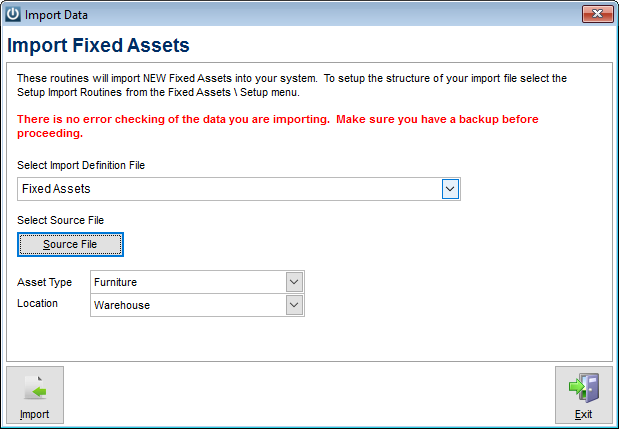
- Hold Your Stock Options.
- Initiate an Exercise-and-Hold Transaction (cash for stock)
- Initiate an Exercise-and-Sell-to-Cover Transaction.
- Initiate an Exercise-and-Sell Transaction (cashless)
When should I execute my stock options?
Assuming you stay employed at the company, you can exercise your options at any point in time upon vesting until the expiry date — typically, this will span up to 10 years.
Is it better to execute an option or sell it?
As it turns out, there are good reasons not to exercise your rights as an option owner. Instead, closing the option (selling it through an offsetting transaction) is often the best choice for an option owner who no longer wants to hold the position.
Can you execute option at any time?
The holder of an American-style option contract can exercise the option at any time before expiration. Therefore, an option writer may be assigned an exercise notice on an open short option position at any time before expiration.
What happens when I execute an option?
Upon execution, the option disappears from your account, your cash balance is reduced by an amount of money equal to 100 times the strike price and 100 shares of the underlying stock are deposited into your account. Compare the option strike price to the current stock price.
How are options exercised?
To exercise an option means to take action on the right to buy or sell the underlying position in an options contract at the predetermined strike price, at or before expiration. The order to exercise your options depends on the position you have.
Do I pay tax when I exercise stock options?
You have taxable income or deductible loss when you sell the stock you bought by exercising the option. You generally treat this amount as a capital gain or loss. However, if you don't meet special holding period requirements, you'll have to treat income from the sale as ordinary income.
What happens if I don't sell my call option?
If you don't exercise an out-of-the-money stock option before expiration, it has no value. If it's an in-the-money stock option, it's automatically exercised at expiration.
What happens if call option expires?
When a call option expires in the money, it means the strike price is lower than that of the underlying security, resulting in a profit for the trader who holds the contract. The opposite is true for put options, which means the strike price is higher than the price for the underlying security.
Can I sell my option before it expires?
The buyer can also sell the options contract to another option buyer at any time before the expiration date, at the prevailing market price of the contract. If the price of the underlying security remains relatively unchanged or declines, then the value of the option will decline as it nears its expiration date.
Do you need money to buy the shares when executing a call option?
If you own a call option, you have the right to execute it, sell it, or let it expire. Of these, the only one that requires money is execution, which is when you buy the underlying shares at the strike price.
How is a call option exercised?
When exercising a call option, the owner of the option purchases the underlying shares (or commodities, fixed interest securities, etc.) at the strike price from the option seller, while for a put option, the owner of the option sells the underlying to the option seller, again at the strike price.
How can I make money on options without exercise?
Selling the Call Options If your call option is in-the-money with the stock price above the exercise price, you can lock in that equity by just selling the option to someone else. In other words, there really is no need to exercise the option, receive the shares and quickly sell them.
What does it mean to exercise a stock option?
Exercising a stock option means purchasing the issuer’s common stock at the price set by the option (grant price), regardless of the stock’s price at the time you exercise the option. See About Stock Options for more information.
How to exercise vested stock options?
