Calculating your portfolio's beta will give you a measure of its overall market risk. To do so, find the betas for all your stocks. Each beta is then multiplied by the percentage of your total portfolio that stock represents (i.e., a stock with a beta of 1.2 that comprises 10% of your portfolio would have a weighted beta of 1.2 times 10% or.12).
How do you calculate total risk?
I think I already know for Total Risk: 1. change in daily closing price to get daily stock returns, 2. STDEV of daily stock returns 3. calculate variance, i.e. square STDEV of daily stock returns 4. make assumption on number of trading days, i.e. 250 or 252 5. annualized variance, i.e. variance * number of trading days and, 6.
How to determine the risk of a stock?
Calculating your portfolio's beta will give you a measure of its overall market risk. To do so, find the betas for all your stocks. Each beta is then multiplied by the percentage of your total portfolio that stock represents (i.e., a stock with a beta of 1.2 that comprises 10% of your portfolio would have a weighted beta of 1.2 times 10% or .12).
How do you calculate risk/reward in stock trading?
Stock risk and position size calculators. Stocks risk and position size calculator Use this to calculate your risk % based on number of shares of a stocks or maximum number of shares based on risk %. Account size (USD, EUR etc) Shares/Risk % Entry: Stoploss: Side
How do you calculate market risk in economics?
Say you have a capital of 5 lacs. 50% is invested in the market. So if the stocks turn against you 2%, your risk will be 5,000. However, if you were fully invested, 2% adverse move will mean a risk of 10,000. In case you are leveraged by trading in Futures and …

What is total risk formula?
Unsystematic risk is essentially eliminated by diversification, so a portfolio with many assets has almost no unsystematic risk.
What is the total risk of the stock?
How is total risk measured?
How do you calculate the total risk of a portfolio?
What are total risks?
What is total risk in investment?
Which is best measure of total risk?
How do I calculate stock risk in Excel?
How do you calculate risk and return?
What is the risk of a portfolio?
How do you calculate expected return and risk of a portfolio?
...
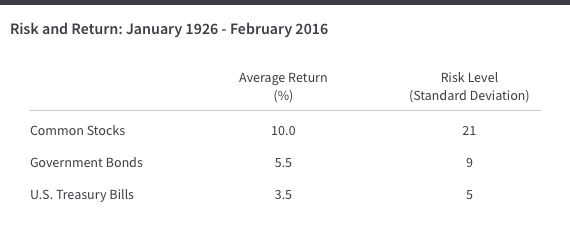
Calculating Expected Return.
| Asset | Weight | Expected Return |
|---|---|---|
| C | 40% | 10% |
What is total risk of portfolio variance equal to?
What is the tool that measures the systematic risk of your portfolio called?
There is a tool that measures the systematic risk of your portfolio. It is called Beta .
What is the security market line?
The security market line is the dashed line that starts from zero on the excess return axis. Notice that the mutual funds distributed randomly above and below the security market line.
What is the beta of a treynor index?
In finance, Beta (a.k.a Treynor Index, or beta coefficient) measures volatility of a specific security by comparing it to a performance of a related benchmark over a period of time.
Do you get excess return per unit of risk?
As a result, you will get a portfolio excess return per unit of risk. Here is a couple of cases that will help you determine whether your portfolio is healthy.
Is Alpha and Beta a risk indicator?
Both Alpha and Beta are backwards-looking risk indicators. This means that all calculations are based on the past data, and past performance is no guarantee of he future results. Therefore, they cannot always differentiate between relatively good and poor investments.
What does it mean when a stock has a low R square?
Generally, stocks with low market risk and high internal risk tend to have r-square values closer to zero or have very low values. The low value signifies that the influence of the variations in the market or the benchmark index is insignificant in explaining the price variations in the stock. Therefore, it can be assumed ...
How to calculate beta?
Beta is calculated by using regression analysis and applying the concept of the line of best fit. It is calculated with respect to a market benchmark index, say, Nifty, or BSE Sensex. However, beta itself is not market risk. It just indicates the sensitivity of a stock to the market’s movement. But you don’t have to get into the fundamentals of such calculations as MS Excel provides simple functions to calculate such statistics.
How can unsystematic risks be reduced?
Unsystematic or internal risks can be reduced by diversification.
What are unsystematic risks?
Unsystematic risks, however, are owed to factors unique to a company or an industry. Management and labour relations, increased competition, entry of new players, and customers’ preference for a company’s products are some of the factors that generate unsystematic risk. Unsystematic risks are also known as internal risks and are diversifiable.
How many observations are needed for a statistical analysis?
