Step by Step Application of Enterprise Value Formula
- Firstly, the current price per share of the company has to be found out from the stock market, and then the number of...
- Now, the current value of the preferred stock is computed by multiplying the stock’s per value by the number of...
- The current outstanding debt balance is calculated by adding financial liabilities...
How do you calculate the enterprise value?
The formula for enterprise value is calculated by adding the company’s market capitalization, preferred stock, outstanding debt, and minority interest together, and then deducting the cash and cash equivalents obtained from the balance sheet.
Are the stock price and enterprise value equal?
The Reality: The reality is that the Stock Price and Enterprise Value are almost never equal. As illustrated in the graph below, Enterprise Value is slow to change because it takes time for management actions to impact free cash flow via changes in the five drivers of Enterprise Value.
How do you value a stock based on price to earnings?
Calculating the value of a stock The formula for the price-to-earnings ratio is very simple: Price-to-earnings ratio = stock price / earnings per share.
How to calculate a company's current stock price?
Finally, with these two numbers in hand, simply divide the P/E ratio by the earnings per share number and you'll have the company's current stock price. It's just that easy.

How is stock price calculated?
The most common way to value a stock is to compute the company's price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio. The P/E ratio equals the company's stock price divided by its most recently reported earnings per share (EPS). A low P/E ratio implies that an investor buying the stock is receiving an attractive amount of value.
How do you calculate market cap from enterprise value?
To calculate enterprise value, add the company's market capitalization to its outstanding preferred stock and all debt obligations, then subtract all of its cash and cash equivalents.
How do you value a company using enterprise value?
Simply put, EV is the sum of a company's market cap and its net debt. To compute the EV, total debt—both short- and long-term—is added to a company's market cap, then cash and cash equivalents are subtracted. This number tells you what you would have to pay to buy every share of the company.
What is enterprise value in stock market?
Enterprise value (EV) is a measure of a company's total value, often used as a more comprehensive alternative to equity market capitalization. EV includes in its calculation the market capitalization of a company but also short-term and long-term debt as well as any cash on the company's balance sheet.
Is enterprise value equal to market value?
Enterprise Value = market value of the common stock or market cap + market value of preferred shares + total debt (including long and short-term debt) + minority interest – total cash and cash equivalents.
Is market cap equal to enterprise value?
Both measures are used to make investment decisions, but they provide different perspectives. Market cap estimates what a company's outstanding common stock is worth. Enterprise value calculates all financial interests of the business, including those of debt holders and subsidiaries.
Does enterprise value include preferred stock?
Enterprise value is a measurement of the total value of a company that shows how much it would cost to buy the entire company, including its debt. To calculate it, add together market capitalization, preferred stock, and debt, then subtract cash and cash equivalents.
How do you value shares in a private company?
Methods for valuing private companies could include valuation ratios, discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis, or internal rate of return (IRR). The most common method for valuing a private company is comparable company analysis, which compares the valuation ratios of the private company to a comparable public company.
Is NPV same as enterprise value?
Shown above is the formula for terminal value that gets added to NPV, the sum of which calculation is enterprise value. Once we subtract debt and add cash, we arrive at an equity value of $237.58 per share.
Why do we subtract cash from enterprise value?
Answer: Cash is subtracted in the Enterprise Value formula because it's a non-operating asset and Equity Value (which is included in the Enterprise Value) implicitly accounts for it.
How do you calculate share price on a balance sheet?
To calculate this market value, multiply the current market price of a company's stock by the total number of shares outstanding. The number of shares outstanding is listed in the equity section of a company's balance sheet.
How is EV EBITDA stock price calculated?
Example CalculationCalculate the Enterprise Value (Market Cap plus Debt minus Cash) = $69.3 + $1.4 – $ 0.3 = $70.4B.Divide the EV by 2017A EBITDA = $70.4 / $5.04 = 14.0x.Divide the EV by 2017A EBITDA = $70.4 / $5.50 = 12.8x.
Step by Step Application of Enterprise Value Formula
The Calculation of Enterprise Value equation can be done in the following six simple steps:
Examples of Enterprise Value Formula
Let’s take a few simples to advanced examples to understand Enterprise Value.
Relevance and Use
The importance of enterprise value revolves around the fact that it helps in the assessment of the worth of a company.
Calculate Enterprise Value in Excel
Let us take the case of Apple Inc. mentioned in EV Formula Example #2 to demonstrate in excel template the working towards the calculation of the Enterprise Value:
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to Enterprise Value Formula. Here we discuss its uses along with simple to advanced practical examples to understand Enterprise Value. Here we also provide you with Enterprise Value Formula Calculator with a downloadable excel template. You can learn more about Excel Modeling from the following articles –
What is enterprise multiple?
Enterprise Multiples are based on the relation between the value of a company in terms of the market value of its total capital from all sources and the operating earnings. The Operating Earnings Operating Earnings is the amount of profit a company earns after deducting direct and indirect costs from sales revenue.
Why is firm value accepted?
This is mainly because it also takes the other significant implications into account that the acquirer will have to deal with as the new owner of the acquired company.
