
Just follow the 5 easy steps below:
- Enter the number of shares purchased
- Enter the purchase price per share, the selling price per share
- Enter the commission fees for buying and selling stocks
- Specify the Capital Gain Tax rate (if applicable) and select the currency from the drop-down list (optional)
- Click on the 'Calculate' button to estimate your profit or loss.
What if I had invested stock calculator?
S&P 500 Periodic Reinvestment Calculator (With Dividends)
- The S&P 500 Periodic Investment Calculator. Starting Month & Year - When to start the scenario. Ending Month & Year - When to end the scenario. ...
- Methodology for the S&P 500 Periodic Reinvestment Calculator. The tool uses data published by Robert Shiller, which you can find here. ...
- FAQ on the Periodic Reinvestment Tool. How often do you update the data? ...
How do you calculate the total value of a stock?
4 ways to calculate the relative value of a stock
- Price-to-earnings ratio (P/E) What it is. Offers a snapshot of what you’ll pay for a company’s future earnings. ...
- Price/earnings-to-growth ratio (PEG) What it is. Considers a company’s earnings growth. ...
- Price-to-book ratio (P/B) What it is. A snapshot of the value of a company’s assets. ...
- Free cash flow (FCF)
How do you calculate the value of shares?
How do you calculate the value of a stock? The most common way to value a stock is to compute the company’s price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio . The P/E ratio equals the company’s stock price divided by its most recently reported earnings per share (EPS).
How do you estimate stock price?
The stock AMC, +5.04% rose $1.03, or 7.8%, in morning trading Monday, but pared earlier intraday gains of as much as 30.1%, while trading volume ballooned to 245.6 million shares.
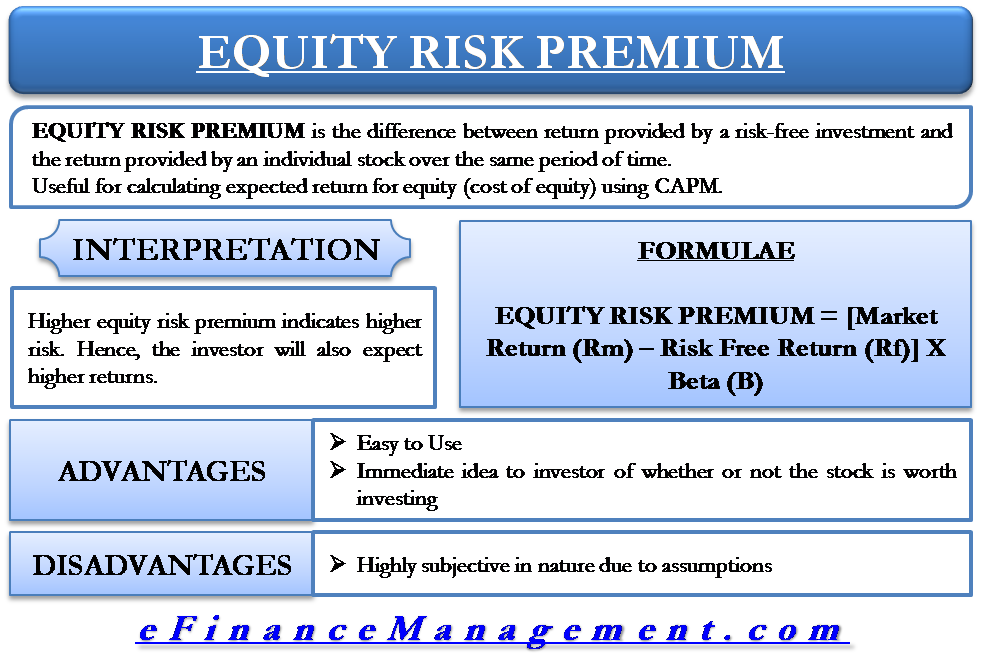
How Do You Calculate Profit on Stock?
If you want to calculate the profit on a stock, you'll need the total amount of money you used to purchase your stock and the total value of your shares at the current price. You'll also need to know any fees associated with your transactions So if you bought 10 shares of Company X at $10 each and sold them for $20 each and incurred fees of $10, you stand to walk away with a profit of $90. Put simply, $200- $100- $10 = $90. Remember that this is just the dollar value and not the percentage change.
