- Basic Safety Stock Formula. This short version of a safety stock formula takes the number of products sold per day and multiplies it by the number of days' worth of ...
- Standard Deviation Safety Stock Formula. This safety stock formula is helpful when dealing with multiple uncertain variables. It is expressed as Z × σLT × D avg.
- Average – Max Safety Stock Formula. This formula is best suited for short lead times, as it doesn't take long-lead-time variables into account.
- Safety Stock with Variable Demand Formula. The safety stock with variable demand formula is best for situations where the lead time is reliable, but the demand varies.
- Safety Stock with a Variable Lead Time. As before, "Z" represents the desired service level and "σLT" represents the lead time deviation (see the standard deviation formula for more information ...
- Find the average of a set of data.
- Calculate the sum of the average and the data set.
- Divide the sum by the sample proportion to get the variance.
- Add the variance to the average for the final result.
How to calculate safety stock?
Calculate Safety Stock Using Standard Deviation. To calculate safety stock you must do the following: Find the average of a set of data; Calculate the sum of the average and the data set; Divide the sum by the sample proportion to get the variance; Add the variance to the average for the final result; Safety Stock Formula Using Standard Deviation
How do you calculate safety stock?
Method 1 Method 1 of 3: Determining Safety Stock from Demand
- Look to historic demand and demand variability to determine how to avoid stockouts. ...
- Determine average demand. Average demand is the total quantity of a material or goods required each day over a fixed period.
- Consider future demand for particular stock items. ...
- Calculate demand variability. ...
- Determine your service factors, aka Z-scores. ...
How is safety stock calculated?
Safety stock is calculated by multiplying maximum daily usage (which is the maximum number of units sold in a single day) with the maximum lead time (which is the longest time it has taken the vendor to deliver the stock), then subtracting the product of average daily usage (which is the average number of units sold in …
How to calculate standard deviation?
Understanding STDEV
- Add together all the cash flows you have put in the spreadsheet to calculate a total.
- Divide the total by the number of historical entries to calculate the mean average cash flow.
- Subtract the mean average cash flow from each recorded cash flow to calculate the difference. ...
- Square each cash flow difference by multiplying it against itself. ...

What is the formula for safety stock?
What is the safety stock formula? The safety stock formula is therefore: [maximum daily use x maximum lead time] – [average daily use x average lead time] = safety stock.
What is standard deviation safety stock?
When dealing with uncertainties and multiple variables, the best way to calculate safety stock is to use standard deviation to determine variations in supply and demand. The definition of standard deviation is a quantity calculated to indicate the extent of deviation for a group as a whole.
Does standard deviation affect safety stock?
even so, there will be enough inventory to meet demand in 50 percent of cycles. If Z-score equals 1, the safety stock will protect against one standard deviation; there will be enough inventory 84 percent of the time. This percentage of cycles where safety stock prevents stockouts is called the cycle service level.
How do you calculate safety stock from a normal distribution?
Use the safety stock formula So, if a company's chosen service level is 90% (or 1.28), the standard deviation of their lead time is 16.6 days and their average demand is 150 units of inventory, the equation would read: 1.28 x 16.6 x 150 = 3,187 units of safety stock.
How do you calculate stock?
You'll need the original purchase price and the current value of your stock in order to make the calculation. Subtract the total purchase price from the current price of the stock then divide that by the original purchase price and multiply that figure by 100. This gives you the total percentage change.
What is safety stock example?
Examples of Safety Stock Suppose a company has a team to research the market demand, and it has estimated that the demand for an umbrella is nearly one thousand units every month. As a precaution, the company can decide to have one hundred units as safety stock because the demand is never constant.
How to calculate lead time?
#1 – Average – Max Method 1 Max sales = the day with the highest number of items sold. 2 Average sales = average daily sales 3 Lead time = in this contest, the lead time is the time period from the point a business places an order to restock its supplies until the supplier actually delivers them. 4 The lead time is calculated in terms of days. 5 Max lead time = the maximum number of days taken by the supplier to deliver the stock since placing its order.