Why are liquid assets considered cash?
Most of the highly liquid assets are considered equivalent to cash because they are readily convertible to cash. Since they reduce the acquisition price in effect, they are subtracted for the calculation of enterprise value. Alphabet (Google) has a cash and cash equivalents of $16,549mn.
How to calculate preferred stock cost?
They calculate the cost of preferred stock by dividing the annual preferred dividend by the market price per share.#N#are hybrid securities that have features of both equity and debt. They are treated more as debt, in this case, because they pay a fixed amount of dividends and have a higher priority in asset and earning claims than common stock. In an acquisition, they normally must be repaid just like debt.
Why subtract cash equivalents from EV?
We subtract this amount from EV because it will reduce the acquiring costs of the target company. It is assumed that the acquirer will use the cash. Cash Equivalents Cash and cash equivalents are the most liquid of all assets on the balance sheet. Cash equivalents include money market securities, banker's acceptances.
What are cash equivalents? What are some examples?
Examples of cash equivalents are short-term investments, marketable securities. Marketable Securities Marketable securities are unrestricted short-term financial instruments that are issued either for equity securities or for debt securities of a publicly listed company.
What is the EBITDA multiple?
EBITDA Multiple The EBITDA multiple is a financial ratio that compares a company's Enterprise Value to its annual EBITDA. This multiple is used to determine the value of a company and compare it to the value of other, similar businesses.
What is investment in finance?
An investment is any asset or instrument purchased with the intention of selling it for a price higher than the purchase price at some future point in time (capital gains), or with the hope that the asset will directly bring in income (such as rental income or dividends). Valuation Methods.
What is a stock option writer?
A seller of the stock option is called an option writer, where the seller is paid a premium from the contract purchased by the stock option buyer. , warrants, and convertible securities, aside from just the basic shares outstanding.
What is it called when you own stock?
An individual who owns stock in a company is called a shareholder and is eligible to claim part of the company’s residual assets and earnings (should the company ever be dissolved). The terms "stock", "shares", and "equity" are used interchangeably. current market price.
What Is Enterprise Value (EV)?
As its name implies, enterprise value (EV) is the total value of a company, defined in terms of its financing. It includes both the current share price (market capitalization) and the cost to pay off debt (net debt, or debt minus cash).
Key Takeaways
Enterprise value calculates the potential cost to acquire a business based on the company’s capital structure.
Enterprise Value Explained
The first time people see the enterprise value formula, most have the same reaction: Huh? Why would you add money a company owes to its value and subtract cash on hand? After all, a company with more cash should be more valuable than one with less, all other things being equal—and that’s true.
What Does EV Tell You?
Conceptually, enterprise value gives you a realistic starting point for what you would need to spend to acquire a public company outright. In reality, it typically takes a premium to EV for an acquisition offer to be accepted. This is for a few reasons:
Enterprise Value (EV) Calculations
A company’s enterprise value is not reflected solely in its shareholder contribution, the amount of money contributed to a business by shareholders; it also takes into account company debt, both short- and long-term, and cash reserves. While “debt” and “cash” are clear and simple terms, market cap deserves a bit of explanation.
How is Enterprise Value Different from Market Cap?
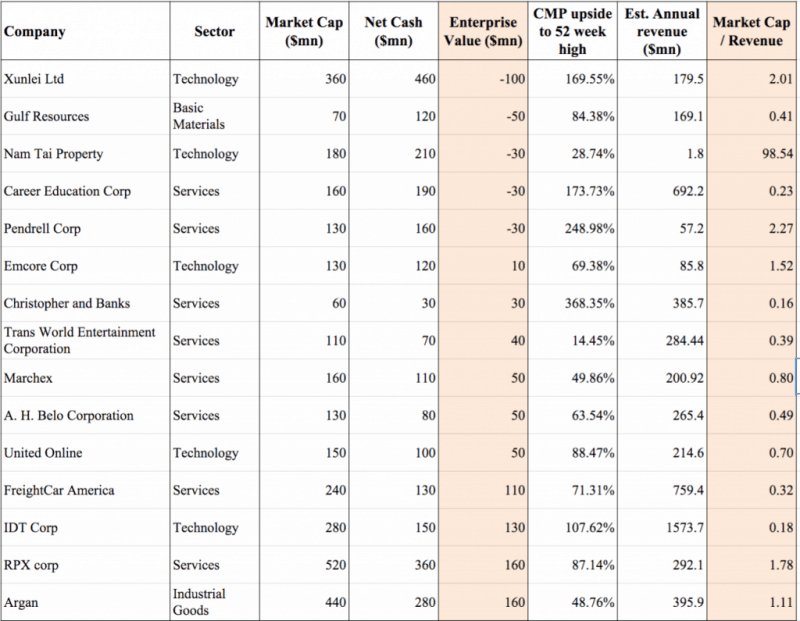
For businesses with either material cash reserves or debt, enterprise value is a more thorough calculation that provides clearer insight than market cap into the real value of the business. As the table below illustrates, companies with identical market caps may have vastly different enterprise values based on their cash and debt positions.