How Do You Calculate Gain or Loss Percentage on Stock With a Calculator?
You'll need the original purchase price and the current value of your stock in order to make the calculation. Subtract the total purchase price from the current price of the stock then divide that by the original purchase price and multiply that figure by 100. This gives you the total percentage change.
What is the percentage return on a $10/share investment?
The per-share gain is $7 ($17 – $10). Thus, your percentage return on your $10/share investment is 70% ($7 gain / $10 cost).
How much is 70% return on investment?
By multiplying the percentage return on the investment (70%) by the total dollar amount invested, investors will know how much in dollar terms they have made on this investment (70% return on $1,000 is $1,700; providing a dollar gain of $700).
How to find net gain or loss in stock?
In order to find the net gain or loss of your stock holding, you will have to determine the difference between what you paid for it and ultimately what you sold it for on a percentage basis. To do so, subtract the purchase price from the current price and divide the difference by the purchase price of the stock.
Is it hard to predict a stock's gain or loss?
But it's not an exact science. There are many factors that are hard to predict, such as human emotions, overall market behavior, and global events. As such, a stock can either be a winner or a loser and depending on the outcome, an investor will have to determine the gains or losses in their portfolio. In order to find the net gain ...
How to calculate ROI?
ROI is calculated by subtracting the initial value of the investment from the final value of the investment (which equals the net return), then dividing this new number (the net return) by the cost of the investment, then finally, multiplying it by 100.
How much of the ROI comes from capital gains?
Further dissecting the ROI into its component parts reveals that 23.75% came from capital gains and 5% came from dividends. This distinction is important because capital gains and dividends are taxed at different rates in most jurisdictions.
What does it mean when ROI is negative?
Alternatively, when ROI calculations yield a negative figure, it means that net returns are in the red because total costs exceed total returns. (In other words, this investment produces a loss.) Finally, to calculate ROI with the highest degree of accuracy, total returns and total costs should be considered. For an apples-to-apples comparison between competing investments, annualized ROI should be considered.
Why is ROI calculation so complicated?
This type of ROI calculation is more complicated because it involves using the internal rate of return (IRR) function in a spreadsheet or calculator.
Why is ROI expressed as a percentage?
First, ROI is typically expressed as a percentage because it is intuitively easier to understand (as opposed to when expressed as a ratio). Second, the ROI calculation includes the net return in the numerator because returns from an investment can be either positive or negative.
What is ROI in investing?
Return on investment (ROI) is an approximate measure of an investment's profitability. ROI has a wide range of applications; it can be used to measure the profitability of a stock investment, when deciding whether or not to invest in the purchase of a business, or evaluate the results of a real estate transaction.
Why is ROI important?
The biggest benefit of ROI is that it is a relatively uncomplicated metric; it is easy to calculate and intuitively easy to understand . ROI's simplicity means that it is often used as a standard, universal measure of profitability. As a measurement, it is not likely to be misunderstood or misinterpreted because it has the same connotations in every context.
What is net gain in stock?
Net Stock Investment Gain ($): After paying commissions, the amount you gained (or lost) while holding the stock based on your buying and selling price
What does number of shares mean?
Number of Shares - The number of shares you sell in the stock transaction
How to calculate CAGR?
If you choose to compute a CAGR, you'll also need to enter how long you held the stock into the tool. You can either enter years explicitly or enter a buy and sell date: 1 Use Dates - Enter the Starting Date when you bought the stock and the Ending Date when you sold. 2 Use a fixed period - Enter the number of years you held the investment (decimals are okay).
What is net return on investment?
Net Return on Investment: The total percentage gain or loss on your investment, or net return on investment.
Do ETFs pay dividends?
Note that price return isn't the only type of investment return – importantly, many stocks, ETFs, CEFs and ADRs also pay dividends. Use our stock return calculator or ETF return calculator for real-life examples showing the effects of reinvesting dividends.
How much does the S&P 500 return?
