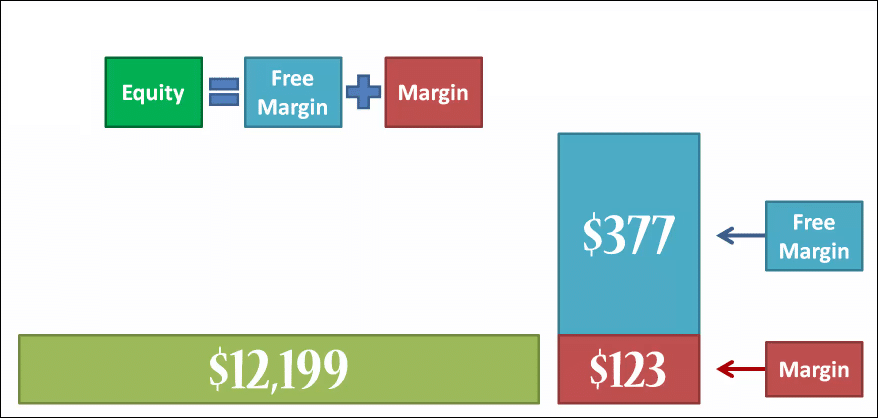
An initial margin requirement is a straightforward calculation. It is the number of shares multiplied by the stock price multiplied by the margin rate. Initial margin requirement = number of shares x stock price x margin rate
Full Answer
How do you calculate equity of a stockholder?
Shareholder’s Equity = Total Assets – Total Liabilities. As per another method, the stockholder’s equity formula of a company can be derived by summing up paid-in share capital, retained earnings, and accumulated other comprehensive income and then deducting treasury stock from the summation.
How do you calculate equity on a margin loan?
Equity is determined by subtracting the outstanding margin loan from the current value of the securities in the account. In the example presented, say, after buying $20,000 worth of stock, the value of those shares increased to $22,000. The margin loan remains at $10,000, resulting in investor equity of $12,000.
What is the equity percentage of a margin account?
The equity percentage of a margin account is the investor's equity divided by the account value. In the examples presented, with $12,000 of equity divided into $22,000, the equity percentage is 54.5 percent. If the equity is at $8,000 and divided into $18,000, the percentage is 44.4 percent.
What do I need to know about margin trading?
Before using margin, you must be fully aware of the trading risks and requirements. You must ensure your account holds the minimum equity to cover a trade before you place it. If the equity in your account is not sufficient or Fidelity believes the risk is too great, we can sell your assets at any time.

How do I calculate margin?
To calculate margin, start with your gross profit, which is the difference between revenue and COGS. Then, find the percentage of the revenue that is the gross profit. To find this, divide your gross profit by revenue. Multiply the total by 100 and voila—you have your margin percentage.
What is the formula for calculating stockholders equity?
Stockholders' equity can be calculated by subtracting the total liabilities of a business from total assets or as the sum of share capital and retained earnings minus treasury shares.
How do you calculate margin on a product?
To calculate manually, subtract the cost of goods sold (COGS) from the net sales (gross revenues minus returns, allowances, and discounts). Then divide this figure by net sales, to calculate the gross profit margin in a percentage.
How do you calculate profit margin ratio?
The formula is:(Total Revenue - Total Expenses) / Total Revenue.Net sales = revenue - returns, refunds and discounts.Net income = revenue - total expenses.Profit margin = (net income / net sales) x 100.Gross profit = revenue - (direct materials + direct labor + factory overhead)More items...•
Is total equity the same as stockholders equity?
Equity and shareholders' equity are not the same thing. While equity typically refers to the ownership of a public company, shareholders' equity is the net amount of a company's total assets and total liabilities, which are listed on the company's balance sheet.
Is shareholders equity the same as stockholders equity?
Shareholders' equity (SE) is also known as stockholders' equity, both with the same meaning. This term refers to the amount of equity a corporation's owners have left after liabilities or debts have been paid. Equity simply refers to the difference between a company's total assets and total liabilities.
How do I calculate margin and markup?
To calculate markup subtract your product cost from your selling price. Then divide that net profit by the cost. To calculate margin, divide your product cost by the retail price.
What is margin and markup formula?
By definition, the markup percentage calculation is cost X markup percentage, and then add that to the original unit cost to arrive at the sales price. For example, if a product costs $100, the selling price with a 25% markup would be $125: Gross Profit Margin = Sales Price – Unit Cost = $125 – $100 = $25.
What is the margin of a product?
Margin (also known as gross margin) is sales minus the cost of goods sold. For example, if a product sells for $100 and costs $70 to manufacture, its margin is $30. Or, stated as a percentage, the margin percentage is 30% (calculated as the margin divided by sales).
