The most common way to value a stock is to compute the company's price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio. The P/E ratio equals the company's stock price divided by its most recently reported earnings per share (EPS). A low P/E ratio implies that an investor buying the stock is receiving an attractive amount of value.
How do you evaluate a stock?
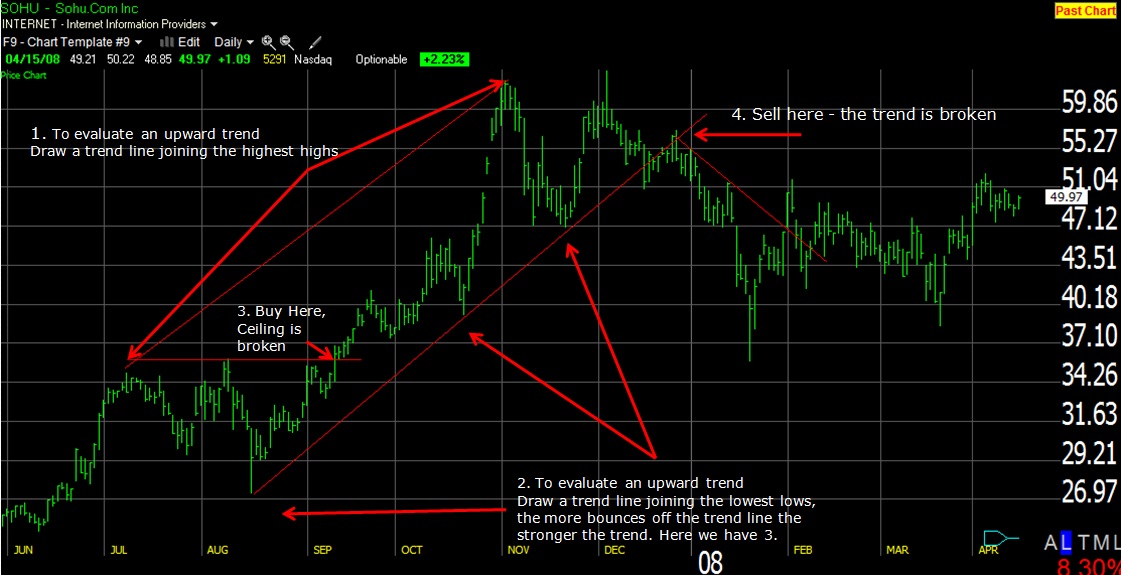
To evaluate a stock, review its performance against a benchmark. You may be satisfied with a stock that generated an 8% return over the past year, but what if the rest of the market is returning a few times that amount?
How can you tell if a stock's earnings are growing?
You'll even be able to observe the rate at which they are. Price to Earnings Ratio (P/E): The ratio of a company's share price compared to its EPS. Projected Earnings Growth (PEG): A stock's P/E ratio divided its the growth rate of its earnings.
Should you buy or sell a stock based on earnings per share?
But, if you're a stock market investor, you should drill down even further during your fundamental analysis when you're looking at buying (or selling) a stock. When you do, it will lead you to the most important metric of all, earnings per share (EPS). Earnings per share (EPS) is the most important metric to use when you're analyzing a stock.
How do you know if a stock is a good investment?
To counter this, most investors look at the stock’s total returns that include all dividend or interest payments in addition to the price return. Consider the actual performance of the stock over a period, as though you had invested in it on that first day of the period.

What is the best way to evaluate a stock?
The most common way to value a stock is to compute the company's price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio. The P/E ratio equals the company's stock price divided by its most recently reported earnings per share (EPS). A low P/E ratio implies that an investor buying the stock is receiving an attractive amount of value.
What is a good price earnings for a stock?
So, what is a good PE ratio for a stock? A “good” P/E ratio isn't necessarily a high ratio or a low ratio on its own. The market average P/E ratio currently ranges from 20-25, so a higher PE above that could be considered bad, while a lower PE ratio could be considered better.
How do you evaluate a stocks affect and earning potential?
The P/E ratio helps investors determine the market value of a stock as compared to the company's earnings. In short, the P/E shows what the market is willing to pay today for a stock based on its past or future earnings. A high P/E could mean that a stock's price is high relative to earnings and possibly overvalued.
Is 30 a good PE ratio?
P/E 30 Ratio Explained A P/E of 30 is high by historical stock market standards. This type of valuation is usually placed on only the fastest-growing companies by investors in the company's early stages of growth. Once a company becomes more mature, it will grow more slowly and the P/E tends to decline.
Is PE ratio a good indicator?
To many investors, the price-earnings ratio is the single most indispensable indicator for any stock purchase.
How do you tell if a stock is a good buy?
