
It's easy to calculate as long as you know a given company's stock price and earnings per share (EPS). The equation looks like this: P/E ratio = price per share ÷ earnings per share Let's say a company is reporting basic or diluted earnings per share of $2, and the stock is selling for $20 per share.
Full Answer
How do you calculate expected return on a stock?
Expected return is calculated by multiplying potential outcomes (returns) by the chances of each outcome occurring, and then calculating the sum of those results (as shown below). In the short term, the return on an investment can be considered a random variable. Random Walk Theory The Random Walk Theory is a mathematical model of the stock market.
What if I had invested stock calculator?
S&P 500 Periodic Reinvestment Calculator (With Dividends)
- The S&P 500 Periodic Investment Calculator. Starting Month & Year - When to start the scenario. Ending Month & Year - When to end the scenario. ...
- Methodology for the S&P 500 Periodic Reinvestment Calculator. The tool uses data published by Robert Shiller, which you can find here. ...
- FAQ on the Periodic Reinvestment Tool. How often do you update the data? ...
How to calculate expected total return for any stock?
The ‘quick and easy’ way to find total return is to:
- Calculate return from change in price-to-earnings multiple
- Add in current dividend yield
- Add in expected business growth rate on a per share basis
How to choose the best stock valuation method?
Popular Stock Valuation Methods
- Dividend Discount Model (DDM) The dividend discount model is one of the basic techniques of absolute stock valuation. ...
- Discounted Cash Flow Model (DCF) The discounted cash flow model is another popular method of absolute stock valuation. ...
- Comparable Companies Analysis
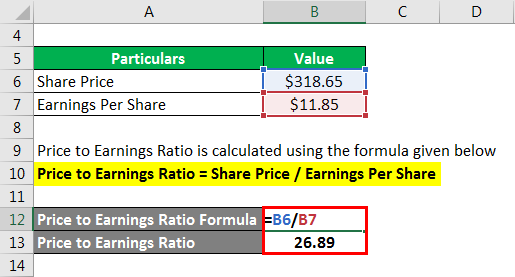
How do you calculate EPS stock price?
Determining Market Value Using P/E Multiply the stock's P/E ratio by its EPS to calculate its actual market value. In the above example, multiply 15 by $2.50 to get a market price of $37.50.
How do you calculate price per share with EPS and earnings yield?
Key TakeawaysThe basic definition of a P/E ratio is stock price divided by earnings per share (EPS).EPS is the bottom-line measure of a company's profitability and it's basically defined as net income divided by the number of outstanding shares.Earnings yield is defined as EPS divided by the stock price (E/P).
How do you calculate price per earnings?
P/E Ratio is calculated by dividing the market price of a share by the earnings per share. P/E Ratio is calculated by dividing the market price of a share by the earnings per share. For instance, the market price of a share of the Company ABC is Rs 90 and the earnings per share are Rs 10. P/E = 90 / 9 = 10.
How do you use PE ratio to value a company?
For example, if a company has earnings of $10 billion and has 2 billion shares outstanding, its EPS is $5. If its stock price is currently $120, its PE ratio would be 120 divided by 5, which comes out to 24. One way to put it is that the stock is trading 24 times higher than the company's earnings, or 24x.
Is EPS and PE the same?
P/E is the price-to-earnings ratio and EPS is the earnings per share. Earnings per share: This measure is calculated by taking the net income earned by the corporate and dividing it by the number of outstanding shares issued.
What does 10x PE mean?
PE Ratio Formula For instance, if the PE multiple is 10x. It implies that for each $1 of earning, the investor has paid $10. Hence, it will take ten years of earnings for the investor to recover the price paid.
What does 10x earnings mean?
A P/E of 10x means a company is trading at a multiple that is equal to 10 times earnings. A company with a high P/E is considered to be overvalued. Likewise, a company with a low P/E is considered to be undervalued.
What should be the PE ratio to buy a stock?
So, what is a good PE ratio for a stock? A “good” P/E ratio isn't necessarily a high ratio or a low ratio on its own. The market average P/E ratio currently ranges from 20-25, so a higher PE above that could be considered bad, while a lower PE ratio could be considered better.
Is 30 a good PE ratio?
P/E 30 Ratio Explained A P/E of 30 is high by historical stock market standards. This type of valuation is usually placed on only the fastest-growing companies by investors in the company's early stages of growth. Once a company becomes more mature, it will grow more slowly and the P/E tends to decline.
Price Earnings Ratio Formula
P/E = Stock Price Per Share / Earnings Per ShareorP/E = Market Capitalization / Total Net EarningsorJustified P/E = Dividend Payout Ratio / R – Gwh...
P/E Ratio Formula Explanation
The basic P/E formula takes current stock price and EPS to find the current P/E. EPS is found by taking earnings from the last twelve months divide...
Why Use The Price Earnings Ratio?
Investors want to buy financially sound companies that offer cheap shares. Among the many ratios, the P/E is part of the research process for selec...
Limitations of Price Earnings Ratio
Finding the true value of a stock cannot just be calculated using current year earnings. The value depends on all expected future cash flows and ea...
Why is the price to earnings ratio so popular?
The ratio is so popular because it's simple, it's effective, and, tautologically, because everyone uses it. Let's go through the basics of valuing a company's stock with this ratio and work out how this calculation can be useful to you. Calculating the value of a stock. The formula for the price-to-earnings ratio is very simple:
Can you predict the future of a stock?