What is a 95% service level?
A 95% service level means that there may be a stockout in 5% of the cases. A high service level increases the business’s cost to avoid stockout, but many firms do it nonetheless.
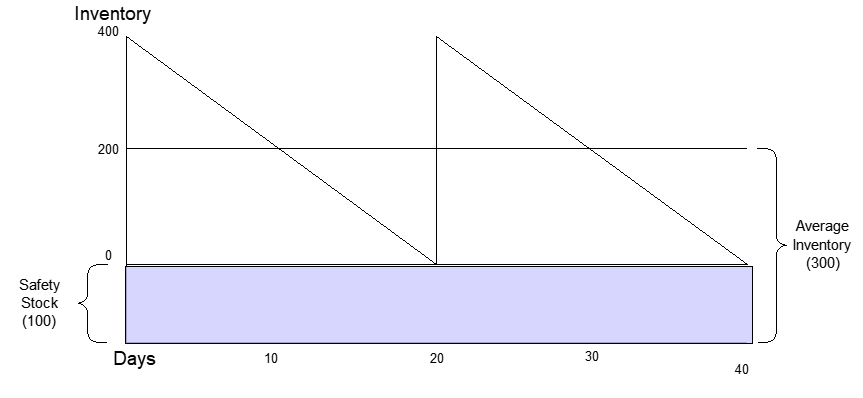
What is safety stock?
Safety Stock is defined as the additional quantities of goods stored as a safety net above the required amount to prevent going out of stock due to emergencies. An example of emergency is when sold off goods undergo damage on their way to be delivered. In such a case, safety stock can be used to ensure that the customer receives ...
Why are stocks bought and stored during good harvests?
During good harvests, stocks are bought and stored to keep prevent prices from falling below price levels or a target range, while stocks are released during harvests to prevent prices from rising above price levels or a target range. read more. and is obtained above the normal forecasted level.
What is service level in inventory?
Service level is the probability that the amount of inventory on hand during the lead time is sufficient to meet expected demand – that is, the probability that a stockout will not occur. The uncertainty of supply and demand makes it difficult to calculate the amount of stock needed to satisfy customers needs while avoiding stockouts.
What causes stockouts?
Stockouts are usually caused by: Changes in consumer demand. Incorrect stock forecasts. Variability in lead times for raw materials. Trying to plan for these variables and maintain a target inventory level can be difficult. However, this is where a safety stock formula comes in.
How does running out of stock affect your business?
Some of the direct impacts on your business include: Loss of revenue. Loss of gross profit.
Why do retailers use safety stock?
One of the main reasons that retailers and manufacturers implement a safety stock strategy is to prevent stockouts. Stockouts are usually caused by: Changes in consumer demand.
How to find lead time variability?
To find lead time variability, calculate your average lead time then find the square root of the average of squared differences.
Why is safety stock management important?
Safety stock management is a critical part of being a retailer and a manufacturer. It will help to reduce the chance of stock outs, which lead to inefficiency, unhappy customers, and ultimately, lost sales and reduced profits.
When dealing with uncertainties and multiple variables, the best way to calculate safety stock is to use standard deviation to determine variations in
When dealing with uncertainties and multiple variables, the best way to calculate safety stock is to use standard deviation to determine variations in supply and demand. The definition of standard deviation is a quantity calculated to indicate the extent of deviation for a group as a whole.
Why is it important to calculate safety stock?
It is important to calculate your safety stock carefully because while too little stock will result in shortages, too much stock will inflate your inventory costs. Luckily, there are ways to determine how much safety stock you will need on hand. Steps.
What would happen if lead time was zero?
If lead time were zero, then you would need no safety stock, as product could be produced instantly upon demand. Of course, lead time can never be reduced to zero, but lowering it as much as possible is the best way to run a leaner business. This means both tightening your supply chains and your production processes.