Here are nine things to consider.Price. The first and most obvious thing to look at with a stock is the price. ... Revenue Growth. Share prices generally only go up if a company is growing. ... Earnings Per Share. ... Dividend and Dividend Yield. ... Market Capitalization. ... Historical Prices. ... Analyst Reports. ... The Industry.More items...
How do you analyze a stock before buying?
How To Study a Stock Before InvestingReviewing Financial Statements: Share market analysis is first and foremost a numbers game. ... Industry Analysis: ... Researching Stocks: ... Price Targets: ... Conclusion.
How do you analyze stocks for beginners?
How to do Fundamental Analysis of Stocks:Understand the company. It is very important that you understand the company in which you intend to invest. ... Study the financial reports of the company. ... Check the debt. ... Find the company's competitors. ... Analyse the future prospects. ... Review all the aspects time to time.
How to evaluate a stock?
To evaluate a stock, review its performance against a benchmark. You may be satisfied with a stock that generated an 8% return over the past year, but what if the rest of the market is returning a few times that amount? Take the time to compare the stock’s performance with different market indexes, such as the Dow Jones Industrial Average, the S&P 500, or the NASDAQ Composite. These indexes can act as the benchmark against which to compare your own investments' performance. 1
What is the purpose of looking at the change in a stock price?
Looking at the change in a stock's price by itself is a naive way to evaluate the performance of a stock. Everything is relative, and so that return must be compared to make a proper evaluation. In addition to looking at a company’s total returns, comparing them to the market and weighing them relative to competitors within the company's industry, there are several other factors to consider in evaluating a stock’s performance.
How to calculate real return?
This is called a real return and can be done simply by subtracting inflation from the annual return of your investment.
Do dividends add to total return?
If the stock pays dividends, for instance, those cash flows must be added to the total return of the investment.
Is the S&P 500 a good yardstick?
If you invest in small speculative penny stocks, the S&P 500 will not be the right yardstick, as that contains only large-cap stocks listed on major stock exchanges. You may also want to look at how the economy has done during the same period, how inflation has risen, and other broader economic considerations.
Is a stock outperforming the market?
It could happen that a stock is outperforming the market but is nevertheless underperforming its own industry, so make sure to consider the stock’s performance relative to its primary competitors as well as companies of similar size in its industry.
Why is the stock price low when the analyst weights profits higher than management?
In other words, their analysis shows the stock is undervalued according to the financial data they’ve looked at, but the trading price is low because the management team isn’t doing a very good job overall.
How do new investors get better returns?
New investors will get a better return by simply investing in low-fee index funds or mutual funds that track the market, rather than attempting to beat the market by picking individual stocks.
What does value investor believe?
They believe that there are opportunities to make money by identifying undervalued stocks by using intrinsic value.
Why do valuations differ?
Differences in valuation can arise as a result of individual analysts placing a higher weighting of importance on different factors. For example, a business’s management team might be held as a high value-determining factor when another analyst might place a higher weighting on profits as the driver of value.
What is value investing?
Value investing is one of the primary ways to create long-term returns in the stock market. The fundamental investment strategy is to buy a company stock trading for less than its intrinsic value, as calculated by one of several methods.
What is a buy and hold investor?
Buy-and-hold investors are a classic example of value investors. They look for strong earnings growth, and they look for it over a very long period if possible. They buy stocks to hold for the long-term in order to see their undervalued stock’s price rise once the market corrects the pricing errors the investor took advantage of at the time of purchase.
Why is there still a level of subjectivity in the stock market?
Obviously, there is still a level of subjectivity due to the nature of many of the qualitative factors and assumptions being made. After the intrinsic value is estimated, it is compared to the current market price of a stock to determine whether the stock is overvalued or undervalued.
How to compare the value of different stocks?
All publicly traded companies report earnings to the Securities and Exchange Commission on a quarterly basis in an unaudited filing known as the 10-Q , and annually in an audited filing known as the 10-K.
How to learn more about individual stocks?
One way to learn more about individual stocks is through professional stock research. The brokerage firm where you have your account may provide research from its own analysts and perhaps from outside sources. You can also find independent research from analysts who aren't affiliated with a brokerage firm, as well as consensus reports that bring together opinions from a variety of analysts. Some of this research is free, while other research comes with a price tag.
What is the most widely quoted measure of stock value?
Even though P/E is the most widely quoted measure of stock value, it's not the only one. You'll also see stock analysts discussing measures such as ROA (return on assets), ROE (return on equity), and so on. While all of these acronyms may seem confusing at first, you may find, as you get to know them, that they can help answer some of your questions about a company, such as how efficient it is, how much debt it's carrying, and so on.
What does EPS mean in stock?
