
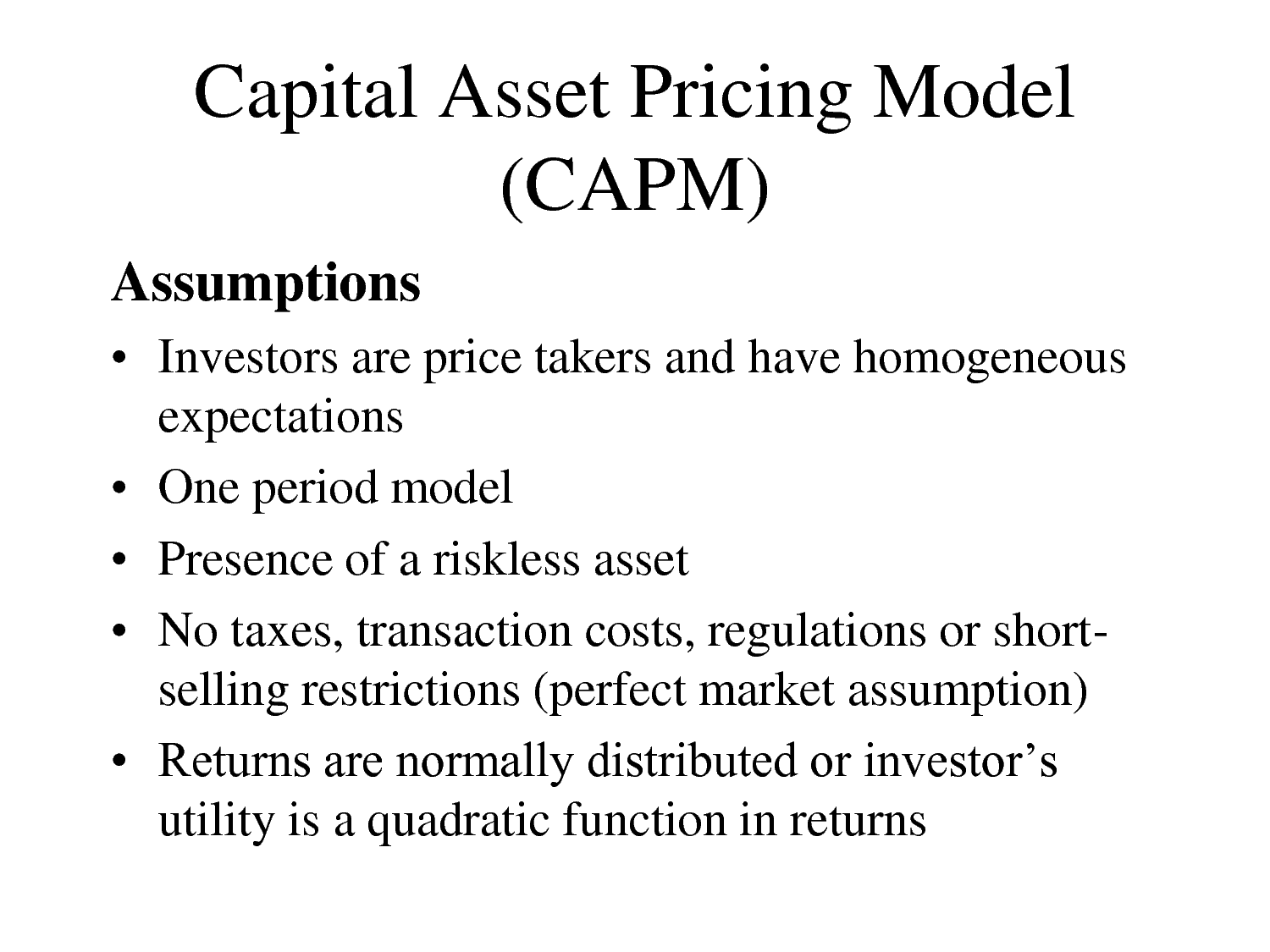
Here is a straightforward formula for calculating the Beta Coefficient of a Stock:
- Obtain the stock’s historical share price data.