What Kinds of Businesses Should Calculate Enterprise Value?
As you’d likely guess, the greater the difference between a company’s cash and debt, the more important an enterprise value calculation becomes, particularly when thinking about acquisitions.
What is enterprise value?
Enterprise value is basically a modification of market cap, as it incorporates debt and cash for determining a company's valuation. Market capitalization is not intended to represent a company's book value. Instead, it represent's a company's value as determined by market participants.
Why is enterprise value more accurate?
As a result, enterprise value provides a much more accurate takeover valuation because it includes debt in its value calculation. Why doesn't market capitalization properly represent a firm's value? It leaves a lot of important factors out, such as a company's debt on the one hand and its cash reserves on the other.
What is EBITDA in accounting?
EBITDA = recurring earnings from continuing operations + interest + taxes + depreciation + amortization. The enterprise value/EBITDA metric is used as a valuation tool to compare the value of a company, debt included, to the company’s cash earnings less non-cash expenses.
Why is the EV/sales ratio negative?
The EV/sales ratio can actually be negative at times when the cash held by a company is more than the market capitalization and debt value, implying that the company can essentially be by itself with its own cash.
How to calculate EV?
The market capitalization of a company is calculated by multiplying the share price by the number of shares outstanding. The net debt is the market value of debt minus cash. A company acquiring another company keeps the cash of the target firm, which is why cash needs to be deducted from the firm's price as represented by market cap.
How to calculate market capitalization?
To calculate the market capitalization if not readily available you would multiply the number of outstanding shares by the current stock price. Next, total all debt on the company's balance sheet including both short-term and long-term debt. Finally, add the market capitalization to the total debt and subtract any cash and cash equivalents from ...
What is the P/E ratio?
The price-to-earnings ratio (P/E ratio) is the ratio for valuing a company that measures its current share price relative to its per-share earnings ( EPS ). The price-to-earnings ratio is also sometimes known as the price multiple or the earnings multiple. The P/E ratio doesn't consider the amount of debt that a company has on its balance sheet.
What is enterprise value?
Enterprise value (EV) is a metric that measures the total value of a company. It is more comprehensive than market capitalization because it also accounts for the company’s cash and debt levels.
Why is enterprise value important?
For companies with lots of debt or lots of cash, enterprise value is a much more useful way to measure the “true price” of a company or stock. If you buy a company, then you also receive the company’s cash and debt. If the company has more debt than cash, then the true price of the company is higher because you will end up having to pay the debt.
How much is CVS worth?
CVS Health ( CVS) has a market cap of $93 billion, with $8 billion in cash and $90 billion in debt. This gives them an enterprise value of $93B + $90B – $8B = $175B.
Why is the true value of a company lower?
But if the company has more cash than debt, then the true value of the company is lower because you can subtract the cash from the price.
How to calculate PE ratio?
The PE ratio (price to earnings) can be calculated by dividing a company’s market cap by its earnings in the past 12 months. However, this can be highly misleading for companies with a lot of debt. If someone were to buy such a company outright, they would end up having to cover the interest payments and pay the debt.
Can a stock have a negative enterprise value?
A stock can have negative enterprise value. If the company has no debt but more cash than its market cap, then that makes the enterprise value lower than zero. In theory, you would technically be getting paid for buying such a company outright. But takeovers usually require premiums to be paid above market prices.
Why is the price to earnings ratio so popular?
The ratio is so popular because it's simple, it's effective, and, tautologically, because everyone uses it. Let's go through the basics of valuing a company's stock with this ratio and work out how this calculation can be useful to you. Calculating the value of a stock. The formula for the price-to-earnings ratio is very simple:
Can you predict the future of a stock?
It's impossible to predict the future, so there is no guarantee that any stock will perform as you predict. However, using the price-to-earnings ratio to value a company's stock in a variety of different situations is an effective way to understand the implications for all sorts of various outcomes. It's an easy and quick exercise ...

What Are The Components of EV?
Why Is Enterprise Value used?
- Enterprise Value is often used for multiplesEBITDA MultipleThe EBITDA multiple is a financial ratio that compares a company's Enterprise Value to its annual EBITDA. This multiple is used to determine the value of a company and compare it to the value of other, similar businesses. A company's EBITDA multiple provides a normalized ratio for differences in capital structure, such …
Applications in Financial Modeling
- In financial modelingWhat is Financial ModelingFinancial modeling is performed in Excel to forecast a company's financial performance. Overview of what is financial modeling, how & why to build a model., it is common practice to model Free Cash Flow to Firm (FCFFThe Ultimate Cash Flow Guide (EBITDA, CF, FCF, FCFE, FCFF)This is the ultimate Cash Flow Guide to understand th…
Additional Resources
- Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Enterprise Value. To continue advancing your career, these additional resources will be helpful: 1. Enterprise Value vs Equity ValueEnterprise Value vs Equity ValueEnterprise value vs equity value. This guide explains the difference between the enterprise value (firm value) and the equity value of a business. 2. Investment MethodsInvestment Method…