How To Pick Dividend Stocks – 14 Steps – Summary
- Develop a watch list
- Look at the forward dividend yield
- Calculate the historical dividend growth rate
- Identify the number of years of consecutive dividend increases
- Determine if the company has a stated dividend policy
- Understand the company’s business model
- Review the historical revenue trend
- Investigate the company’s growth strategy
- Calculate the dividend payout ratio using earnings
- Calculate the dividend payout ratio using cash flow
- Evaluate the company’s debt levels and credit ratings
- Evaluate dividend safety
- Make a dividend growth forecast
- Review the stock valuation
How to choose the best dividend stocks?
· When calculating dividend coverage, dividend payouts for preferred stock are subtracted from net income before dividing by the total dividend payments for common shares. In evaluating dividend-paying stocks, keep in mind that there are special kinds of stocks known as real estate investment trusts, or REITs.
How to find good dividend stocks?
· My primary valuation method is often the P/E ratio, relative to 20 times past and/or forward earnings. Of course, regular readers know that this benchmark is not viewed in a vacuum, but in conjunction with past trends in earnings, dividends revenues etc and prospective growth in those earnings and dividends.
What are the best dividend paying stocks?
· How to Pick the Best Dividend Stocks Strong Cash, Low Earnings Expectations. When vetting dividend-paying companies, long-term profitability is a key... Steer Away from Debt. Investors should avoid dividend-paying companies that are saddled with excessive debt. Simply put:... Check Sector Trends. ...
How do you calculate dividends from stocks?
· By dividing the stock's annual dividend by the stock's price, you get a percentage. 1 You can think of that percentage as the interest on your money, with the additional chance at growth through...
What is dividend stock?
In general terms, dividend stocks are ones for which the dividends are a primary reason for ownership. The stock price often is stable or might increase slowly. Investors tend to think of dividends in terms of the dividend yield. That’s the ratio of a stock’s annual dividend to the current stock price; because the yield is based on ...
What is dividend coverage?
The dividend coverage ratio is a common metric for assessing the safety of a dividend. It's the ratio of the company's net income (the earnings after expenses, including taxes, are paid) divided by the dividend. For example, if a company has $50 million in net income and pays out $25 million in dividends, the dividend coverage, or dividend cover, is 2.0. (Note that the net income isn't necessarily the cash flow, which measures the money going into and out of a company's day-to-day operations.
What is the payout ratio?
Since dividends are paid out of company earnings, it’s a good idea to know how much of the earnings went toward dividends. This is called the payout ratio. The higher the payout ratio, the more a company is dedicating earnings toward dividends and less toward growth or one of the other options for employing earnings.
What does it mean when a company's board of directors approves a dividend increase?
When a company’s board of directors approves a dividend increase, it signals confidence in the company’s future earnings growth. Some companies have managed to steadily increase their dividends over decades. Some companies do offer a combination of solid growth and dividends.
What is the average dividend yield of the S&P 500?
As a reference point, the average dividend yield of stocks in the S&P 500 often ranges between about 2% and 4%.
Do dividend stocks pay dividends?
Many stocks pay dividends, but not all stocks are considered “dividend stocks," “income stocks," or yield stocks.
Wednesday, June 10, 2015
In my investing, look for businesses I can understand that have some sort of a competitive advantage that translates into consistent earnings power. I try to determine if I believe this business will be around in 20 years, and still have a consistent earnings power, despite obsolescence, competition and regulation.
How to value dividend stocks
In my investing, look for businesses I can understand that have some sort of a competitive advantage that translates into consistent earnings power. I try to determine if I believe this business will be around in 20 years, and still have a consistent earnings power, despite obsolescence, competition and regulation.
Why should investors educate themselves about broader sector trends?
Beyond studying a specific company's fundamentals, investors should likewise educate themselves about broader sector trends to make sure their chosen companies are positioned to thrive.