- Obtain historical values of a market index, e.g., S&P 500.
- Convert the share price values into daily return values using the following formula: return = (closing share price − opening share price)/opening share price.
- Convert historical stock market index values in a similar way.
- Align the share return data with index return such that there is a 1-on-1 correspondence between them. For share price return, there should be a corresponding index return.
- Using the SLOPE function in a financial calculator to find the slope between both arrays of data and the resultant figure is Beta.
What factors determine the beta of a stock?
Beta is determined by the cyclicality of a firm's revenues. This cyclicality is magnified by the firm's operating and financial leverage. (1) Revenues. The cyclicality of a firm's sales is an important factor in determining beta. In general, stock prices will rise when the economy expands and will fall when the economy contracts.
What is a good beta value for a stock?
- Market value: $9.1 billion
- Dividend yield: N/A
- Forward P/E ratio: 13.4
- Analysts' ratings: 6 Strong Buy, 3 Buy, 0 Hold, 1 Sell, 0 Strong Sell
- Analysts' consensus recommendation: 1.60 (Buy)
How to interpret the beta of a stock?
The beta coefficient can be interpreted as follows:
- β =1 exactly as volatile as the market
- β >1 more volatile than the market
- β <1>0 less volatile than the market
- β =0 uncorrelated to the market
- β <0 negatively correlated to the market
What is the process of calculating asset Beta?
Asset beta is a measure of the relative volatility of an investment without regard to the effects of debt. You can calculate asset beta by adjusting the investment’s levered beta using its debt-to-equity ratio and its tax rate. Asset beta is a way to compare the volatilities of two investments.

How is the beta of a stock calculated?
Beta could be calculated by first dividing the security's standard deviation of returns by the benchmark's standard deviation of returns. The resulting value is multiplied by the correlation of the security's returns and the benchmark's returns.
How do you find the beta formula?
Beta can be calculated by dividing the asset's standard deviation of returns by the market's standard deviation. The result is then multiplied by the correlation of the security's return and the market's return.
How do you calculate beta of a stock in Excel?
To calculate beta in Excel:Download historical security prices for the asset whose beta you want to measure.Download historical security prices for the comparison benchmark.Calculate the percent change period to period for both the asset and the benchmark. ... Find the variance of the benchmark using =VAR.More items...
How do you calculate beta of a stock using CAPM?
CAPM Beta Calculation in ExcelStep 1 – Download the Stock Prices & Index Data for the past 3 years. ... Step 2 – Sort the Dates & Adjusted Closing Prices. ... Step 3 – Prepare a single sheet of Stock Prices Data & Index Data.Step 4 – Calculate the Fractional Daily Return.Step 5 – Calculate Beta – Three Methods.
How do you find the beta and alpha of a stock?
Alpha = R – Rf – beta (Rm-Rf) R represents the portfolio return. Rf represents the risk-free rate of return. Beta represents the systematic risk of a portfolio. Rm represents the market return, per a benchmark.
What is the beta of a stock?
Beta is a way of measuring a stock's volatility compared with the overall market's volatility. The market as a whole has a beta of 1. Stocks with a value greater than 1 are more volatile than the market (meaning they will generally go up more than the market goes up, and go down more than the market goes down).
How do you find the beta of a stock in Yahoo Finance?
You can find the beta for a stock on the summary quote page on Yahoo! Finance.
What is a beta value?
Definition: Beta is a numeric value that measures the fluctuations of a stock to changes in the overall stock market. Description: Beta measures the responsiveness of a stock's price to changes in the overall stock market.
What is the beta of your portfolio?
The beta of a portfolio is the weighted sum of the individual asset betas, According to the proportions of the investments in the portfolio. E.g., if 50% of the money is in stock A with a beta of 2.00, and 50% of the money is in stock B with a beta of 1.00,the portfolio beta is 1.50.