Usually, you have several choices when you exercise your vested stock options: Hold Your Stock Options. Initiate an Exercise-and-Hold Transaction (cash for stock) Initiate an Exercise-and-Sell-to-Cover Transaction. Initiate an Exercise-and-Sell Transaction (cashless)
How long after stock options are exercised do you pay capital gains?
If you had waited to sell your stock options for more than one year after the stock options were exercised and two years after the grant date, you would pay capital gains, rather than ordinary income, on the difference between grant price and the sale price. Top.
How much is the stock price on June 1?
On June 1, the stock price is $70. You sell your 100 shares at the current market value. When you sell shares which were received through a stock option transaction you must: Pay ordinary income tax on the difference between the grant price ($10) and the full market value at the time of exercise ($50).
What are the benefits of owning stock?
benefits of stock ownership in your company, (including any dividends) potential appreciation of the price of your company's common stock. the ability to cover the stock option cost, taxes and brokerage commissions and any fees with proceeds from the sale. Top.
Do stock options expire?
Just remember that stock options will expire after a period of time. Stock options have no value after they expire.
Do stock options have value after expiration?
Stock options have no value after they expire. The advantages of this approach are: you’ll delay any tax impact until you exercise your stock options, and. the potential appreciation of the stock, thus widening the gain when you exercise them. Top.
How to exercise an option?
When you exercise your option, you buy (call) or sell (put) the underlying stock at the price stated in the contract. If your options have value relative to the actual stock price, you are "in the money.". A call option allows you to buy stock at the stated strike price.
What happens if you own put options at $100?
Likewise, if you owned put options for stock at the strike price of $100, and it is currently selling at $50, you are "in the money" because you can force someone to buy the stock at twice the price it's currently trading for.
How to minimize risk in options trading?
1. Evaluate the risk in your options position. Trading options is inherently risky, but offsetting options can minimize the risk involved. However, when you minimize risk, you may also lessen your opportunity to profit from your position. For example, suppose you own put options with a strike price of $50.
What happens if you exercise an option before the expiration date?
Exercising an option well before the expiration date means losing potential value. However, waiting it out comes with a risk that the stock price won't move the way you've predicted. For example, suppose you are in the money on call options that don't expire for 6 months.
How does a call option work?
A call option allows you to buy stock at the stated strike price. You'll make money if the stock is trading at a higher price than your stock price, because you can buy shares at your lower strike price. You could then turn around and sell those shares at the actual price to make money.
What is strike price in stock?
When you buy options, you are buying the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell shares of the underlying stock at a specific price, called the strike price. When you exercise the option, you complete the action you bought the right to do. American-style options can be exercised at any time, whereas European-style options can only be ...
What happens if you exercise put options?
If you have put options, you have the right to sell stock at the strike price listed on your contract. You'll make money if you exercise your options when the stock is selling at a much lower price on the open market. You are essentially forcing someone to buy shares at a higher price.
What is stock option?
Simply put, a stock option is a privilege giving its holder the right to purchase a particular stock at a price agreed upon by the assignor and the holder (called the “grant price”) within a specified time. Note that a stock option is a right, not an obligation, to purchase the stock, meaning that the option holder may choose to not exercise ...
What does it mean to exercise a stock option?
Exercising a stock option means purchasing the shares of stock per the stock option agreement. The benefit of the option to the option holder comes when the grant price is lower than the market value of the stock at the time the option is exercised. Here’s an example:
How long do you have to hold stock to pay capital gains tax?
In regard to long-term capital gains taxes, consider that you will pay a more favorable long-term capital gains tax rate if you exercise your options, hold the shares for more than a year, and then sell your shares more than two years after the option grant date.
Why exercise options before expiration date?
Here are four reasons to consider exercising your options before the expiration date: You have good reason to believe that the company’s prospects have turned negative and you want to exercise your options and sell your shares before the stock price declines.
What is vesting date?
A vesting date is a common feature of stock options granted as part of an employee compensation package. The purpose of the vesting date is to ensure the employee’s commitment to his job position and to making the company a success.