The graphic used for illustration is based on just 13 observations, but is advisable that the minimum number of observations should be greater than or equal to 30. It may be 30 weeks, 30 months, 30 quarters, or 30 years. This will help derive meaningful conclusions from the statistical analysis explained above.
Is systemic risk a diversifiable risk?
Unsystematic risks are also known as internal risks and are diversifiable. In other words, these risks can be mitigated by adding stocks from different industries. Systematic risks, however, are non-diversifiable. Diversification cannot help in bring down the market risks.
What are the two types of risk in stocks?
Basically, stocks are subject to two types of risk - market risk and nonmarket risk . Nonmarket risk, also called specific risk, is the risk that events specific to a company or its industry will adversely affect the stock's price.
How to reduce non market risk?
Nonmarket risk can be reduced through diversification. By owning several different stocks in different industries whose stock prices have shown little correlation to each other, you reduce the risk that nonmarket factors will adversely affect your total portfolio.
How to calculate beta of portfolio?
To do so, find the betas for all your stocks. Each beta is then multiplied by the percentage of your total portfolio that stock represents (i.e., a stock with a beta of 1.2 that comprises 10% of your portfolio would have a weighted beta of 1.2 times 10% or .12). Add all the weighted betas together to arrive at your portfolio's overall beta.
What is the beta of a stock?
Beta, which can be found in a number of published services, is a statistical measure of the impact stock market movements have historically had on a stock's price.
What is standard deviation in stock market?
Standard Deviation. Standard deviation, which can also be found in a number of published services, measures a stock's volatility, regardless of the cause . It basically tells you how much a stock's short-term returns have moved around its long-term average return. The most common way to calculate standard deviation is to figure ...
Can you eliminate market risk?
No matter how many stocks you own, you can't totally eliminate market risk. However, you can measure a stock's historical response to market movements and select those with a level of volatility you are comfortable with. Beta and standard deviation are two tools commonly used to measure stock risk. Beta, which can be found in a number ...
How are stock prices determined?
All stock prices are determined by two things: 1 The minimum price someone is willing to sell it 2 The maximum price someone is willing to pay for it
What does beta mean in stocks?
What beta means is the historical reaction of the stock price when compared to other stocks traded at the same market place. Take Maruti Suzuki for example.
Is 10 stocks all long directional?
That said, 10 stocks all long is more of a directional bet on the market than being 10 stocks long and 10 stocks short (all in the sp500) Because they roughly cancel each other out on the directional play.... you can look into stock's individual beta to get even more precise.
Is there a yardstick to judge the risk of investing?
There’s is no stable yardstick to perfectly judge how much risk you may confront by investing in any particular stock or sector. However, one has to assume the risk by judging the market situations relatively that too on micro and macro level.
Is it safe to trade stock below book value?
A cheaper stock or a stock trading below its book value not necessarily safe. You should always invest in the sectors which you think are more resistant to recession because at the end of the day recession is not just “rainy days”, it can very well be “rainy years”. Related Answer. Quora User.
How is portfolio risk measured?
Portfolio Risk is measured by calculating the standard deviation of the portfolio. In this regard, standard deviation alone is not sufficient to calculate the portfolio risk.
Why is it important to calculate portfolio risk?
Therefore, calculating portfolio risk can help them realize, and duly craft their portfolios so that the risk strategy of the portfolio matches the risk profile they want to maintain.
What are the three variables used to calculate portfolio risk?
Therefore, portfolio risk calculation includes three main variables: the weightage of the respective assets in the portfolio, the standard deviation of those assets, as well as the covariance of those assets. Using these three variables, the following formula is used to calculate portfolio risk:
What is portfolio risk?
Portfolio Risk can be defined as the probability of the assets or units of stock that the company holds to sink, thereby causing a significant loss to the company in terms of their investment being lost. A portfolio is defined as the combination or the collection of stocks or investment channels within the company.
What is portfolio in investing?
A portfolio is defined as the combination or the collection of stocks or investment channels within the company. Within the portfolio, there are different investment stocks that the investor holds, and all of them individually have different risk assessments.
What is covariance in stocks?
In other words, it is a measure of the extent to which both the stocks act responds similarly, to market trends and other macroeconomic factors.
What does a correlation of +1 mean?
For example, if two stocks have a correlation of +1, this implies that they either will increase or decrease hand in hand. On the other hand, if two stocks have a correlation of -1, it implies that if one stock generates a positive return, the other stock is unlikely to generate a positive return too. See also Mortgage - Usages and How It Work.
What is market risk?
Hence, market risk is the tendency of security prices to move together. If the market is declining, then even the share prices of good performing companies fall. Market risk constitutes almost two-thirds of total systematic risk. Therefore, sometimes the systematic risk is also referred to as market risk.