Is dividend investing a reliable method of wealth accumulation?
Dividend investing is a reliable method of wealth accumulation that offers the inflation protection bonds don't.
Why do stocks have high P/E?
The reason stocks tend to have high P/E ratios is that investors try to predict which stocks will enjoy progressively larger earnings. An investor may buy a stock with a P/E ratio of 30 if they think it will double its earnings every year (shortening the payoff period significantly).
Why do investors use the PEG ratio?
Because the P/E ratio isn't enough in and of itself, many investors use the price to earnings growth (PEG) ratio. Instead of merely looking at the price and earnings, the PEG ratio incorporates the historical growth rate of the company's earnings. This ratio also tells you how company A's stock stacks up against company B's stock.
How to calculate PEG ratio?
This ratio also tells you how company A's stock stacks up against company B's stock. The PEG ratio is calculated by taking the P/E ratio of a company and dividing it by the year-over-year growth rate of its earnings. The lower the value of your PEG ratio, the better the deal you're getting for the stock's future estimated earnings.
What does a PEG ratio mean?
A PEG of 1 means you're breaking even if growth continues as it has in the past.
How long does it take to pay back a stock?
The reason for this is simple: A P/E ratio can be thought of as how long a stock will take to pay back your investment if there is no change in the business. A stock trading at $20 per share with earnings of $2 per share has a P/E ratio of 10, which is sometimes seen as meaning that you'll make your money back in 10 years if nothing changes.
Why is it important to compare P/E ratios?
The reason for this is simple: A P/E ratio can be thought of as how long a stock will take to pay back your investment if there is no change in the business.
What is book value?
The book value usually includes equipment, buildings, land and anything else that can be sold, including stock holdings and bonds. With purely financial firms, the book value can fluctuate with the market as these stocks tend to have a portfolio of assets that goes up and down in value.
What to do if your dividend stock does not meet your selection criteria?
If at any point in the process, your dividend stock does not meet your selection criteria, stop and move to a different stock. Because making money from dividends means picking the right dividend stocks. And avoiding the rest. As a dividend stock picker, these 14 steps work well for me.
What are the selection criteria for dividend stocks?
Selection criteria for dividend stocks: Debt to equity less than or equal to 1. Or, the financial means to justify a higher debt to equity ratio.
What is the first rule of investing?
One of the first rules of investing is to understand what you are investing in.
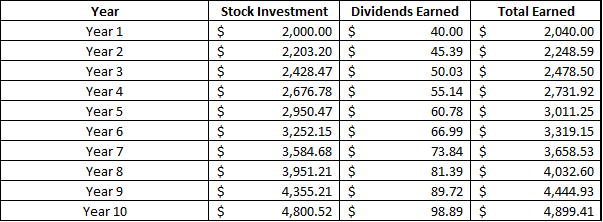
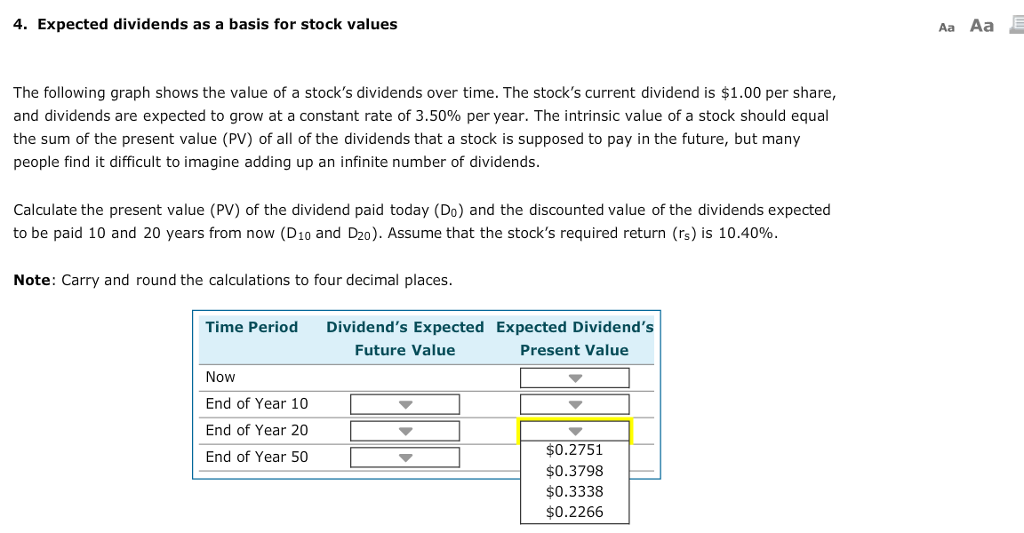
What is dividend discount model?