What are the tax considerations for incentive stock options?
There are three main forms of taxes that must be considered when exercising an ISO: the alternative minimum tax (AMT), your current income tax, and long-term capital gains tax.
What is an employee stock option?
An employee stock option is a contract between an employee and her employer to purchase shares of the company’s stock, typically common stock, at an agreed upon price within a specified time period.
What type of option to take on if the stock price moves up?
Depending on which direction you expect the underlying stock to move determines what type of options contract to take on: If you think the stock price will move up: buy a call option, sell a put option. If you think the stock price will stay stable: sell a call option or sell a put option.
How to trade options?
1. Open an options trading account. Before you can start trading options, you’ll have to prove you know what you’re doing. Compared with opening a brokerage account for stock trading, opening an options trading account requires larger amounts of capital.
What is a call option?
As a refresher, a call option is a contract that gives you the right, but not the obligation, to buy a stock at a predetermined price — called the strike price — within a certain time period (Learn all about call options.) A put option gives you the right, but not the obligation, to sell shares at a stated price before the contract expires. (Learn all about put options.)
How to choose an option broker?
Trading stock options can be complex — even more so than stock trading. When you buy a stock, you just decide how many shares you want, and your broker fills the order at the prevailing market price or a limit price you set. Options trading requires an understanding ...
How long do American options last?
Expiration dates can range from days to months to years. Daily and weekly options tend to be the riskiest and are reserved for seasoned option traders.
What happens if an option is left unprotected?
If the option position is left unprotected, it's naked. Based on your answers, the broker typically assigns you an initial trading level based on the level of risk (typically 1 to 5, with 1 being the lowest risk and 5 being the highest). This is your key to placing certain types of options trades.
What are the types of options you want to trade?
The types of options you want to trade. For instance, calls, puts or spreads. And whether they are covered or naked. The seller or writer of options has an obligation to deliver the underlying stock if the option is exercised. If the writer also owns the underlying stock, the option position is covered.
What happens when you execute an order?
But where and how your order is executed can impact the overall cost of the transaction, including the price you pay for the stock.
What is order flow in stock trading?
This is called “payment for order flow.”. For a stock that trades in an over-the-counter (OTC) market, your broker may send the order to an “OTC market maker.”. Many OTC market makers also pay brokers for order flow. Your broker may route your order -- especially a limit order -- to an electronic communications network ...
What is automated system in broker?
In deciding how to execute orders, your broker has a duty to seek the best execution that is reasonably available for its customers' orders. That means your broker must evaluate the orders it receives from all customers in the aggregate and periodically assess which competing markets, market makers, or ECNs offer the most favorable terms of execution.
Does a broker have options?
Your Broker Has Options for Executing Your Trade. Just as you have a choice of brokers, your broker generally has a choice of markets to execute your trade. For a stock that is listed on an exchange, your broker may direct the order to that exchange, to another exchange, or to a firm called a "market maker.".
Does a trade execution take time?
While trade execution is usually seamless and quick, it does take time. And prices can change quickly, especially in fast-moving markets. Because price quotes are only for a specific number of shares, investors may not always receive the price they saw on their screen or the price their broker quoted over the phone.
How do put options work?
There are a number of ways to close out, or complete, the option trade depending on the circumstances. If the option expires profitable or in the money, the option will be exercised. If the option expires unprofitable or out of the money, nothing happens, and the money paid for the option is lost.
What is put option?
A put option is a contract that gives its holder the right to sell a number of equity shares at the strike price, before the option's expiry. If an investor owns shares of a stock and owns a put option, the option is exercised when the stock price falls below the strike price. Instead of exercising an option that's profitable, ...
What happens if you don't own shares in Max?
If Max doesn't own shares, the option can be exercised to initiate a short position in the stock. A short position is when an investor sells the stock first with the goal of buying the stock or covering it later at a lower price. Since Max doesn't own any shares to sell, the put option will initiate a short position at $11.
What does it mean when a put option increases in value?