What is beta in the CAPM?
Beta is the standard CAPM measure of systematic risk. It gauges the tendency of the return of a security to move in parallel with the return of the stock market as a whole. One way to think of beta is as a gauge of a security's volatility relative to the market's volatility.
What is beta in stock market?
Stock Beta is one of the statistical tools that quantify the volatility in the prices of a security or stock with reference to the market as a whole or any other benchmark used for comparing the performance of the security. It is actually a component of Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)
What does it mean when the beta of a stock is negative?
The Stock Beta can have three types of values: Beta < 0: If the Beta is negative, then this implies an inverse relationship between the stock and the underlying market or the benchmark in comparison. Both stock and the market or the benchmark will move in the opposite direction. Beta = 0: If the Beta is equal to zero, ...
What does a beta of 1 mean?
Beta of 1 implies that the volatility of the stock is exactly the same as that of the underlying market or the index in both qualitative and quantitative terms. Beta of greater than 1 implies that the stock is more volatile than the underlying market or index. A negative Beta is possible but highly unlikely.
What does it mean when the beta is greater than zero?
Beta > 0: If the Beta is greater than zero, then there is a strong direct relationship between the stock and the underlying market or the benchmark. Both stock and the market or the benchmark will move in the same direction. Some further insight is as follows:
What does it mean when the beta is 0?
Beta = 0: If the Beta is equal to zero, then this implies that there is no relation between the movement of the returns of the stock and the market or the benchmark, and hence both are too dissimilar to have any common pattern in price movements . Beta > 0: If the Beta is greater than zero, then there is a strong direct relationship between ...
What is a statistical tool?
It is one single statistical tool that investors frequently use to assess the risk that the stock may add to their portfolio, allowing them to gauge the risk in both qualitative and quantitative terms and to assess the risk and rewards associated with the stock.
Is a negative beta of gold a good thing?
A negative Beta is possible but highly unlikely. Most investors believe that gold and stock based on gold tend to perform better when the market dives. Whereas a Beta of zero is possible in the case of government bonds acting as risk-free securities providing a low yield to the investors.
How to calculate beta of a stock?
Here is a straightforward formula for calculating the Beta Coefficient of a Stock: 1 Obtain the stock’s historical share price data. 2 Obtain historical values of a market index, e.g., S&P 500. 3 Convert the share price values into daily return values using the following formula: return = (closing share price − opening share price)/opening share price. 4 Convert historical stock market index values in a similar way. 5 Align the share return data with index return such that there is a 1-on-1 correspondence between them. For share price return, there should be a corresponding index return. 6 Using the SLOPE function in a financial calculator to find the slope between both arrays of data and the resultant figure is Beta.
What does beta mean in stocks?
Beta can give you an estimate of the stock’s risk and some idea of market volatility. Ideally, the Beta will tell you the difference between a stock’s risk and the risk of an entire index market.
What is the beta coefficient?
Generally, analysts regard the Beta Coefficient as a measure of systematic or “general market” risk. Analysts often use the mathematical symbol β to represent the Beta in calculations. To explain, systematic is the level of risk or volatility of equity in the entire market or index.
Why do analysts use the beta coefficient?
Analysts examine the Beta Coefficient, or Beta of stock, because the Beta measures risk and volatility. Specifically, the Beta can give you an estimate of the stock’s risk and some idea of market volatility. Ideally, the Beta will tell you the difference between a stock’s risk and the risk of an entire index market.
Why is beta a limited tool?
Hence, the Beta is a limited tool because it only measures some risks associated with individual stocks or indexes. However, a rough estimate of risk is better than no estimate of risk.
What does a value of 5 mean?
A value of 1 means it moved with the market, a value of 2 means it moved up and down with the market but twice as much, and a value of .5 means it moved up and down half as much as the market did. Strategic Beta for Funds & ETFs.
Can you use beta in stock analysis?