The dividend discount model is a means to discount back to present value the company’s future growing dividend payments. This is 1 reason I make a dividend growth forecast.
Is dividend real money?
Dividends are real money paid to us in cash from a company’s cash flow, not accounting earnings.
What is dividend payout ratio?
Earnings per share divided by dividends per share gives you the dividend payout ratio based on earnings. It is expressed as a percentage.
Do dividend stocks have growing earnings?
Dividend stocks with growing dividends have growing earnings. And growing earnings come partly from growing revenues.
How to evaluate a stock?
To evaluate a stock, review its performance against a benchmark. You may be satisfied with a stock that generated an 8% return over the past year, but what if the rest of the market is returning a few times that amount? Take the time to compare the stock’s performance with different market indexes, such as the Dow Jones Industrial Average, the S&P 500, or the NASDAQ Composite. These indexes can act as the benchmark against which to compare your own investments' performance. 1
What is the purpose of looking at the change in a stock price?
Looking at the change in a stock's price by itself is a naive way to evaluate the performance of a stock. Everything is relative, and so that return must be compared to make a proper evaluation. In addition to looking at a company’s total returns, comparing them to the market and weighing them relative to competitors within the company's industry, there are several other factors to consider in evaluating a stock’s performance.
How to calculate real return?
This is called a real return and can be done simply by subtracting inflation from the annual return of your investment.
Is the S&P 500 a good yardstick?
If you invest in small speculative penny stocks, the S&P 500 will not be the right yardstick, as that contains only large-cap stocks listed on major stock exchanges. You may also want to look at how the economy has done during the same period, how inflation has risen, and other broader economic considerations.
Do dividends add to total return?
If the stock pays dividends, for instance, those cash flows must be added to the total return of the investment.
Is a stock outperforming the market?
It could happen that a stock is outperforming the market but is nevertheless underperforming its own industry, so make sure to consider the stock’s performance relative to its primary competitors as well as companies of similar size in its industry.
What to know before buying dividend stocks?
Before you buy any dividend stocks, it's important to know how to evaluate them. These metrics can help you to understand how much in dividends to expect, how reliable a dividend might be, and, most importantly, how to identify red flags.
What is dividend investing?
Dividend investing is a strategy that gives investors two sources of potential profit: the predictable income from regular dividend payments and capital appreciation of the stock over time . Buying dividend stocks can be a great approach for investors looking to generate income or to build wealth by reinvesting dividend payments.
How to mitigate risk in a portfolio?
One way to effectively mitigate risk in your portfolio is by investing in a dividend-focused exchange-traded fund ( ETF) or mutual fund. These fund options enable investors to own diversified portfolios of dividend stocks that generate passive income.
Do dividends have to be taxed?
While most dividends qualify for the lower tax rates, some dividends are classified as "ordinary" or non-qualified dividends and are taxed at your marginal tax rate. Several kinds of stocks are structured to pay high dividend yields and may come with higher tax obligations because of their corporate structures.
Is it better to buy dividend stocks with a low yield?
