- Subtract the starting value of the stock portfolio from then ending value of the portfolio. You can use any time period you want.
- Add any dividends received during the time period to the increase in price to find the total gain. ...
- Divide the gain by the starting value of the portfolio to find the total rate of return. ...
- Add 1 to the result. In this example, add 1 to 0.5 to get 1.5.
- Divide 1 by the number of years it took to achieve the total rate of return. In this example, divide 1 by 3 to get 0.3333.
- Raise one plus the total rate of return to the power of 1 divided by the number of years. "Power" means using exponents, which requires a calculator.
- Subtract 1 from the result to find the annualized rate of return. ...
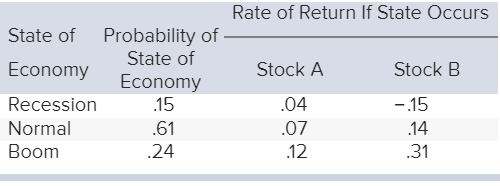
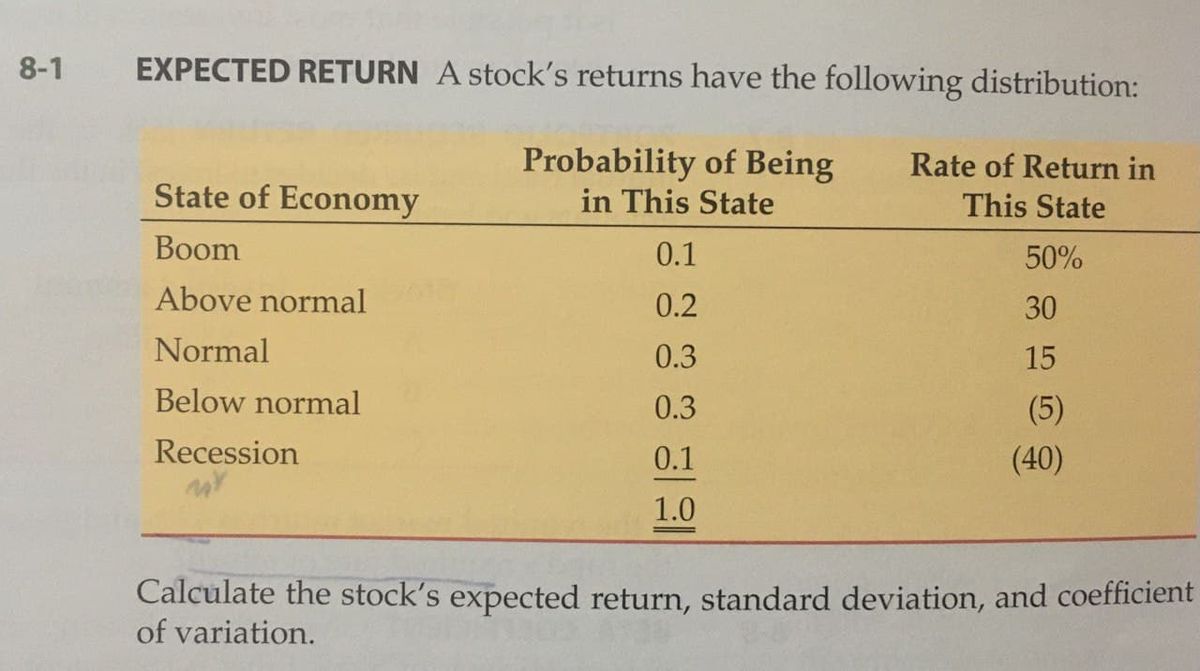
How do I calculate the expected return of a stock?
- Find the initial cost of the investment
- Find total amount of dividends or interest paid during investment period
- Find the closing sales price of the investment
- Add sum of dividends and/or interest to the closing price
- Divide this number by the initial investment cost and subtract 1
How is the expected return for a stock calculated?
Key Takeaways
- The expected return is the amount of profit or loss an investor can anticipate receiving on an investment.
- An expected return is calculated by multiplying potential outcomes by the odds of them occurring and then totaling these results.
- Expected returns cannot be guaranteed.