EPS is one indication of a company's current strength. You can divide the current price of a stock by its EPS to get the price-to-earnings ratio, or P/E multiple, the most commonly quoted measure of stock value. In a nutshell, P/E tells you how much investors are paying for a dollar of a company's earnings. For example, if Company A has ...
How to find EPS?
If you check those reports, the company's annual report, or its Web site, you'll find its current earnings-per-share, or EPS. That ratio is calculated by dividing the company's total earnings by the number of shares. You can then use this per-share number to compare the results of companies of different sizes. EPS is one indication of a company's current strength.
Is there a perfect P/E ratio?
There's no perfect P/E, though there is a market average at any given time. Over the long term that number has been about 15, though higher in some periods and lower in others. Value investors tend look for stocks with relatively low P/E ratios—below the current average—while growth investors often buy stocks with higher than average P/E ratios.
Is P/E a reliable measure?
You've probably seen stories in the financial press about companies restating earnings. This happens when an accounting error or other discrepancy comes to light, and a company must reissue reports for past periods. Inaccurate or inconsistent earnings statements may make P/E a less reliable measure of stock value.
What does higher earnings mean?
The more profitable a company is, the higher its EPS. Higher earnings can show investors that a company will be able to pay more dividends now and in the future.
What does the P/E ratio tell you?
The P/E ratio of a company is supposed to tell you whether its stock is “undervalued” or “overvalued.”. All things being equal, if the P/E ratio of a stock is lower than expected (compared to peers and/or the general market), it is said to be undervalued and selling at a bargain price.
What does PEG mean in stock?
PEG looks at the combination of a company’s stock price, its earnings per share, and expected growth rate. By taking the company’s growth into consideration, it helps to correct for the implicit bias the P/E ratio has against fast-growth companies.
What does it mean when a stock has a higher dividend yield?
The higher the dividend yield of a stock, the higher its desirability.
Why is a lower P/S ratio attractive?
A lower P/S ratio is more attractive as it shows investors are not paying much per dollar of revenue. In the example above, they are paying 50 cents for every $1 in sales.
Why is fundamental analysis important?
Fundamental analysis can be very useful in assessing whether a stock presents hidden value and whether it can potentially make you some money.
How to calculate net assets?
Net Assets = Total Assets – Total Liabilities. These values can be obtained from a company’s balance sheet or statement of financial position.
How to value a stock?
The most common way to value a stock is to compute the company's price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio . The P/E ratio equals the company's stock price divided by its most recently reported earnings per share (EPS). A low P/E ratio implies that an investor buying the stock is receiving an attractive amount of value.
Why do investors use adjusted earnings to calculate P/E?
Non-repeating events can cause significant increases or decreases in the amount of profits generated, which is why some investors prefer to calculate a company's P/E ratio using a per-share earnings number adjusted for the financial effects of one-time events. Adjusted earnings numbers tend to produce more accurate P/E ratios.
What is a stock?
A single share of a company represents a small ownership stake in the business. As a stockholder, your percentage of ownership of the company is determined by dividing the number of shares you own by the total number of shares outstanding and then multiplying that amount by 100. Owning stock in a company generally confers to the stock owner both corporate voting rights and income from any dividends paid.
What is GAAP earnings?
GAAP is shorthand for Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, and a company's GAAP earnings are those reported in compliance with them. A company's GAAP earnings are the amount of profit it generates on an unadjusted basis, meaning without regard for one-off or unusual events such as business unit purchases or tax incentives received. Most financial websites report P/E ratios that use GAAP-compliant earnings numbers.
How to calculate forward P/E ratio?
The forward P/E ratio is simple to compute. Using the P/E ratio formula -- stock price divided by earnings per share -- the forward P/E ratio substitutes EPS from the trailing 12 months with the EPS projected for the company over the next fiscal year . Projected EPS numbers are provided by financial analysts and sometimes by the companies themselves.
Why should investors consider companies' strengths and weaknesses when gauging a stock's value?
Aside from metrics like the P/E ratio that are quantitatively computed, investors should consider companies' qualitative strengths and weaknesses when gauging a stock's value. A company with a defensible economic moat is better able to compete with new market participants, while companies with large user bases benefit from network effects. A company with a relative cost advantage is likely to be more profitable, and companies in industries with high switching costs can more easily retain customers. High-quality companies often have intangible assets (e.g., patents, regulations, and brand recognition) with considerable value.
Why do P/S ratios vary?
Across industries, P/S ratios can vary greatly because sales volumes can vary greatly. Companies in industries with low profit margins typically need to generate high volumes of sales.
Why do investors prefer PEG?
Some investors may prefer the price-to-earnings growth ( PEG) ratio instead, because it factors in the earnings growth rate. 7 Other investors may prefer the dividend-adjusted PEG ratio because it uses the basic P/E ratio. It also adjusts for both the growth rate and the dividend yield of the stock. 8.