Sadly, a yield that looks too good to be true often is. It's better to buy a dividend stock with a lower yield that's rock solid than to chase a high yield that may prove illusory. Moreover, focusing on dividend growth -- a company's history and ability to raise its stock dividend -- often proves more profitable.
Is high yield bad for stocks?
High yield isn't everything. Inexperienced dividend investors often make the mistake of buying stocks with the highest dividend yields. While high-yield stocks aren't bad, high yields are typically the result of a stock's price falling due to the risk of the dividend being cut. That's a dividend yield trap .
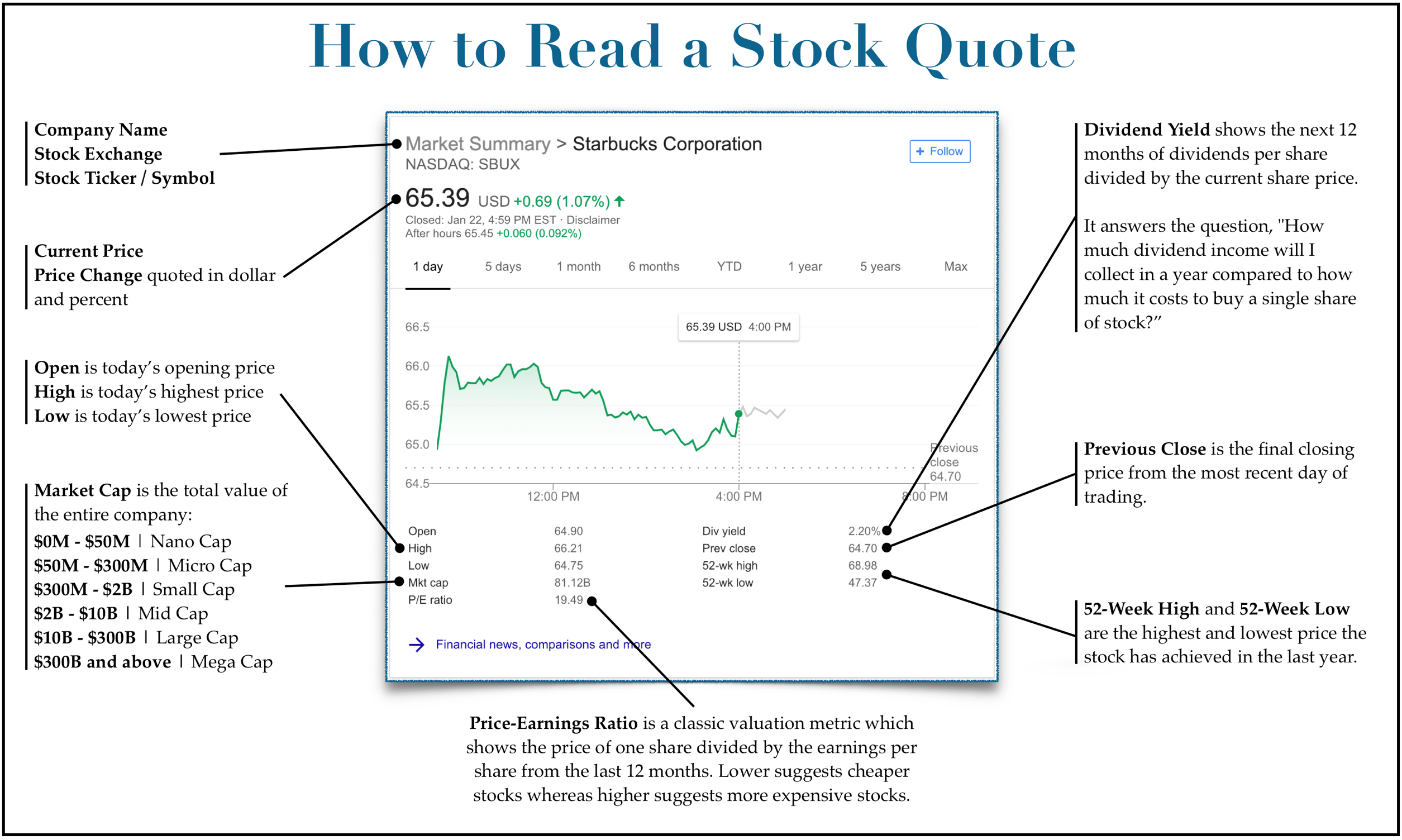
How to calculate P/E ratio?
