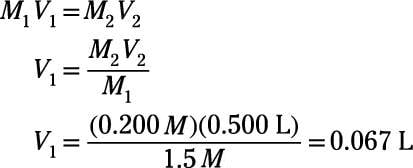
A solution can be diluted by adding more solvent to the stock solution (the starting solution before dilution) in the same vessel. The dilution equation (dilution formula or dilution expression) is: c 1 V 1 = c 2 V 2 c 1 = concentration of stock solution (before dilution) in mol L -1 V 1 = volume of stock solution present before dilution in L
How to calculate concentrations when making dilutions?
- Calculate the minimum diluent volume per step: 50 μL per well * 2 for duplicates = 100 μL minimum. ...
- Calculate Move Volume: Move Volume = 120 μL / (3-1) = 60 μL
- Calculate Total Mixing Volume: Total Mixing Volume = 120 μL + 60 μL = 180 μL
How do you calculate the concentration of two mixed solutions?
- If you aren’t measuring the volume yourself, you may need to convert the mass of the solute into volume using the density formula.
- For example, if you’re finding the concentration of 3.45 grams of salt in 2 liters of water, you would find the volume of salt using the density formula. ...
- Add the volume of the solute to the volume of your solvent, ma. ...
How do you dilute and concentrate a solution?
Question
- List the information you have and the information you need V = 183.7 183.7 dm3 dm 3, m = 0.27 0.27 g g The volume (V) and the ...
- Make sure all given units are correct and convert them if necessary All the units are correct.
- What equations will be necessary to calculate the concentration? ...
How to calculate dilution ratios quickly and easily?
Calculate the dilution ratio. There is an easy way to calculate the amount you need to add. Total amount of product = the amount of product you wanna end up with. Amount of product = is the first number in the dilution ratio. In the case of 25:1 this means 25. Ratio number = the second number. In the case of 25:1 this means 1.

How do you find the concentration of a diluted solution from a stock solution?
The calculator uses the formula M1V1 = M2V2 where "1" represents the concentrated conditions (i.e., stock solution molarity and volume) and "2" represents the diluted conditions (i.e., desired volume and molarity). To prepare a solution of specific molarity based on mass, please use the Mass Molarity Calculator.
How do you calculate diluted concentration?
The formula for calculating a dilution is (C1) (V1) = (C2) (V2) where...C1 is the concentration of the starting solution.V1 is the volume of the starting solution.C2 is the concentration of the final solution.V2 is the volume of the final solution.
How do you find the concentration of the volume of a stock solution?
Divide the mass of the solute by the total volume of the solution. Write out the equation C = m/V, where m is the mass of the solute and V is the total volume of the solution. Plug in the values you found for the mass and volume, and divide them to find the concentration of your solution.
What is the concentration of the diluted solution?
Dilution is the addition of solvent, which decreases the concentration of the solute in the solution. Concentration is the removal of solvent, which increases the concentration of the solute in the solution.
How do you find the original concentration of a diluted sample?
These all mean the same thing, that there is 1 volume part of sample and 4 volume parts of whatever liquid is being used to dilute the sample for a total of 5 volume parts. To calculate the concentration of our diluted sample we multiply by the inverse of our dilution factor .
How do you find the concentration of an original solution?
How to Calculate the Number of Moles in a SolutionWeigh the amount of solute (the compound being dissolved) in grams. ... Measure the amount of the solvent that you have. ... Divide the moles of solute found in Step 1 by the liters of solvent found in Step 2 to find the initial concentration of a solution.
How do you calculate concentration from dilution factor?
The dilution factor is the inverse of the concentration factor. For example, if you take 1 part of a sample and add 9 parts of water (solvent), then you have made a 1:10 dilution; this has a concentration of 1/10th (0.1) of the original and a dilution factor of 10.
What is C1V1 C2V2?
C1V1=C2V2 is used to calculate an unknown quantity where two solutions/mixtures are proportional … C1V1 = Concentration/amount (start) and Volume (start) C2V2 = Concentration/amount (final) and Volume (final) 1.
How do you find the dilution of a solution?
You can solve for the concentration or volume of the concentrated or dilute solution using the equation: M1V1 = M2V2, where M1 is the concentration in molarity (moles/Liters) of the concentrated solution, V2 is the volume of the concentrated solution, M2 is the concentration in molarity of the dilute solution (after ...