What is exchange rate risk?
Exchange rate risk is the uncertainty associated with changes in the value of foreign currencies. Therefore, this type of risk affects only the securities of companies with foreign exchange transactions or exposures such as export companies, MNCs, or companies that use imported raw material or products.
What is reinvestment risk?
Reinvestment risk is associated with reinvesting interest/ dividend income. If price risk is negative (i.e., fall in price), reinvestment risk would be positive (i.e. increase in earnings on reinvested money). Interest rate changes are the main source of risk for fixed income securities such as bonds and debentures.
How does interest rate risk affect fixed income?
Interest rate risk arises due to changes in market interest rates. In the stock market, this primarily affects fixed income securities because bond prices are inversely related to the market interest rate. In fact, interest rate risks include two opposite components: Price Risk and Reinvestment Risk. Both of these risks work in opposite directions. Price risk is associated with changes in the price of a security due to changes in interest rate. Reinvestment risk is associated with reinvesting interest/ dividend income. If price risk is negative (i.e., fall in price), reinvestment risk would be positive (i.e. increase in earnings on reinvested money). Interest rate changes are the main source of risk for fixed income securities such as bonds and debentures.
What does it mean to be risk averse?
Risk Averse Definition Someone who is risk averse has the characteristic or trait of preferring avoiding loss over making a gain. This characteristic is usually attached to investors or market participants who prefer investments with lower returns and relatively known risks over investments with potentially higher returns but also with higher uncertainty and more risk.
What is market risk premium?
Market Risk Premium The market risk premium is the additional return an investor expects from holding a risky market portfolio instead of risk-free assets.
Why are equity shares subject to a high level of purchasing power risk?
are subject to a high level of purchasing power risk because income from such securities is fixed in nominal terms. It is often said that equity shares are good hedges against inflation and hence subject to lower purchasing power risk.
How to determine risk of an investment?
One of the most common methods of determining the risk an investment poses is standard deviation. Standard deviation helps determine market volatility or the spread of asset prices from their average price. When prices move wildly, standard deviation is high, meaning an investment will be risky.
What is the most common method of determining the risk an investment poses?
One of the most common methods of determining the risk an investment poses is standard deviation.
What is the most common metric used to assess volatility?
Traders and analysts use a number of metrics to assess the volatility and relative risk of potential investments, but the most common metric is standard deviation . Read on to find out more about standard deviation, and how it helps determine risk in the investment industry.
What does it mean when a stock has a low standard deviation?
When prices move wildly, standard deviation is high, meaning an investment will be risky. Low standard deviation means prices are calm, so investments come with low risk.
What is risk measurement?
Risk measurement is a very big component of many sectors of the finance industry. While it plays a role in economics and accounting, the impact of accurate or faulty risk measurement is most clearly illustrated in the investment sector.
When using standard deviation to measure risk in the stock market, what is the underlying assumption?
When using standard deviation to measure risk in the stock market, the underlying assumption is that the majority of price activity follows the pattern of a normal distribution. In a normal distribution, individual values fall within one standard deviation of the mean, above or below, 68% of the time. Values are within two standard deviations 95% of the time.
Is a large trading range risky?
But remember, risk is not necessarily a bad thing in the investment world. The riskier the security, the greater potential it has for payout.
What Is The Risk/Reward calculation?
Understanding Risk vs. Reward
- Investing money into the markets has a high degree of risk and you should be compensated if you're going to take that risk. If somebody you marginally trust asks for a $50 loan and offers to pay you $60 in two weeks, it might not be worth the risk, but what if they offered to pay you $100? The risk of losing $50 for the chance to make $100 might be appealing. That's a 2:1 risk/reward, …
Special Considerations
- Before we learn if our XYZ trade is a good idea from a risk perspective, what else should we know about this risk/reward ratio? First, although a little bit of behavioral economicsfinds its way into most investment decisions, risk/reward is completely objective. It's a calculation and the numbers don't lie. Second, each individual has their own tolerance for risk. You may love bungee jumping, …
Limiting Risk and Stop Losses
- Unless you're an inexperienced stock investor, you would never let that $500 go all the way to zero. Your actual risk isn't the entire $500. Every good investor has a stop-loss or a price on the downside that limits their risk. If you set a $29 sell limit price as the upside, maybe you set $20 as the maximum downside. Once your stop-loss orderreaches $20, you sell it and look for the next …
The Bottom Line
- Every good investor knows that relying on hope is a losing proposition. Being more conservative with your risk is always better than being more aggressive with your reward. Risk/reward is always calculated realistically, yet conservatively.