputs
- Implied volatility is not directly observable, so it needs to be solved using the five other inputs of the Black-Scholes model, which are: 1. The market priceof the option. 2. The underlying stock price. 3. The strike price. 4. The time to expiration. 5. The risk-free interest rate. Implied volatility is calculated by taking the market price of the...
The Iterative Search
- Suppose that the value of an at-the-money call option for Walgreens Boots Alliance, Inc. (WBA) is $3.23 when the stock price is $83.11, the strike price is $80, the risk-free rate is 0.25%, and the time to expirationis one day. Implied volatility can be calculated using the Black-Scholes model, given the parameters above, by entering different values of implied volatility into the option prici…
Historical Volatility
- Historical volatility, unlike implied volatility, refers to realized volatilityover a given period and looks back at past movements in price. One way to use implied volatility is to compare it with historical volatility. From the example above, if the volatility in WBA is 23.6%, we look back over the past 30 days and observe that the historical volatilityis calculated to be 23.5%, which is a mo…
The Bottom Line
- The Black-Scholes formula has been proven to result in prices very close to the observed market prices. And, as we've seen, the formula provides an important basis for calculating other inputs, such as implied volatility. While this makes the formula quite valuable to traders, it does require complex mathematics. Fortunately, traders and investors who use it do not need to do these cal…