How to find the concentration of a solution?
To calculate the concentration of a solution, start by converting the solute, or the substance being dissolved, into grams. If you're converting from milliliters, you may need to look up the solute's density and then multiply that by the volume to convert to grams. Next, convert the solvent to liters.
How to find the molar mass of a solute?
Add the atomic masses of the solute together to find the molar mass. Look at the elements in the chemical formula for the solute you’re using. List the atomic mass for each element in the solute since atomic and molar mass are the same. Add together the atomic masses from your solute to find the total molar mass.
What is the solute in chemistry?
The solute is the substance that you’re mixing in to form your solution. If you’re given the mass of the solute in your problem, write it down and be sure to label it with the correct units. If you need to find the mass of the solute, then weigh it on a lab scale and record the measurement.
How to identify a dilution solution?
You can identify a dilution solution by the amount of solute in the total volume, expressed as a proportion. For example, a chemical may be prepared in a 1:10 dilution of alcohol, indicating that a 10 mL bottle contains one milliliter of chemical and nine milliliters of alcohol. You can calculate the necessary volume of each component to prepare a dilution solution.
How many milliliters of alcohol are in a 10 ml bottle?
For example, a chemical may be prepared in a 1:10 dilution of alcohol, indicating that a 10 mL bottle contains one milliliter of chemical and nine milliliters of alcohol. You can calculate the necessary volume of each component to prepare a dilution solution.
What is the easiest way to express the concentration of a solution?
Mass percent composition (also called mass percent or percent composition) is the easiest way to express the concentration of a solution because no unit conversions are required. Simply use a scale to measure the mass of the solute and the final solution and express the ratio as a percentage.
What are the units of concentration?
The most common units are molarity, molality, normality, mass percent, volume percent, and mole fraction. Here are step-by-step directions for calculating concentration, with examples.
How to find moles of KCl?
Start by looking up the number of grams per mole of potassium and chlorine on a periodic table. Then add them together to get the grams per mole for KCl. K = 39.1 g/mol.
How many H+ ions are in sulfuric acid?
You know there are 2 moles of H+ ions (the active chemical species in an acid-base reaction) for every 1 mole of sulfuric acid because of the subscript in the chemical formula. So, a 1 M solution of sulfuric acid would be a 2 N (2 normal) solution.
What is volume percent?
Volume percent is the volume of solute per volume of solution. This unit is used when mixing together volumes of two solutions to prepare a new solution. When you mix solutions, the volumes aren't always additive, so volume percent is a good way to express concentration.
How to find mass percent?
Calculate Mass Percent: mass solute divided by mass final solution multiplied by 100%.
What is concentration in science?
Concentration is an expression of how much solute is dissolved in a solvent in a chemical solution. There are multiple units of concentration. Which unit you use depends on how you intend to use the chemical solution.
What is the process of reducing a solute's concentration in a solution?
As aforementioned, the dilution of a solution refers to the process of reducing a solute’s concentration in a solution. You can do this by adding water to the solution or by adding more solvent to the solution. Therefore, to dilute concentration means that you add more solvent without adding more solute. This results in a solution which is ...
Why is diluting a solution important?
Diluting a solution is an important laboratory process since stock solutions are typically bought and stored in forms which are very concentrated. In order for you to utilize a solution in a laboratory like for titration or for any other kind of process, you must accurately dilute it first to a lesser concentration.
What is molarity in chemistry?
Molarity refers to the concentration of a given solution. By definition, it’s the number of moles of a solute or substance dissolved in a liter of a solution.
What is dilution in medicine?
Medication dilution is a lot like dilution of a solution since it also refers to the process of decreasing a solution’s concentration when you add more solvent to it. The formulas which are typically used for this process are only useful for diluting medications from a higher concentration percentage to a lower one.
What is the process of adding a solvent to a solution?
Dilution of a solution refers to the process of adding a solvent to a solution for the purpose of decreasing the solution’s concentration. The process maintains the constancy of solute amount but it increases the solution’s total amount which, in turn, decreases the final concentration. You can also dilute a solution by mixing a solution ...
Why is it important to calculate medication dosages?
This is important because dosages must be very accurate before they’re administered to infants and young children.
What is the molar mass of water?
You express this in grams per mole. Molar mass is a type of constant property possessed by each substance. For instance, the molar mass of water is around 18 g/mol.
