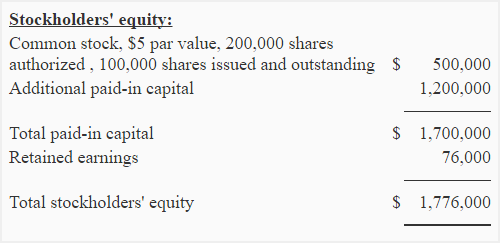How to Find the Value of Common Stock in Accounting
- Step 1. Download a company’s most recent Form 10-Q quarterly report or Form 10-K annual report from the investor...
- Step 2. Locate the balance sheet in the financial report. Identify the amount of the company’s total stockholders’...
- Step 3. Check if the company lists preferred stock in the stockholders’ equity section.
Is a common stock considered an asset?
While this is headed in the correct direction, management can still change this by putting out a low value that's artificial. For example, if the company has one million shares it issues and the stated value is $0.01 for each share, $10,000 will be the stated value of the stock.
How many shares of common stock must be issued?
Dec 26, 2019 · The formula for calculating the book value per share of common stock is: Book value per share = Stockholder’s equity / Total number of outstanding common stock For example, if there are 10,000 outstanding common shares of a company and each share has a par value of $10, then the value of outstanding share amounts to $100,000.
How are the dividends on common stock determined?
Nov 26, 2003 · A stated value is an amount assigned to a corporation's stock for internal accounting purposes when the stock has no par value. Like par value —which is the face value of a stock stated in the...
How to calculate common stock outstanding from a balance sheet?
Instead, he issues 1,000 shares to himself with a stated value of $1 per share for $500,000. When the company issues the shares to Tom, the common stock account is credited for $1,000, the cash account is debited for $500,000, and the additional paid in capital account is credited for $499,000. Notice the stated-value does not reflect the fair market value or the actual amount …

Why are common stocks listed in the equity section?
Common stocks are listed in the equity section because stocks are considered as an asset. From the total number of stocks, we can calculate the number of outstanding stocks. Outstanding stocks are stocks that are issued to the public and owned by stockholders, investors, and company members. If we deduct the number of treasury stocks ...
What is a claim on a company's assets?
The claims on a company’s assets are comprised of liability and equity. Liability includes the claims on the company’s assets by external firms or individuals. Mortgage and loans are examples of liabilities of a company.
What is equity in a company?
Equity is the claim of shareholders claims on the company assets. By purchasing stocks of the company, they have the right to claim ownership in the company. Their ownership percentage is determined by the ratio of shares owned to the total number of outstanding shares.
What is Treasury stock?
Treasury stocks are stocks that have been repurchased by the company that issued the stocks in the first place. These shares have no voting rights or dividend payments. Neither does this stock receive any assets after the company liquidates. To summarize the formula, Outstanding stocks = Issued stocks – Treasury stocks.
What happens when a company goes public?
When a company goes public from private, it offers an opportunity for investors to claim partial ownership in the company by buying its stocks. This initial offering is known as IPO and this is when the company becomes a publicly owned company.
Is equity a common stock?
Keep in mind that equity is not just comprised of common stocks. It also includes retained earnings, treasury stock, and preferred stocks. When you add up the liabilities and stockholder equity, their sum will always be equal to the total value of the company’s assets.
What is the stated value of a stock?
A stated value is an amount assigned to a corporation's stock for internal accounting purposes when the stock has no par value. Like par value —which is the face value of a stock stated in the corporate charter—stated value is nominal, typically between $0.01 and $1.00. The stated value has no relation to market price .
Why is stated value important?
Because it is generally illegal for a company to pay dividends or repurchase shares if doing so impairs the legal capital, the stated value helps to provide shareholders with some protection. However, in practice, with the stated value per share as low as one penny, monetary interest is modest or de minimus.
Does stated value have a relation to market price?
The stated value has no relation to market price. A company can choose to issue no par value stock, but for its own records, it must assign a stated value to satisfy the minimum requirement for legal capital in the state where it incorporates.
What Does Stated Value Stock Mean?
Many companies choose not to establish a par value in their charters because it allows them to escape the minimum legal capital requirements that many states have. Since most states’ laws refer to a par value when determining the minimum capitalization thresholds, corporations are able to side step this issue by creating no-par value stock.
Example
When Tom incorporates his business, he decides to not include a par value in the corporate charter. Instead, he issues 1,000 shares to himself with a stated value of $1 per share for $500,000.
How long is cookie lawinfo-checkbox-necessary?
The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Advertisement". cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary. 11 months. This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary".
What is a cookie used for?
The cookie is used to store information of how visitors use a website and helps in creating an analytics report of how the website is doing. The data collected including the number visitors, the source where they have come from, and the pages visted in an anonymous form.
What does it mean when a stock price exceeds its book value?
A market price that exceeds a stock’s book value per share means that investors place additional value on a company’s future earning potential. A book value that exceeds market value suggests that investors, in general, are pessimistic about a company’s future.
Why is book value important?
Because a balance sheet includes only historical information, book value typically differs from a stock’s market value, which includes investors’ expectations about a company’s future. Book value alone reveals limited information about a stock, but you can gain insight into investors’ sentiments by comparing book value to market value.