A put option increases in value, meaning the premium rises, as the price of the underlying stock decreases. Conversely, a put option's premium declines or loses value when the stock price rises. Put options provide investors a sell-position in the stock when exercised.
What is the alternative to exercising an option?
An alternative to exercising an option is to sell the option contract back to the market. Selling the option is both the easiest and the most commonly used method of closing an option position. In other words, there is no exchange of shares; instead, the investor has a net gain or loss from the change in the option's price.
What does it mean when an option is exercised?
"Exercising the option" means the buyer is opting to take advantage of the right to sell the shares at the strike price. The opposite of a put option is a call option, which gives the contract holder ...
How much did Max save by buying the option?
By buying the option, Max has saved himself $300 (less the cost of the option), since he has sold 100 shares at $11, for a total $1,100, instead of having to sell the shares at $8 for a total $800. Max could have sold his stock at $11 and not bought a put option.
What happens when you convert a call option into stock?
When you convert a call option into stock by exercising, you now own the shares. You must use cash that will no longer be earning interest to fund the transaction, or borrow cash from your broker and pay interest on the margin loan. In both cases, you are losing money with no offsetting gain. Instead, just hold or sell the option and avoid additional expenses.
How long does an option expire in October?
October expiration is in two weeks. 1. Time Value. A number of factors determine the value of an option, including the time left until expiration and the relationship of the strike price to the share price. If, for example, one contract expires in two weeks and another contract, on the same stock and same strike price, expires in six months, ...
What is call option?
For example, a call option is a contract that grants its owner the right, but not the obligation, to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock by paying the strike price per share, up to the expiration date. Conversely, a put option represents the right to sell the underlying shares.
What are the two sides of an option contract?
Remember, there are always two sides to an options contract: the buyer and the seller. The obligation of a call seller is to deliver 100 shares at the strike price. The obligation of a put seller is to purchase 100 shares at the strike price.
What happens when you exercise an option?
When you exercise an option, you usually pay a fee to exercise and a second commission to buy or sell the shares. . This combination is likely to cost more than simply selling the option, and there is no need to give the broker more money when you gain nothing from the transaction.
Do you have to exercise your rights as an option owner?
The important thing to understand is that the option owner has the right to exercise. If you own an option, you are not obligated to exercise; it's your choice. As it turns out, there are good reasons not to exercise your rights as an option owner.
Can you sell an option at fair value?
Or, if you own an option that is deep in the money, you may not be able to sell it at fair value. If bids are too low, however, it may be preferable to exercise the option to buy or sell the stock. Do the math.
What to do when you own options?
Essentially, there are 4 things you can do if you own options: hold them, exercise them, roll the contract, or let them expire. If you sell options, you can also be assigned. If you are an active investor trading options with some percentage of your overall investment funds, ...
What does it mean to exercise an option?
To exercise an option means to take action on the right to buy or sell the underlying position in an options contract at the predetermined strike price, at or before expiration. The order to exercise your options depends on the position you have.
What to do if you are bullish on a stock?
If you are bullish and you own calls on the underlying stock, you may want to exercise the options contract to own the stock immediately. To help offset a short/long position. You might use options to offset losses from an existing position.
Why exercise options before they expire?
In addition to wanting to capture realized gains on your options, you may want to exercise: To get the dividend.
What is the assignment of an option?
Assignment. If you sell an option, you have an obligation to sell stock if you are short a call, and an obligation to buy stock if you are short a put. The owner of call or put options has the right to assign the contract to the seller. This is known as assignment.
When do you roll an option?
Rolling your options. Before expiration—and, more commonly, near the end of the contract—you can also choose to roll the contract. This involves closing out your existing options position (by selling to close a long position or buying to close a short position) that is about to expire and simultaneously purchasing a substantially similar options ...
Is closing out an option taxable?
Be aware that closing out an options position triggers a taxable event, so you would want to consider the tax implications and the timing of closing a trade on your specific situation. You should consult your tax advisor if you have additional questions.
