The Shiller P/E is calculated by dividing the daily stock price by the multi-year inflation adjusted earnings, E10. Here we use a similar calculation for individual companies. When we calculate today's Shiller P/E ratio of a stock, we use today's price divided by E10.
What is the Shiller PE ratio for S&P 500?
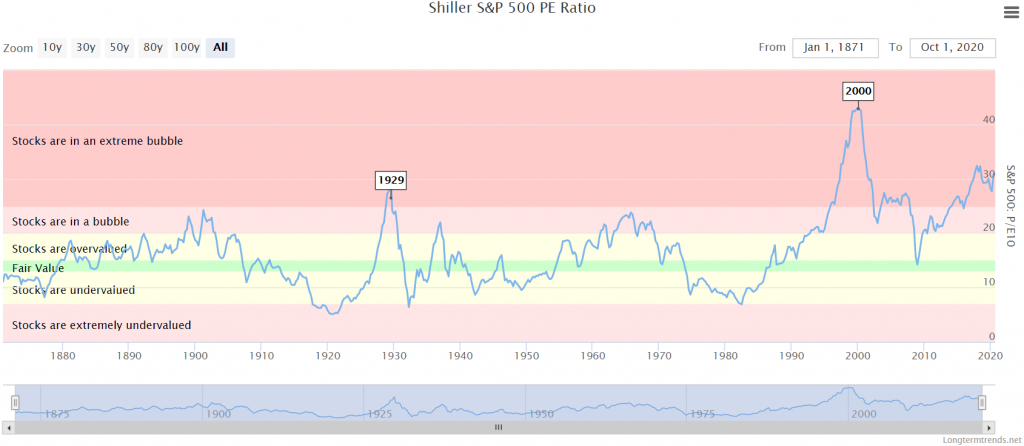
Shiller PE ratio for the S&P 500. Price earnings ratio is based on average inflation-adjusted earnings from the previous 10 years, known as the Cyclically Adjusted PE Ratio (CAPE Ratio), Shiller PE Ratio, or PE 10 — FAQ . Data courtesy of Robert Shiller from his book, Irrational Exuberance .
How do you calculate the Shiller PE of a stock?
1 Use the annual earnings of the S&P 500 companies over the past 10 years. 2 Adjust the past earnings for inflation using CPI; past earnings are adjusted to today's dollars. 3 Average the adjusted values for E10. 4 The Shiller PE equals the ratio of the price of the S&P 500 index over E10.
What is the Shiller PE?
The Shiller PE is a valuation measure, much like its cousin the price to earnings ratio. However, the Shiller PE tries to work around the shortcomings of the current PE ratio – either inappropriate earnings or over or undervaluation – by averaging results over a longer time frame.
What is Shiller PE (CAPE) ratio?
The Shiller PE (CAPE) Ratio: Current Market Valuations. The cyclically-adjusted price-to-earnings (CAPE) ratio of a stock market is one of the standard metrics used to evaluate whether a market is overvalued, undervalued, or fairly-valued. This metric was developed by Robert Shiller and popularized during the Dotcom Bubble when he argued ...

What is the Shiller PE ratio currently?
Price earnings ratio is based on average inflation-adjusted earnings from the previous 10 years, known as the Cyclically Adjusted PE Ratio (CAPE Ratio), Shiller PE Ratio, or PE 10 — FAQ. Data courtesy of Robert Shiller from his book, Irrational Exuberance ....Shiller PE Ratio.Mean:16.95Max:44.19(Dec 1999)2 more rows
Is the Shiller PE ratio accurate?
The Shiller P/E ratio may be as accurate an indicator as there is. But investors would still do well to focus on the long term.
How do I find a company's PE?
How to calculate a company's P/E ratio. This ratio is calculated by dividing a company's stock price by the company's earnings-per-share (EPS.) For example, if a company's share price is currently $30 and the EPS is currently $10, the P/E ratio would be 3.
What is Case Shiller PE?
The cyclically adjusted price-to-earnings ratio, commonly known as CAPE, Shiller P/E, or P/E 10 ratio, is a valuation measure usually applied to the US S&P 500 equity market. It is defined as price divided by the average of ten years of earnings (moving average), adjusted for inflation.
What is the most accurate stock valuation method?
The dividend discount model (DDM) is one of the most basic of the absolute valuation models. The dividend discount model calculates the "true" value of a firm based on the dividends the company pays its shareholders.
Why is Shiller PE better?
The main advantage of the Shiller PE ratio is that it eliminates the fluctuations in the regular PE ratio caused by variations in profit margins during business cycles. The regular PE uses the trailing 12 months earnings per share (EPS).
What is a good PE ratio to buy stocks?
So, what is a good PE ratio for a stock? A “good” P/E ratio isn't necessarily a high ratio or a low ratio on its own. The market average P/E ratio currently ranges from 20-25, so a higher PE above that could be considered bad, while a lower PE ratio could be considered better.
What is a good PE ratio for stocks?
There's no specific number that indicates expensiveness, but, typically, stocks with P/E ratios of below 15 are considered cheap, while stocks above about 18 are thought of as expensive.
Is high PE ratio good?
In general, a high P/E suggests that investors are expecting higher earnings growth in the future compared to companies with a lower P/E. A low P/E can indicate either that a company may currently be undervalued or that the company is doing exceptionally well relative to its past trends.
Does the Shiller PE work in emerging markets?
We find that the Shiller-PE is a reliable long-term valuation indicator for developed and emerging markets and we use the indicator to predict real returns on local equity markets over the next five years.
What is Shiller model?