P/E ratio: This is the price-to-earnings ratio. The P/E ratio is calculated by dividing a company's share price by its earnings per share. The P/E ratio is a metric that can be used along with dividend yield to determine if a dividend stock is fairly valued.
How to invest in dividend stocks?
There are two main ways to invest in dividend stocks: Through mutual funds — such as index-funds or exchange-traded funds — that hold dividend stocks, or by purchasing individual dividend stocks.
Why do investors choose individual dividend stocks?
Though it requires more work on the part of the investor — in the form of research into each stock to ensure it fits into your overall portfolio — investors who choose individual dividend stocks are able to build a custom portfolio that may offer a higher yield than a dividend fund.
What does a high dividend yield mean?
Among other things, a too-high dividend yield can indicate the payout is unsustainable, or that investors are selling the stock, driving down its share price and increasing the dividend yield as a result.
What does it mean when a stock payout ratio is too high?
A payout ratio that is too high — generally above 80%, though it can vary by industry — means the company is putting a large percentage of its income into paying dividends. In some cases dividend payout ratios can top 100%, meaning the company may be going into debt to pay out dividends. (Read our full guide on how to research stocks.)
What does it mean when a company's dividend is higher than its yield?
If a company’s dividend yield is much higher than that of similar companies, it could be a red flag. At the very least, it’s worth additional research into the company and the safety of the dividend. Then look at the stock’s payout ratio, which tells you how much of the company’s income is going toward dividends.
What is dividend aristocrat?
The Dividend Aristocrats are large companies with reliable dividend payments and high liquidity , and the index as a whole may offer more diversification than high-yield dividend indexes (which are typically heavily weighted toward the financials and utilities sectors).
Do dividend stocks have stability?
Companies that pay dividends tend to be well-established, so dividend stocks may also add some stability to your portfolio. That's one reason they're included on our list of low-risk investments.
What is the fundamental analysis of a stock?
To determine the intrinsic value of a stock, fundamental analysis is undertaken. Qualitative, quantitative and perceptual factors are all taken into account to build a valuation model.
What are the factors that determine the intrinsic value of a stock?
Perceptual Factors. Perceptual factors are derived by determining the expectations and perceptions of a stock that investors have. All of these factors are put together as objectively as possible to build a mathematical model used for determining the intrinsic value of a stock.
Why is the stock price low when the analyst weights profits higher than management?
In other words, their analysis shows the stock is undervalued according to the financial data they’ve looked at, but the trading price is low because the management team isn’t doing a very good job overall.
Why do valuations differ?
Differences in valuation can arise as a result of individual analysts placing a higher weighting of importance on different factors. For example, a business’s management team might be held as a high value-determining factor when another analyst might place a higher weighting on profits as the driver of value.
Why is there still a level of subjectivity in the stock market?
Obviously, there is still a level of subjectivity due to the nature of many of the qualitative factors and assumptions being made. After the intrinsic value is estimated, it is compared to the current market price of a stock to determine whether the stock is overvalued or undervalued.
What are qualitative factors?
Qualitative factors are specific aspects relating to what a business does and how it is conducted. Such factors are unable to be measured. For example, company morale, governance, relationships with consumers, and business model.
Can tangible assets be found on financial statements?
It’s easy to measure the book value of tangible assets such as equipment and buildings, but intellectual and intangible assets are more difficult to record and can’t be found on financial statements.