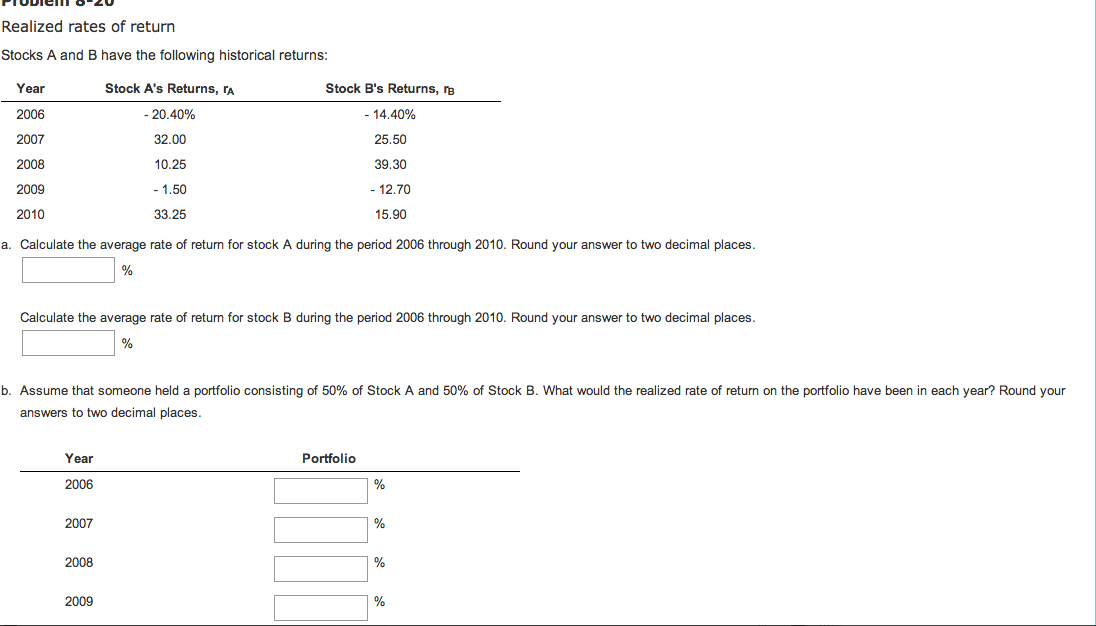
How to calculate stock's realized annual return?
How to calculate an annual return Here's how to do it correctly:
- Look up the current price and your purchase price.
- If the stock has undergone any splits, make sure the purchase price is adjusted for splits. If it isn't, you can adjust it yourself. ...
- Calculate your simple return percentage:
How to calculate stock returns manually?
Total Stock Return Calculator (Click Here or Scroll Down) The formula for the total stock return is the appreciation in the price plus any dividends paid, divided by the original price of the stock. The income sources from a stock is dividends and its increase in value. The first portion of the numerator of the total stock return formula looks ...
What is the purpose of the rate of return?
The rate of return (RoR) is used to measure the profit or loss of an investment over time. The metric of RoR can be used on a variety of assets, from stocks to bonds, real estate, and art. The effects of inflation are not taken into consideration in the simple rate of return calculation but are in the real rate of return calculation.
What is the compound annual rate of return?
The CAGR is the mean annual rate of return of an investment over a specified period of time longer than one year, which means the calculation must factor in growth over multiple periods.
How does the RoR work?
The RoR works with any asset provided the asset is purchased at one point in time and produces cash flow at some point in the future. Investments are assessed based, in part, on past rates of return, which can be compared against assets of the same type to determine which investments are the most attractive.
What is discount rate?
The discount rate represents a minimum rate of return acceptable to the investor, or an assumed rate of inflation. In addition to investors, businesses use discounted cash flows to assess the profitability of their investments.
Is the simple rate of return a nominal rate of return?
The simple rate of return is considered a nominal rate of return since it does not account for the effect of inflation over time. Inflation reduces the purchasing power of money, and so $335,000 six years from now is not the same as $335,000 today.
What is the ROE of a company?