How do you calculate profit margin quizlet?
The equation to calculate net profit margin is: net margin = net profit / revenue.
What is shareholders' equity?
Shareholders' equity represents the financial net worth of a company. This number reflects the amount a company would return to shareholders if it liquidated its assets and repaid its debts.
Why is it important to understand shareholders' equity?
Understanding shareholders' equity can help investors determine whether a company is performing well financially, which helps them make proper decisions on whether they want to invest in that company. This can also help one gain an understanding of how a company funds their operations—whether by seeking loans or funding through other means.
What's the difference between a shareholder and an equity holder?
A shareholder is someone who holds stock shares in a company but doesn't hold the entire equity stake in the company. An equity holder refers to an owner, or multiple owners, who holds the entire equity of a company and doesn't possess any shares.
How to calculate shareholders' equity
To calculate shareholders' equity, you can subtract a company's total liabilities from its total assets. Companies include this information on their balance sheets. Another method to calculate equity includes subtracting the value of treasury shares from a company's share capital and retained earnings.
Shareholders' equity calculation examples
As of December 2019, a company in which you hold stocks reports $2 million in current assets and $1.3 million in fixed assets. The company also has short-term liabilities equaling $500,000 and long-term liabilities equaling $1 million.
What is stockholders equity?
Stockholders' equity (aka "shareholders' equity") is the accounting value ("book value") of stockholders' interest in a company. Keep in mind, the shareholders' interest is a residual one: Creditors have first claim on a company's assets. You get a sense of that priority of claims in the following expression of the basic accounting equation:
What are the components of stockholders' equity?
Assuming a company has any operating history whatsoever, the two basic components of stockholders' equity are: Paid-in capital. Retained earnings. Paid-in capital. As the name suggests, paid-in-capital (or 'contributed capital') is the money the company has raised from investors through the sale (s) of its stock.
What is Treasury stock?
Treasury stock#N#Treasury stock is created when a company repurchases its own common or preferred shares and holds them in treasury instead of retiring them. Treasury stock is issued, but not outstanding; it has no voting rights and does not receive dividends (for reporting purposes, retired shares are treated as authorized, but not issued). A company can hold treasury stock for multiple purposes: 1 To distribute to employees as part of a stock option plans. 2 To maintain control and ownership, for example to fend off a hostile takeover bid.
What is the major source of change in a company's equity?
Excluding these transactions, the major source of change in a company's equity is retained earnings, which are a component of comprehensive income. However, there are other sources and thus, ...
Why do corporations have a low par value?
Corporations like to set a low par value because it represents their "legal capital", which must remain invested in the company and cannot be distributed to shareholders. Another reason for setting a low par value is that when a company issues shares, it cannot sell them to investors at less than par value.
What is par value in stock?
The par value of issued stock is an arbitrary value assigned to shares in order to fulfill state law. The par value is typically set very low (a penny per share, for example) and is unrelated to the issue price of the shares or their market price.
What is retained earnings?
As the name suggests, retained earnings is the cumulative amount of net income the company has earned from the time it was created that it has not distributed to shareholders as dividends. Losses are included in the calculation, too: they subtract from retained earnings.
Why is it important to understand the stockholder's equity formula?
From the point of view of an investor, it is essential to understand the stockholder’s equity formula because it is the representation of the real value of the stockholder’s investment in the business. The stockholder’s equity is available as a line item in the balance sheet of a company or a firm.
What is shareholder equity?
In other words, the shareholder’s equity formula finds the net value of a business or the amount that can be claimed by the shareholders if the assets of the company are liquidated, and its debts are repaid. It is represented as follows –.
What is stockholders equity?
Stockholders' equity is the residual amount of funds in a business that theoretically belong to its owners. The amount of stockholders' equity can be calculated in a number of ways, including the following:
What to do if a balance sheet is not available?
If a balance sheet is not available, summarize the total amount of all assets and subtract the total amount of all liabilities. The net result of this simple formula is stockholders' equity. If the preceding options are not available, it will be necessary to compile the amount from individual accounts in a company's general ledger.
Is stockholders equity a theoretical concept?
The amount of stockholders' equity is really more of a theoretical concept, for it does not accurately reflect the amount of funds that would be distributed to shareholders if a business were to be liquidated . The following valuation issues should also be considered: Intangibles.
Is there a stockholder's equity formula for a nonprofit?
If so, the stockholders' equity formula is: There is no such formula for a nonprofit entity, since it has no shareholders. Instead, the equivalent classification in the balance sheet of a nonprofit is called " net assets .".
Common Stock & Additional Paid-In Capital (APIC)
Often referred to as paid-in capital, the “Common Stock” line item on the balance sheet consists of all contributions made by the company’s equity shareholders.