What Is Safety Stock?
Stock inventory usually consists of cycle stocks, or the inventory that is expected to be sold within a given period, and safety stock. Safety stock acts as a buffer amount that accounts for uncertainties such as:
How Can Safety Stock Improve Inventory Management?
Effective inventory management relies on the cushion that safety stock provides. Tracking current stock levels accurately while considering present and future market conditions and accounting for supply lead times is just the start of effective inventory control.
Why Do Businesses Need Safety Stock?
Running out of stock is an expensive issue for businesses across the globe. Stockouts result in $984 billion worth of lost sales worldwide, with North American companies alone losing $144.9 billion, according to a study by IHL Group.
How to Calculate Safety Stock
Safety stock is about more than just having a few extra units available. Different formulas help inventory managers determine how much safety stock they need and calculate some critical variables.
Complementary Formulas
These equations provide additional information to supplement safety stock calculations. They can be used to ensure that each aspect relating to safety stock is accounted for.
Common Safety Stock Challenges & Risks
Safety stock is a valuable tool to combat stockouts, but it can have some disadvantages. There are a few factors inventory managers need to consider when developing safety stock strategies.
Safety Stock Examples
Here's how safety stock works in practice: A snow shovel manufacturer knows that demand is low during the warmer months but can fluctuate significantly in the winter depending on several hard-to-predict aspects of the weather.
What happens if you don't calculate safety stock?
In fact, if you do not properly calculate safety stock, you can actually increase the risk of a stockout. If a stockout happens, it can only be downhill from here. If your customers find that your business is not meeting demand, they’ll easily find another establishment that can.
Why do we carry safety stock?
Safety stock is carried in order to prevent issues caused by something known as stockouts. A stockout refers to changes in customer demand (usually when demand is higher than what is expected for a certain product), an incorrect forecast of supply and demand, or variability in lead times for raw materials.
How to calculate demand average?
The best time frame to work with is how quickly a product is reordered. To calculate demand average, then, you have to take the sum of a total sales volume in your time frame and divide it by the number of buying days. In a two week period, the number of buying days would be 14.
Why is inventory important?
One of the most first things to know about running a business is that your inventory is an important part of keeping your company alive and thriving. When your inventory is well-stocked and flowing, customers are happy, revenue is coming in, and your business is growing. If stock ever falls behind, however, it can lead to a serious disaster.
What happens if stock falls behind?
If stock ever falls behind, however, it can lead to a serious disaster. Imagine if the supply chain gets a little tangled: your customers may order items that are no longer in stock and have to wait a prolonged time for their goods, or worse, receive the wrong items.
What is actual time?
Actual time: the actual, real-time it took to replenish the order of a certain product. Variance: the difference between the actual time and the expected time. If you have positive numbers in your variance category, they represent the number of days over the expected times.
Can you increase your stockout if you don't calculate safety stock?
In fact, if you do not properly calculate safety stock, you can actually increase the risk of a stockout.
How to calculate safety stock?
When determining the appropriate level of safety stock, it's important to first find the standard deviation before proceeding with the calculations to determine the exact variations in supply and demand.#N#To calculate the standard deviation, follow these four steps-#N#1. Calculate the average of a set of data.#N#2. Find the sum of the average and the data from the set .#N#3. Take that total and divide it by the sample proportion to get the variance figure.#N#4 . Add the variance to the average.#N#Once this calculation is completed, it can be applied to the formula for calculating safety stock, which can be expressed as-#N#Z x sLT x D avg#N#Where Z refers to the desired service level, sLT refers to the standard deviation of lead time, and D avg refers to the demand average.#N#Calculating the optimal volume of safety stock is easy to understand once all of the figures are in place and can be done in four steps.
What is service level?