How Does the P/E Ratio Work?
Before you can use it, you have to learn what the P/E ratio is. It's easy to calculate as long as you know a given company's stock price and earnings per share (EPS). The equation looks like this:
What is the average P/E ratio for a healthcare company?
For instance, Fidelity research in early 2021 pegged the average health care company's P/E ratio at nearly 70. On the other hand, in the banking sector, companies tended to have a P/E ratio of just under 11.5. 3 4
What does negative P/E mean?
A negative P/E means that a company is not profitable. In these cases, the P/E ratio tells you how much money the company lost with every dollar you invested.
Why do you look at your portfolio through the P/E lens?
But looking at your portfolio through the P/E lens can help you avoid getting swept away in bubbles or panics. It can also help you know whether a stock is getting overvalued and no longer earning enough to warrant its price. Warning. You should never rely on P/E ratios alone when you choose investments.
Why are there differences between sectors?
That's partly because different businesses have different expectations. In the software sector, for example, companies often have higher growth rates and higher returns on equity. That means they can sell at larger P/E ratios.
What is the P/E ratio?
A price-to-earnings ratio, or P/E ratio, is the measure of a company's stock price in relation to its earnings. When trying to decide whether to invest in a certain stock, using the P/E can help you explore the stock's future direction.
What is the most important metric to use when you're analyzing a stock?
Earnings per share (EPS) is the most important metric to use when you're analyzing a stock.
What is EPS calculation?
The EPS calculation is just a starting point in an overall fundamental analysis strategy, but it is one of the most important parts—one that other fundamental metrics are derived from. There are even three different types of EPS numbers: Trailing EPS: Uses the previous year's numbers and is considered the true EPS.
What is the most important metric in fundamental analysis?
The Most Important Metric in Fundamental Analysis Is EPS. Brian Lund is the former investing expert for The Balance. He's made numerous appearances on CNBC and is the author of "Trading: The Best of the Best". To the average person, a company's gross revenue is the barometer for success, but as a smart stock market investor, ...
What does P/S stand for in accounting?
Price to Sales (P/S): A company's market capitalization divided by its total sales for the year.
What is trailing EPS?
Trailing EPS: Uses the previous year's numbers and is viewed as the true EPS.
Which is better, Company B or EPS?
Based on the EPS, Company B is by far the better choice. This is why it makes sense to look at EPS as a comparison tool because it more fully shows the theoretical value per share that a company is worth, something you can't tell with just revenue numbers alone.
What is the barometer of success?
To most people, gross revenue is the barometer for success. But, if you're a stock market investor, you should drill down even further during your fundamental analysis when you're looking at buying (or selling) a stock. When you do, it will lead you to the most important metric of all, earnings per share (EPS).
How to tell if a stock is overvalued?
Computing a stock's price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio is one of the quickest ways to learn whether a company is overvalued or undervalued. If a company's stock is undervalued, then it may be a good investment based on the current price. If it is overvalued, then you need to evaluate whether the company's growth prospects justify the stock price.
What is the price-to-earnings ratio?
The P/E ratio measures the relationship between a company's stock price and its earnings per issued share. The P/E ratio is calculated by dividing a company's current stock price by its earnings per share (EPS). If you don't know the EPS, you can calculate it by determining the company's earnings (subtract the company's preferred dividends from its net income) and then dividing the earnings by the number of shares outstanding.
What happens when you invert the P/E ratio?
If you invert the P/E ratio, you can find out the earnings yield, which represents your share of earnings for every share you own.
How to compare P/E ratios?
Since a company that is growing rapidly may be worth a high P/E ratio, you can compare among ratios by also calculating a company's P/E ratio as a multiple of the company's projected earnings growth rate. Simply divide a company's P/E ratio by either the earnings growth rate from the past few years or an analyst-supplied projection for the next few years. Companies with low — say, below 1 — P/E-to-earnings-growth (PEG) ratios may be worth somewhat higher P/E ratios.
How much is the P/E ratio of a stock?
Now that we know the EPS, we can compute the P/E ratio. If the stock currently trades for $30 per share, then the P/E ratio would simply be $30 divided by $2, or 15.
Does capital efficiency matter in P/E?
Capital efficiency matters, but P/E ratios don't take this factor into consideration. If a manufacturing company requires $50 in capital to produce $1 in earnings, then it shouldn't be worthy of the same ratio as a technology company that requires just $3 in capital to produce $1 in earnings.
Is a good P/E ratio bad?
When you start your analysis, take a look what type of company you're investigating. A good P/E ratio in one industry or asset class can be bad in another. If you're looking for a value stock, you want the P/E ratio to be low. The opposite is actually true of growth investments. If a company has high-flying earnings, it's likely a lot of investors will want to buy its stock.