What is call price?
The call price is the amount a company must pay preferred shareholders if it buys back its preferred shares. If the preferred shares do not have a call price, find the par value per share instead. Dividends in arrears are those the company owes preferred shareholders for missed dividend payments. In this example, assume ...
How to get $60 million in a call?
Add the dividends in arrears to the call price. Multiply your result by the number of preferred shares outstanding. In this example, add $55 and $5 to get $60. Multiply $60 by 1 million to get $60 million.
How to calculate common stock?
The formula for common stock can be derived by using the following steps: Step 1: Firstly , determine the value of the total equity of the company which can be either in the form of owner’s equity or stockholder’s equity. Step 2: Next, determine the number of outstanding preferred stocks and the value of each preferred stock.
What is the formula for common stock?
However, in some of the cases where there is no preferred stock, additional paid-in capital, and treasury stock, then the formula for common stock becomes simply total equity minus retained earnings. It is the case with most of the smaller companies that have only one class of stock.
What is common stock?
The term “common stock” refers to the type of security for ownership of a corporation such that the holder of such securities has voting rights that can be exercised for various corporate events. Examples of such events include a selection of the board of directors or other major corporate decision.
Why is common stock important?
The common stock is very important for an equity investor as it gives them voting rights which is one of the most prominent characteristics of common stock. The common stockholders are entitled to vote on various corporate subjects which may include acquisition of another company, who should constitute the board and other similar big decisions. Usually, each common stockholder gets one vote for every share. Another striking feature of common stock is that these stocks usually outperform another form of securities, like bonds and preferred stocks, in the long run. However, common stock comes with a strong downside, that in case a company goes into bankruptcy, then the common stockholders get nothing until the creditors are fully paid off. In other words, when the company has to sell off its assets, then the cash generated from the sale will first go to the lenders, creditors, and other stakeholders, then the common stockholders are paid if anything is left. As such, common stock is another appropriate example of the trade-off between risk and returns, such that these stocks offer a higher return as they are riskier than another form of securities.
What is common stock?
Common stock is a type of stock that gives the right to the common stockholders to have an equal right to vote at the meeting and receive the same dividend. Theoretically, common stock can be issued at par value, no par value, at stated value, or for non-cash assets.
What does it mean when a corporation issues common stock at par value?
When a corporation issues common stock at par value, the amount of cash or non-cash assets received equal to the value of the common stock. This means that the outstanding value of common stock and the asset received are at the same value.
What is the journal entry for issuing common stock?
To sum up, the journal entry for issuing common stock varies depending on each type of issuance. This includes the common stock issued at par value, at no par value, at the stated value, and finally the common stock issued for noncash assets.
What is par value stock?
When par value stock is issued at a premium, the assets received both cash or noncash assets are higher than the value of the common stock. For example, a cash receipt of $12 per share for common stock of $10 par value. The excess of $2 ($12 minus $10) is called a premium or capital contribution in excess of par value.
Why is par value stock issued at a discount?
When par value stock is issued at a discount, the assets received both cash or noncash assets is lower than the value of the common stock. In practice, the discount on the stock is prohibited in most jurisdictions. This is because the regulators want to protect the creditors of the company who issues the common stock. When issuing at discount, the company is putting its creditors at risk of not being able to repay the debts to creditors. This is because there might not be enough assets to recover the debt owed to creditors in case of default.
What happens when a corporation issues a par value stock?
When a corporation issues par value of the common stock, it can be issued at par, at a premium, or a discount. Each of these cases can be exchanged for either cash or non-cash assets depending on the agreed approach.
Why is a company issued at discount?
When issuing at discount, the company is putting its creditors at risk of not being able to repay the debts to creditors. This is because there might not be enough assets to recover the debt owed to creditors in case of default. READ: Six Common Performance Measures for Inventory Management.
How to calculate par value of shares?
The par value of common stock for the company is simply: Par value of common stock = (Par value per share) x (Number of issued shares)
What is par value?
The par value of a common share is an arbitrary value assigned to shares to fulfill state requirements. The par value is unrelated to the price at which the shares are first issued or their market price once they begin trading. The par value is stated in the company's articles of incorporation and figures on the paper stock certificates ...
Why do companies have a low par value?
Companies like to set a very low par value because it represents their legal capital, which must remain invested in the company and cannot be distributed to shareholders. Another reason for setting a low par value is that when a company issues shares, it cannot sell them to investors at less than par value. How does one calculate the par value of ...
Do bonds have a par value?
Bonds have a par value, of course – it's just the principal amount. However, stocks can also have a par value. Here you'll learn what that par value represents and how to calculate the company's par value of common stock for the purpose of financial accounting.
What is par value in stock?
The par value of a stock is an arbitrary number assigned to each share of stock when it is first sold to investors. The par value has no actual relation to the market value of each share; it's just an accounting requirement to create an initial point of reference for future accounting transactions. The process to figure out ...
Where to find par value on balance sheet?
Because par values represent legal capital, the information we need will be found in the equity section of the balance sheet, along with the other capital accounts.