Calculate the proceeds from the sale and then divide it into the dividend per share for the after-tax cost of preferred stock. $110 / $975= 11.3 percent. This is the after-tax cost of preferred stock to the company. In effect, it means that the company will pay 11.3 percent per year for the privilege of using the shareholder's net $975 investment.
How to calculate the after tax cost of preferred stock?
The most important thing to know when calculating the after tax cost of preferred stock is that, unlike interest payments (which is an expense), dividends are paid out with after-tax income. Understand what preferred stock is. Preferred stock has characteristics of both debt and equity securities.
How does a sale of preferred stocks affect your return?
How a sale of preferred stock impacts your return depends on your holding period and the amount of capital gains and losses you have from other transactions. Your holding period, or the amount of time you owned the preferred stocks before selling them, is either short term or long term.
What are the tax implications of pre-preferred stocks?
Preferred stocks are capital assets and are subject to the same taxation as common stocks when they're sold at a gain or loss. Your preferred shares have additional tax implications, however, as they generally provide you with fixed dividend payments when the corporation is profitable.
What is the after-tax real rate of return?
Janet Berry-Johnson is a CPA with 10 years of experience in public accounting and writes about income taxes and small business accounting. What Is the After-Tax Real Rate of Return? The after-tax real rate of return is the actual financial benefit of an investment after accounting for the effects of inflation and taxes.

How do you calculate after tax return on preferred stock?
Calculate the proceeds from the sale and then divide it into the dividend per share for the after-tax cost of preferred stock. $110 / $975= 11.3 percent. This is the after-tax cost of preferred stock to the company.
What is the rate of return on the preferred stock?
Divide the expected dividend per share by the price per share of the preferred stock. With our example, this would be $12/$200 or . 06. Multiply this answer by 100 to get the percentage rate of return on your investment.
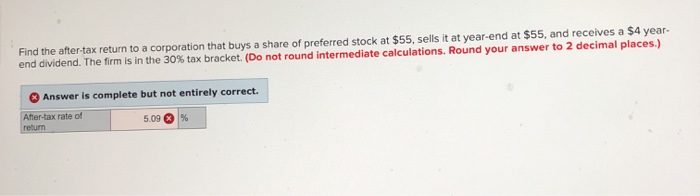
What is their after tax rate of return on their investment?
The after-tax real rate of return is the actual financial benefit of an investment after accounting for the effects of inflation and taxes. It is a more accurate measure of an investor's net earnings after income taxes have been paid and the rate of inflation has been adjusted for.
What is after tax return on capital?
What Is an After-Tax Return? An after-tax return is any profit made on an investment after subtracting the amount due for taxes. Many businesses and high-income investors will use the after-tax return to determine their earnings.
How do you calculate required rate of return?
To calculate RRR using the CAPM:Subtract the risk-free rate of return from the market rate of return.Multiply the above figure by the beta of the security.Add this result to the risk-free rate to determine the required rate of return.
How do you calculate preferred return compounded annually?
To calculate the preferred return amount, multiply the total equity investment from limited partners by the preferred return percentage. If the preferred return is 8% and limited partners invested $1 million, the annual preferred return is $80,000 (0.08 * $1,000,000).
What Is the After-Tax Real Rate of Return?
The after-tax real rate of return is the actual financial benefit of an investment after accounting for the effects of inflation and taxes. It is a more accurate measure of an investor’s net earnings after income taxes have been paid and the rate of inflation has been adjusted for. Both of these factors will impact the gains an investor receives, and so must be accounted for. This can be contrasted with the gross rate of return and the nominal rate of return of an investment.
What investments have less discrepancy between nominal and after tax rates of return?
Tax-advantaged investments, such as Roth IRAs and municipal bonds, will see less of a discrepancy between nominal rates of return and after-tax rates of return.
Does the commission on stocks diminish returns?
The commission he paid to buy and sell the stock also diminishes his return. Thus, in order to truly grow their nest eggs over time, investors must focus on the after-tax real rate of return, not the nominal return.
Is the real rate of return after taxes positive?
As long as the real rate of return after taxes is positive, however, an investor will be ahead of inflation. If it’s negative, the return will not be sufficient to sustain an investor’s standard of living in the future. Take the Next Step to Invest. Advertiser Disclosure. ×.
What is the Cost of Preferred Stock?
The Cost of Preferred Stock represents the rate of return required by preferred shareholders and is calculated as the annual preferred dividend paid out (DPS) divided by the current market price.
Cost of Preferred Stock Overview
The recommended modeling best practice for hybrid securities such as preferred stock is to treat it as a separate component of the capital structure.
Cost of Preferred Stock Formula
The cost of preferred stock represents the dividend yield on the preferred equity securities issued.
Nuances to the Cost of Preferred Stock
Sometimes, preferred stock is issued with additional features that ultimately impact its yield and the cost of the financing.
Cost of Preferred Stock Excel Template
Now that we’ve defined the concept behind the cost of preferred equity, we can move on to an example modeling exercise in Excel. To access the model template, fill out the form below:
Cost of Preferred Stock Example Calculation
In our modeling exercise, we’ll be calculating the cost of preferred stock for two different dividend growth profiles:
Step 1
Determine the dividend on the preferred stock. Preferred stock generally pays a fixed dividend, so you will know how much the stock is going to pay the stock owner each year. For example, assume the dividend of the preferred stock is $12 per share annually.