It's impossible to predict the future, so there is no guarantee that any stock will perform as you predict. However, using the price-to-earnings ratio to value a company's stock in a variety of different situations is an effective way to understand the implications for all sorts of various outcomes. It's an easy and quick exercise ...
Who used the P/E ratio?
The P/E ratio was used by the late Benjamin Graham. Not only was he Warren Buffett's mentor, but he is also credited with coming up with " value investing ." 1
Why do investors prefer PEG?
Some investors may prefer the price-to-earnings growth ( PEG) ratio instead, because it factors in the earnings growth rate. 7 Other investors may prefer the dividend-adjusted PEG ratio because it uses the basic P/E ratio. It also adjusts for both the growth rate and the dividend yield of the stock. 8.
Why do you look at your portfolio through the P/E lens?
But looking at your portfolio through the P/E lens can help you avoid getting swept away in bubbles or panics. It can also help you know whether a stock is getting overvalued and no longer earning enough to warrant its price. Warning. You should never rely on P/E ratios alone when you choose investments.
Why is P/E important in investing?
The lower the P/E, the cheaper the stock. Value investors often use a stock’s P/E to determine if a company is under- or overvalued, or whether the stock is a good buy at the current price.
What is EPS in stock?
EPS is a company’s net earnings divided by the number of shares outstanding. When you multiply a stock’s EPS by its current price to earnings, you get the current stock price, or how much investors are currently willing to pay for a dollar of earnings. The lower the P/E, the cheaper the stock.
Is a fully valued stock undervalued?
The rule of thumb is that a fully valued stock should have a P/E that equals its earnings growth rate. If the P/E is below the EPS growth rate, the stock is undervalued; if the P/E is above the EPS rate, the stock is overvalued. It's that simple. 00:00.
What is the price to earnings ratio?
The price-to-earnings ratio is one of the most common financial ratios used to value stocks. This ratio measures the price investors are willing to pay for each dollar of the company’s earnings per share, or EPS. When investors like a company’s future growth potential, they will typically pay more for its stock, resulting in a high P/E ratio.
Why use P/E ratio?
You can use P/E ratios to calculate a stock’s actual market value and to compare it with other stocks in the same industry.
What is industry average P/E?
The industry average P/E ratio is only a guide to estimate a stock’s relative value. Some stocks continually trade at a P/E that differs from the industry average and might never align with their competitors.
Why do high risk companies have a low P/E?
When investors like a company’s future growth potential, they will typically pay more for its stock, resulting in a high P/E ratio. High-risk companies with bleak outlooks typically trade at a low P/E. You can use P/E ratios to calculate a stock’s actual market value and to compare it with other stocks in the same industry.
How to tell if a stock is overvalued or undervalued?
As stated earlier, to determine whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued, it should be compared to other stock in its sector or industry group. Sectors are made up of industry groups, and industry groups are made up of stocks with similar businesses such as banking or financial services.
What is the P/E ratio?
The price-to-earnings ratio (P/E) is one of the most common ratios used by investors to determine if a company's stock price is valued properly relative to its earnings. The P/E ratio is popular and easy to calculate, but it has shortcomings that investors should consider when using it to determine a stock's valuation.
Why is the PEG ratio important?
Since the P/E ratio does not factor in future earnings growth, the PEG ratio provides more insight into a stock's valuation. By providing a forward-looking perspective, the PEG is a valuable tool for investors in calculating a stock's future prospects.
Why do investors use P/E?
Investors not only use the P/E ratio to determine a stock's market value but also in determining future earnings growth. For example, if earnings are expected to rise, investors might expect the company to increase its dividends as a result. Higher earnings and rising dividends typically lead to a higher stock price.
What does a high P/E mean?
A high P/E could mean that a stock's price is high relative to earnings and possibly overvalued.
What is the first part of the P/E equation?
The first part of the P/E equation or price is straightforward as the current market price of the stock is easily obtained. On the other hand, determining an appropriate earnings number can be more difficult. Investors must determine how to define earnings and the factors that impact earnings. As a result, there are some limitations to the P/E ratio as certain factors can impact the P/E of a company. Those limitations include:
When to use PEG ratio?
Since stock prices are typically based on investor expectations of future performance by a company, the PEG ratio can be helpful but is best used when comparing if a stock price is overvalued or undervalued based on the growth in the company's industry.
How to Calculate Share Price?
To calculate a stock’s market cap, you must first calculate the stock’s market price. Take the most recent updated value of the firm stock and multiply it by the number of outstanding shares to determine the value of the stocks for traders.
Share Price Formula in IPO
Via the primary market, firm stocks are first issued to the general public in an Initial Public Offering (IPO) to collect money to meet financial needs.
Conclusion
Stock prices are also depending on market sentiments. A stock at higher value looks cheaper in a bull market and a stock with lower value looks expensive in a bear market.
Frequently Asked Questions
Let's suppose Heromoto's P/E ratio has been 18.53 in the past. 2465 divided by 148.39 = 16.6 times the current P/E ratio. The present stock price should be 18 times its historical P/E ratio if it were trading at its historical P/E ratio of 18. 2754 is equal to 148.39. On this criteria, Heromoto's present stock price is undervalued.