Return on equity, often abbreviated as ROE, is a financial metric used to judge the strength of a business by answering this key question: How much profit does it generate as a function of the cash it has to work with?
Is the return of an investor lower than the ROE?
Yet it's important to remember that an investor's return, judged in terms of their share of generated earnings, will almost always be much lower than a company's ROE. That's due to the fact that shares are typically purchased at a substantial premium to the carrying value of equity on a company's books.
Why is ROI expressed as a percentage?
First, ROI is typically expressed as a percentage because it is intuitively easier to understand (as opposed to when expressed as a ratio). Second, the ROI calculation includes the net return in the numerator because returns from an investment can be either positive or negative.
What is ROI in investing?
Return on investment (ROI) is an approximate measure of an investment's profitability. ROI has a wide range of applications; it can be used to measure the profitability of a stock investment, when deciding whether or not to invest in the purchase of a business, or evaluate the results of a real estate transaction.
What is ROI in business?
Return on investment (ROI) is a simple and intuitive metric of the profitability of an investment. There are some limitations to this metric, including that it does not consider the holding period of an investment and is not adjusted for risk. However, despite these limitations, ROI is still a key metric used by business analysts to evaluate ...
Why is ROI important?
The biggest benefit of ROI is that it is a relatively uncomplicated metric; it is easy to calculate and intuitively easy to understand . ROI's simplicity means that it is often used as a standard, universal measure of profitability. As a measurement, it is not likely to be misunderstood or misinterpreted because it has the same connotations in every context.
Does leverage magnify ROI?
Combining Leverage with Return on Investment (ROI) Leverage can magnify ROI if the investment generates gains. However, by the same token, leverage can also amplify losses if the investment proves to be a losing investment.
How to find out how much your stock is moving?
Find your average daily return to evaluate your stocks. Choose a period of time to evaluate your stock’s performance such as a year or a 6-month period. Add together the daily return values and then divide by the number of days in the time period to find out how much your stock’s price moves on an average day.
How to know how well your stock is performing?
One of the best ways to evaluate how well your stocks are performing is to calculate their daily return. Basically, it tells you how much a stock’s value changed over a day. Using this information, you can determine whether you want to invest more in a company or try investing elsewhere.
What is a stock ticker symbol?
A stock ticker symbol is a unique series of letters assigned to a company for trading purposes. Every company on the stock market has one. Enter your company’s ticker symbol or their name into the company search field to look up their stock info.
What is required rate of return?
The required rate of return (RRR) is the minimum amount of profit (return) an investor will seek or receive for assuming the risk of investing in a stock or another type of security. RRR is also used to calculate how profitable a project might be relative to the cost of funding that project. RRR signals the level of risk that's involved in ...
Why is required rate of return so difficult to determine?
The required rate of return is a difficult metric to pinpoint because individuals who perform the analysis will have different estimates and preferences. The risk-return preferences, inflation expectations, and a firm's capital structure all play a role in determining the required rate.
What does RRR mean in finance?
RRR signals the level of risk that's involved in committing to a given investment or project. The greater the return, the greater the level of risk. A lesser return generally means that there is less risk. RRR is commonly used in corporate finance when valuing investments.
What is weighted average cost of capital?
The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is the cost of financing new projects based on how a company is structured. If a company is 100% debt financed, then you would use the interest on the issued debt and adjust for taxes, as interest is tax deductible, to determine the cost.
How do analysts make decisions?
Analysts make equity, debt, and corporate expansion decisions by placing a value on the periodic cash received and measuring it against the cash paid. The goal is to receive more than you paid. Corporate finance focuses on how much profit you make (the return) compared to how much you paid to fund a project.
When dealing with corporate decisions to expand or take on new projects, what is the required rate of return?
When dealing with corporate decisions to expand or take on new projects, the required rate of return (RRR) is used as a benchmark of minimum acceptable return, given the cost and returns of other available investment opportunities.
Does RRR factor inflation?
When looking at an RRR, it is important to remember that it does not factor in inflation. Also, keep in mind that the required rate of return can vary among investors depending on their tolerance for risk. 1:29.