Step 2
Determine the selling price of the preferred stock. Businesses will have to deal with flotation costs in calculating a stock price, but an individual investor can simply look at the price that the stock is being offered for. For example, assume preferred stock in company ABC is being offered at $200 a share.
Step 3
Divide the expected dividend per share by the price per share of the preferred stock. With our example, this would be $12/$200 or .06. Multiply this answer by 100 to get the percentage rate of return on your investment. In our example, .06 x 100 = 6 so the rate of return for the preferred stock is 6 percent per year.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stocks are capital assets and are subject to the same taxation as common stocks when they're sold at a gain or loss.
What is the tax rate on dividends?
Most people will pay tax on qualified dividends at the rate of 10 percent . But if your taxable income for the year isn't taxed beyond the 15 percent tax bracket, your qualified dividend income is tax free, while very high income earners are taxed at the maximum rate of 15 percent.
How are dividends taxed?
The general rule is that dividends are taxed at ordinary income rates. If the dividends are qualified, meaning the preferred shares satisfy a number of eligibility requirements, they're taxed at those lower long-term capital gains rates. Most people will pay tax on qualified dividends at the rate of 10 percent. But if your taxable income for the year isn't taxed beyond the 15 percent tax bracket, your qualified dividend income is tax free, while very high income earners are taxed at the maximum rate of 15 percent. In most cases, the 1099-DIV you receive will tell you whether the dividend payments are qualified.
How long do you have to hold stock?
Your holding period, or the amount of time you owned the preferred stocks before selling them, is either short term or long term. A long-term holding period simply means you acquired the shares more than one year ago, whereas a short-term holding period is one year or less of ownership as of the date of sale. Long-term capital gains are potentially taxed at lower rates than you pay on most of your other income. Those higher rates are referred to as “ordinary income tax rates” and apply to short-term preferred stock gains. Since you combine all capital gains and losses together before calculating the tax, all losses are treated the same. Losses can offset your current and future capital gains. And if you have more losses than you need, up to $3,000 is deductible from income on your return that's subject to ordinary income tax rates.
What is tax basis?
Your tax basis is the total cost to acquire the preferred shares, which is usually the fair market value of the stock plus associated costs, such as the commission you're charged to make the trade. Tax basis is important because it reflects the maximum amount you can receive tax free if you ever sell the shares.
Is capital gains tax deductible?
Since you combine all capital gains and losses together before calculating the tax, all losses are treated the same. Losses can offset your current and future capital gains. And if you have more losses than you need, up to $3,000 is deductible from income on your return that's subject to ordinary income tax rates.
Is dividend income taxable?
Dividends, as well as the profit you earn when selling preferred shares, are equally taxable, but this doesn't necessarily mean you'll owe tax on both types of income.
What is after tax return?
After-tax return is the net return to the investor after ordinary income and capital gains taxes are subtracted.
What is after tax return on investment?
After-tax return on investment is the net return to the investor after ordinary income and capital gains taxes are subtracted. It is calculated as: Tc is the long-term capital gains tax rate and To is the income tax rate on ordinary income.
How to find the taxable equivalent yield of a Treasury bond?
Treasury bonds where the investor itemizes, in which the formula is: Taxable equivalent yield = Treasury yield / (1 - Ts (1 - Tf )), where Tf = the federal income tax rate and Ts = the state income tax rate.
Why are bonds so difficult to calculate after tax returns?
Bonds present a special problem in calculating after-tax returns since some interest is taxed and some is not. Investors face an important item to factor in when making a bond purchase decision. In order to compare tax-exempt bonds to taxable bonds, the investor must calculate the taxable equivalent yield.
What happens when you sell an investment?
Investments are taxed in two ways. First, you are taxed on any income from the investment unless it is tax exempt. Second, you are taxed on any realized gains. Realized gains occur when you sell the investment.
What is the yield of a fully taxable corporate bond?
These four rates would then be compared to the fully taxable corporate bond yielding 4.25%. Then after factoring in his itemization status, Kevin could make a fully informed decision.
Why do investors buy bonds?
Bonds are taxed the same way as stocks. However, investors often buy bonds for the interest earned beyond any possible capital gains. This is why it's important to understand before- and after-tax bond yields.
How do corporations calculate the cost of preferred stock?
They calculate the cost of preferred stock by dividing the annual preferred dividend by the market price per share. Once they have determined that rate, ...
What is Preferred Stock?
Preferred stock is a form of equity that may be used to fund expansion projects or developments that firms seek to engage in. Like other equity capital, selling preferred stock enables companies to raise funds. Preferred stock has the benefit of not diluting the ownership stake of common shareholders, as preferred shares do not hold the same voting rights that common shares do.
What is the term for the first cash flow payment after a liquidation?
Because of the nature of preferred stock dividends, it is also sometimes known as a perpetuity. Perpetuity Perpetuity is a cash flow payment which continues indefinitely.
Does common equity have a par value?
However, preferred stock also shares a few characteristics of bonds, such as having a par value. Common equity does not have a par value.
Is preferred stock more valuable than common stock?
In theory, preferred stock may be seen as more valuable than common stock, as it has a greater likelihood of paying a dividend and offers a greater amount of security if the company folds.