In the final analysis, the Beta is only one of many stock analysis tools you can use. In fact, some analysts and investors never use the Beta. On the other hand, there are many analysts who swear by the Beta. Hence using the Beta is a matter of choice.
What is beta in stock market?
Learn more... Beta is the volatility or risk of a particular stock relative to the volatility of the entire stock market. Beta is an indicator of how risky a particular stock is, and it is used to evaluate its expected rate of return.
How to interpret beta?
Know how to interpret beta. Beta is the risk, relative to the stock market as a whole, an investor assumes by owning a particular stock. That's why you need to compare the returns of a single stock against the returns of an index. The index is the benchmark against which the stock is judged. The risk of an index is fixed at 1. A beta of lower than 1 means that the stock is less risky than the index to which it's being compared. A beta of higher than 1 means the stock is more risky than the index to which it's being compared.
What does it mean when the beta is lower than 1?
The risk of an index is fixed at 1. A beta of lower than 1 means that the stock is less risky than the index to which it's being compared. A beta of higher than 1 means the stock is more risky than the index to which it's being compared.
What is beta analysis?
Beta analyzes a stock's volatility over a set period of time, without regard to whether the market was on an upswing or downswing. As with other stock fundamentals, the past performance it analyzes is not a guarantee of how the stock will perform in the future. Thanks!
What does it mean when the beta is negative?
Usually the rates of return are figured over several months. Either or both of these values may be negative, meaning that investing in the stock or the market (index) as a whole would mean a loss during the period. If only one of the two rates is negative, the beta will be negative.
How to calculate the return of a stock?
Begin calculating returns for the stock market index. 1 Since return is a calculation over time, you won't put anything in your first cell; leave it blank. You need at least two data points to calculate returns, which is why you'll start on the second cell of your index-returns column. 2 What you're doing is subtracting the more recent value from the older value and then dividing the result by the older value. This just gives you the percent of loss or gain for that period. 3 Your equation for the returns column might look something like this: = (B4-B3)/B3
How many data points do you need to calculate returns?
You need at least two data points to calculate returns, which is why you'll start on the second cell of your index-returns column. What you're doing is subtracting the more recent value from the older value and then dividing the result by the older value.
What is beta in equity?
It is used in the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) to estimate the return of an asset. Beta, specifically, is the slope coefficient obtained through regression analysis of the stock return against the market return.
What is earnings beta?
Earnings Beta Approach. Usually, listed companies are large companies that operate in more than one segment. Therefore, it may be problematic to find a comparable firm whose beta would adequately represent the business beta of the private company being valued.
Why is CAPM valuation problematic?
The valuation of private companies using CAPM can be problematic because there is no straightforward method for estimating equity beta. To estimate the beta of a private company, there are two primary approaches. One approach is to obtain a comparable levered beta from an industry average or from a comparable company (or companies) ...
When is it difficult to obtain reliable comparable beta?
When it is difficult to obtain reliable comparable beta, a company’s earnings beta can be used as a proxy for the levered beta. In this method, the company’s historical earnings changes are regressed against the market returns. An appropriate market index can be used as a proxy for the market.
Can the S&P 500 be used as a proxy?
An appropriate market index can be used as a proxy for the market. For instance, if the company is operating in the U.S. market, the S&P 500 can be used as a proxy. Beta obtained from historical data needs to be adjusted to make sure that it reflects the company’s expected future performance.
Can you estimate beta of a stock?
Due to the lack of market data on the stock prices of private companies, it is not possible to estimate stock beta. Therefore, other methods are required to estimate their beta.
Do private companies have historical earnings?
First, private companies do not usually have extensive historical earnings data for reliable regression analysis. Second, accounting earnings are subject to smoothing and accounting policy changes. Therefore, these may not be appropriate for statistical analysis, unless necessary adjustments have been made.
What does it mean when a stock is beta?
Beta is a measure of how sensitive a firm's stock price is to an index or benchmark. A beta greater than 1 indicates that the firm's stock price is more volatile than the market, and a beta less than 1 indicates that the firm's stock price is less volatile than the market. A beta may produce different results because of ...