The service level is a figure that attempts to represent the desired probability of not experiencing a stockout. The higher this service level figure is, the more safety stock is needed to be held in inventory to prevent the risk of running out. The constantly changing nature of supply and demand can make it difficult to predict the correct level of safety stock necessary to meet the demands of customers.#N#For example, let's say we're determining the safety stock of N95 medical masks. While the typical retail industry average for service level stands around 90%, these masks are more high priority so a 95% service level is used. These service level percentages represent the probability of avoiding a stockout and is expressed as a service factor. Using the chart below, we can see that a 95% service level equates to a service factor figure of 1.64.
Why is it important to have safety stock?
There is a delicate and fine balance that needs to be struck when managing supply - carrying too little inventory can cause delays in customers not receiving their products and carrying too much inventory takes up precious storage space and increases carrying costs.#N#That's why it's important for managers to consider storing safety stock to help mitigate the effects of fluctuating consumer demand. Safety stock refers to holding an extra layer of stock to offset any sudden surges in demand. Having this extra inventory helps to reduce the risk of this product becoming out of stock.
When managing inventory control, there can be uncertainty around levels of supply and demand?
When managing inventory control, there can be uncertainty around levels of supply and demand. This is why it is important to use formulas that are more dynamic and aren't very fixed to certain figures.
Why do we need safety stock?
Why safety stock is needed: 1 Stock to protect against variation in Supply or demand (only in case demand is bigger that the forecast) 2 Its purpose is to prevent disruptions in manufacturing or customer deliveries 3 Stock maintained to provide a required customer service level. 4 Safety stock can be maintained on finished goods level, but also at component / raw material level.
What is lead time in inventory?
Lead time is the amount of time from the point at which you determine the need to order to the point at which the inventory is on hand and available for use. It should include supplier or manufacturing lead time, time to initiate the purchase order or work order including approval steps, time to notify the supplier, and the time to process through receiving and any inspection operations.
What is the purpose of safety stock?
Its purpose is to prevent disruptions in manufacturing or customer deliveries. Stock maintained to provide a required customer service level. Safety stock can be maintained on finished goods level, but also at component / raw material level.
What is safety stock?
Safety stock is defined as inventory that is carried to prevent stock outs and back order situations. Stock outs stem from factors such as fluctuating customer demand, forecast inaccuracy, and variability in supplier lead times. Many companies look at their own demand fluctuations and assume that there is not enough consistency to predict future ...
What happens if you don't carry enough inventory?
If you carry too much inventory, you tie up money in working capital; if you don’t carry enough inventory, you face stock outs and reduced service levels. There must be a balance between inventory costs and customer service.
Which approach uses mathematical theories of probability?
The mathematical approach, which uses mathematical theories of probability, imposes order and regularity on aggregates of more or less disparate elements. Different statistical calculations are presented in literature and they will provide better results than the fixed and time-based safety stock calculations.
How to find the variance of a sample?
Which, in layman's terms, means you: 1 Find the average of a set of data 2 Calculate the sum of the average and the data set 3 Take the sum and divide it by the sample proportion to get the variance 4 Add the variance to the average
What is IP inventory?
To properly control inventory, companies should monitor the inventory position (“IP”), and not just on-hand inventory. The inventory position is the net inventory (on hand – backorders) plus the pipeline inventory (anything on order).
What happens when IP is high?
If the IP is high, it is likely that their demand will be filled but when the demand is low it will be less likely. Since the IP is mostly independent of when the customer shows up, we need only average the fill rates for all of the different inventory positions.
Is the standard deviation of Poisson a square root?
Since the standard deviation of the Poisson is the square root of the mean, whenever the demand is high the standard deviation is often relatively low. For instance, if the mean demand were 1000 the standard deviation would be only around 32 which is only 3% of the mean.
Is variance the dimension squared?
Variance is the dimension squared while average is just the dimension. That would be like adding apples and oranges. Even if they got the variance right, the formula for safety stock is missing the variability in demand—usually the larger component of variability.