Shiller formulated the cyclically-adjusted price/earnings ratio (CAPE), based on inflation-adjusted average earnings per share (EPS) over the past 10 years. This method is supposed to smooth the passing effects of the business cycle and one-off events on earnings.
What is Tesla's PE ratio?
The PE ratio is a simple way to assess whether a stock is over or under valued and is the most widely used valuation measure. Tesla PE ratio as of June 27, 2022 is 100.02.
Shiller PE
Prof. Robert Shiller of Yale University invented the Shiller PE Ratio to measure the market's valuation. The Shiller PE is a more reasonable market valuation indicator than the PE ratio because it eliminates fluctuation of the ratio caused by the variation of profit margins during business cycles.
Regular PE Ratio
The highest peak for the regular PE ratio was 123 in the first quarter of 2009. By then the S&P 500 had crashed more than 50% from its peak in 2007. The PE ratio was high because earnings were depressed.
Shiller PE Implied Market Return
In reality, it will never be the case that Shiller PE will reverse exactly to the mean after 8 years. Table below give us a better idea on the range of the future returns will be if the market are within 50% to 150% of the mean.
Excess CAPE Yield (ECY)
As the Shiller PE keeps increasing, Dr. Robert Shiller recently introduced a new metric called the Excess CAPE Yield,” or ECY, to give a more precise picture of the stock market. ECY is calculated by the inverse of Shiller PE, which is really the Shiller’s earning yield, subtracted by the U.S.
Investment Strategies at Different Market Levels
The Shiller PE and the ratio of total market cap over GDP can serve as good guidance for investors in deciding their investment strategies at different market valuations. Historical market returns prove that when the market is fair or overvalued, it pays to be defensive.
How Is the CAPE Ratio Used?
Many investors, traders, and economists use the ratio when forecasting market conditions. Not only is the ratio used to determine the state of the market as a whole, but it can also be used to determine the state of an individual asset like a stock or ETF. Here are a few examples:
What Is the Significance of 10 Years of Data?
The primary driver of the ratio’s stability is the fact that it measures the data over the course of a 10-year moving average, rather than measuring real earnings for this year in comparison to the current price.
Historic and Current Readings
Although there has been plenty of debate surrounding the efficacy of the Shiller P/E ratio in predicting market crashes, the metric does appear to have flashes of warning signs before several market crashes throughout history. For example:
Final Word
Although there are plenty of people who argue against the Shiller P/E ratio as a predictor of future market movements, there’s no arguing the fact that its readings were significantly high prior to most major market crashes throughout recent history.
The Shiller PE
Robert Shiller first proposed a ten year timeframe for his CAPE ratio, targeting it towards the S&P 500 - the most well known American stock index. Subsequently, CAPE has been adapted for a number of other countries and indexes.
Sources of the Shiller PE and CAPE Ratio Calculator
Thank you to Robert Shiller, for providing his monthly data on the S&P 500. Please see his site for an explanation of the calculation of the ratio.
Updated CAPE Ratio Chart
This is a chart that I update regularly based on raw data from Shiller’s website.
Why the CAPE Ratio is Important
Robert Shiller demonstrated using 130 years of back-tested data that the returns of the S&P 500 over the next 20 years are strongly inversely correlated with the CAPE ratio at any given time.
Limitations of the CAPE Ratio
In recent years, many people have questioned whether the metric is still a viable way to measure market valuation.
Final Words
I pay attention to CAPE and Cap/GDP closely, as well as other valuation metrics, because it helps inform my investment decisions.
Interpretation
The price earnings ratio is calculated by dividing a company's stock price by it's earnings per share. In other words, the price earnings ratio shows what the market is willing to pay for a stock based on its current earnings. It is one of the most widely-used valuation metrics for stocks.
Interpretation
Instead of dividing by the earnings of one year (see chart above), this ratio divides the price of the S&P 500 index by the average inflation-adjusted earnings of the previous 10 years. The ratio is also known as the Cyclically Adjusted PE Ratio (CAPE Ratio), the Shiller PE Ratio, or the P/E10.

What Is The Shiller P/E Ratio?
- The Shiller P/E ratio, also known as the cyclically adjusted price-to-earnings (CAPE) ratio, was designed to remove the noise of volatility in earnings readings by looking at the data over the course of 10 years. The ratio was introduced when Shiller and his colleague John Campbell presented research to the U.S. Federal Reserve in December 1996, su...
How Is The Cape Ratio used?
- Many investors, traders, and economists use the ratio when forecasting market conditions. Not only is the ratio used to determine the state of the market as a whole, but it can also be used to determine the state of an individual asset like a stock or ETF. Here are a few examples:
What Is The Significance of 10 Years of Data?
- The primary driver of the ratio’s stability is the fact that it measures the data over the course of a 10-year moving average, rather than measuring real earnings for this year in comparison to the current price. Although Shiller turned the data into an easy-to-use metric, the first time this theory was suggested was by Benjamin Graham — the father of value investing— and David Dodd, co-a…
Historic and Current Readings
- Although there has been plenty of debate surrounding the efficacy of the Shiller P/E ratio in predicting market crashes, the metric does appear to have flashes of warning signs before several market crashes throughout history. For example: 1. The Great Depression. In November of 1929, the Shiller ratio had a reading of 33.1 just before the market crash that resulted in the Great Depr…
Final Word
- Although there are plenty of people who argue against the Shiller P/E ratio as a predictor of future market movements, there’s no arguing the fact that its readings were significantly high prior to most major market crashes throughout recent history. Moreover, by paying attention to the ratio on an individual investment basis, you’ll get a better picture of the value you’re buying into when …