What is beta in finance?
In finance, the beta of a firm refers to the sensitivity of its share price with respect to an index or benchmark. ...
Why do low beta stocks dove down?
This is because their market correlation was much lower, and thus the swings orchestrated through the index were not felt as acutely for those low beta stocks.
What does a beta of less than one mean?
If the opposite is the case, its beta will be a value less than one. A company with a beta of greater than one will tend to amplify market movements (for instance the case for the banking sector), and a business with a beta of less than one will tend to ease market movements.
Is low beta stock volatile?
Low beta stocks are much less volatile; however, another analysis must be done with intra-industry factors in mind. On the other hand, higher beta stocks are selected by investors who are keen and focused on short-term market swings. They wish to turn this volatility into profit, albeit with higher risks.
What is beta in stocks?
Beta is a measure of the volatility — or systematic risk — of a security or portfolio compared to the market as a whole. Beta is used in the capital asset pricing model (CAPM), which describes the relationship between systematic risk and expected return for assets (usually stocks). CAPM is widely used as a method for pricing risky securities ...
What does it mean when a stock has a beta of less than 1.0?
Beta Value Less Than One. A beta value that is less than 1.0 means that the security is theoretically less volatile than the market. Including this stock in a portfolio makes it less risky than the same portfolio without the stock.
What is a beta of 1.0?
A stock with a beta of 1.0 has systematic risk. However, the beta calculation can’t detect any unsystematic risk. Adding a stock to a portfolio with a beta of 1.0 doesn’t add any risk to the portfolio, but it also doesn’t increase the likelihood that the portfolio will provide an excess return.
Why is beta important?
Beta is useful in determining a security's short-term risk, and for analyzing volatility to arrive at equity costs when using the CAPM. However, since beta is calculated using historical data points, it becomes less meaningful for investors looking to predict a stock's future movements.
How does beta work?
How Beta Works. A beta coefficient can measure the volatility of an individual stock compared to the systematic risk of the entire market. In statistical terms, beta represents the slope of the line through a regression of data points.
What is beta in capital asset pricing?
Beta, primarily used in the capital asset pricing model (CAPM), is a measure of the volatility–or systematic risk–of a security or portfolio compared to the market as a whole.
What does a negative beta mean?
Some stocks have negative betas. A beta of -1.0 means that the stock is inversely correlated to the market benchmark. This stock could be thought of as an opposite, mirror image of the benchmark’s trends. Put options and inverse ETFs are designed to have negative betas.
What is beta in stocks?
Beta is a measure of a stock’s sensitivity to changes in the overall market. You can measure the beta in your portfolios with some basic math. Learn more about how to calculate the volatility, or beta, of your portfolio.
What does a beta of 1.0 mean?
A beta of 1.0 indicates that its volatility is the same as the benchmark. In other words, it moves in tandem with the benchmark. A number higher than 1.0 indicates more volatility than the benchmark, while a lower number indicates more stability. For example, a stock with a beta of 1.2 is 20% more volatile than the market, ...
Can you calculate beta using a benchmark?
For this reason, you may wish to calculate beta yourself to get a more precise answer. In some situations, you may prefer to calculate beta using a different benchmark.
Beta as An Indicator
- A stock that swings more than the market over time has a beta greater than 1.0. If a stock moves less than the market, the stock's beta is less than 1.0. High-beta stocks tend to be riskier but provide the potential for higher returns. Low-beta stocks pose less risk but typically yield lower r…
Calculating Beta from Comparable Public Companies
Earnings Beta Approach
The Bottom Line
- Find the risk-free rate. This is the rate of return an investor could expect on an investment in which his or her money is not at risk, such as U.S. Treasury Bills for investments in U.S. dollars and German Government Bills for investments that trade in euros. This figure is normally expressed as a percentage.
- Determine the respective rates of return for the stock and for the market or appropriate index…