Retained Earnings
Next, the “ Retained Earnings ” are the accumulated net profits (i.e. the “bottom line”) that the company held onto as opposed to paying dividends to shareholders.
Treasury Stock
The “ Treasury Stock ” line item refers to shares previously issued by the company that were later repurchased in the open market or directly from shareholders.
Excel Template Download
Now that we’ve gone over the most frequent line items in the shareholders’ equity section on a balance sheet, we’ll create an example forecast model.
How much can you buy stocks on margin?
Buying Stocks on Margin. If you have a margin brokerage account, you can use a margin loan to pay up to 50 percent of the cost of buying stocks. For example, if you have an initial cash balance of $10,000, you can buy up to $20,000 worth of stocks.
What is margin account?
A brokerage margin account allows an investor to buy stocks and other securities with a portion of the purchase price paid with a margin loan from the broker. Margin loans can be a useful investment tool. Limits exist as to the size of loan an investor can have, and the account equity is used to determine those limits.
What is the maintenance margin on a margin account?
If the investor's equity is above 50 percent, the account has the ability to increase the amount of margin loan. The extra loan capacity can be used to buy more investments or can be withdrawn from the account as cash. A margin account also has a minimum maintenance margin. The Securities and Exchange Commission sets the maintenance margin at 25 percent, but a brokerage firm may set it higher. If the equity in a margin account falls below the maintenance margin percentage, the investor will be issued a margin call to add cash or securities to the account to bring up the equity in the account.
What is gross margin?
Gross profit margin is your profit divided by revenue (the raw amount of money made). Net profit margin is profit minus the price of all other expenses (rent, wages, taxes etc) divided by revenue. Think of it as the money that ends up in your pocket.
What is the difference between gross margin and markup?
The difference between gross margin and markup is small but important. The former is the ratio of profit to the sale price and the latter is the ratio of profit to the purchase price (Cost of Goods Sold). In layman's terms, profit is also known as either markup or margin when we're dealing with raw numbers, not percentages. It's interesting how some people prefer to calculate the markup, while others think in terms of gross margin. It seems to us that markup is more intuitive, but judging by the number of people who search for markup calculator and margin calculator, the latter is a few times more popular.
What does it mean when a company has low profit margins?
In general, your profit margin determines how healthy your company is - with low margins you're dancing on thin ice and any change for the worse may result in big trouble. High profit margins mean there's a lot of room for errors and bad luck.
What are some practices that cost you more money in the long run?
There are also certain practices that, despite short term profit, will cost you more money in the long run, e.g., importing resources from a country likely to be subject to economic sanctions in the future, or buying a property that will be underwater in 5 years.
Is margin the same as profit?
Although both measure the performance of a business, margin and profit are not the same. All margin metrics are given in percent values, and therefore deal with relative change, good for comparing things that are operating on a completely different scale.
Is 5% margin good?
Generally, a 5% net margin is poor, 10% is okay, while 20% is considered a good margin. There is no set good margin for a new business, so check your respective industry for an idea of representative margins, but be prepared for your margin to be lower. For small businesses, employees are often your main expense.
Is markup more intuitive than margin?
It's interesting how some people prefer to calculate the markup, while others think in terms of gross margin. It seems to us that markup is more intuitive, but judging by the number of people who search for markup calculator and margin calculator, the latter is a few times more popular.
What to know before using margin?
Before using margin, you must be fully aware of the trading risks and requirements. You must ensure your account holds the minimum equity to cover a trade before you place it. If the equity in your account is not sufficient or Fidelity believes the risk is too great, we can sell your assets at any time.
What is the initial margin requirement?
An initial margin requirement is the amount of funds required to satisfy a purchase or short sale of a security in a margin account. The initial margin requirement is currently 50% of the purchase price for most securities, and it is known as the Reg T or the Fed requirement, which is set by the Federal Reserve Board.
What is margin call risk?
Margin call risk: If the securities you hold fall below the minimum maintenance requirement, your account will incur a margin call. Margin calls are due immediately.
What happens if you have a margin call on Fidelity?
The size of the margin call can cause an accelerated margin call, which might result in account liquidation. If you experience repeated account liquidations, Fidelity can restrict your account, remove the margin and/or options feature, or terminate your account per the Customer Agreement.
What happens if you cover margin call?
By covering the margin call immediately, you reduce the probability of account liquidation and have more control over your investments. If you experience repeated account liquidations, Fidelity can restrict your account, remove the margin feature, or terminate your account per the Customer Agreement.
What would happen if you didn't use margin loan?
If you didn’t use a margin loan, you would have paid $10,000 in cash for the stock. Not only would you have tied up an additional $5,000, but you would have realized only a 10% return on your investment. The 10% difference in the return is the result of leveraging your assets.