Enter your expected rate of return. For a point of reference, the S&P 500 has a historical average annual total return of about 10%, not accounting for inflation. This doesn’t mean you can expect 10% growth every year; you could experience a gain one year and a loss the next. But if you keep your money invested for the long term, the goal is for these gains and losses to average out over time, ideally ending in the black by the end of the investment period.
What is price return?
Price return is simply the annualized change in the price of the stock or mutual fund. If you buy it for $50 and the price rises to $75 in one year, that stock price is up 50%. If the following year the price closes at $60, the stock price fell 20% that year. If it closes at $65 the third year, it increased by 8.3%.
Can you expect 10% growth in a year?
This doesn’t mean you can expect 10% growth every year; you could experience a gain one year and a loss the next. But if you keep your money invested for the long term, the goal is for these gains and losses to average out over time, ideally ending in the black by the end of the investment period.
How much is a $1,000 investment worth?
With a simple annual interest rate, your $1,000 investment has a future value of $1,500.
How to calculate future value with compound interest?
You can calculate future value with compound interest using this formula: future value = present value x (1 + interest rate)n. To calculate future value with simple interest, use this formula: future value = present value x [1 + (interest rate x time)].
How does simple interest work?
In other words, you earn interest on your interest. With simple interest, an investment accrues interest based solely on the initial investment amount. The interest that adds up as the years pass comes from only your principal amount, not the interest earned on that principal. If you're trying to calculate the value of an investment ...
How to calculate future value in Excel?
For instance, on Excel, if you go to the Formulas tab, then the Financial tab, you can click "FV" to generate a future values calculation. However, the equation will look pretty different from what you're used to. You can check out Microsoft's tutorial on how to calculate future value in Excel . . . or, instead of using the Excel-generated formula, you can just enter the numbers you're running and create an equation using the = sign.
What does n mean in future value?
In the future value formula, n stands for the number of interest-compounding periods that occur during a specified time period. For instance, if you're calculating an investment's worth after five years, and interest on the investment is compounded annually, n would be 5 in the equation.
What is the future value of an annuity?
The future value of an ordinary annuity, which is a regular payment made on an asset (such as property) or received from an investment (such as interest on a bond) The future value of a growing annuity, which is an increasing payment made or received on a regular schedule.
Is it a good idea to use future value formula before investing?
But using the future value formula before you invest can increase your chances of picking the right stock at the right time.
How to calculate percentage gain on an investment?
To calculate the percentage gain on an investment, investors need to first determine how much the investment originally cost or the purchase price. Next, the purchase price is subtracted from the selling price of the investment to arrive at the gain or loss on the investment.
What is dividend in investment?
A dividend is a cash payment paid to shareholders and is configured on a per-share basis. Using the Intel example, let's say the company paid a dividend of $2 per share.
What is percentage gain or loss?
The percentage gain or loss calculation will produce the dollar amount equivalent of the gain or loss in the numerator.
Why is it important to calculate the percentage of gain or loss?
Calculating the gain or loss on an investment as a percentage is important because it shows how much was earned as compared to the amount needed to achieve the gain.
What is Dow Jones Industrial Average?
The Dow is an index that tracks 30 stocks of the most established companies in the United States.
How to incorporate transaction costs?
To incorporate transaction costs, reduce the gain (selling price – purchase price) by the costs of investing.
Does investing come without costs?
Investing does not come without costs, and this should be reflected in the calculation of percentage gain or loss. The examples above did not consider broker fees and commissions or taxes. To incorporate transaction costs, reduce the gain (selling price – purchase price) by the costs of investing.
How to value a stock?
The most common way to value a stock is to compute the company's price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio . The P/E ratio equals the company's stock price divided by its most recently reported earnings per share (EPS). A low P/E ratio implies that an investor buying the stock is receiving an attractive amount of value.
What is the book value of a stock?
Price is the company's stock price and book refers to the company's book value per share. A company's book value is equal to its assets minus its liabilities (asset and liability numbers are found on companies' balance sheets). A company's book value per share is simply equal to the company's book value divided by the number of outstanding shares. ...
What is a stock?
A single share of a company represents a small ownership stake in the business. As a stockholder, your percentage of ownership of the company is determined by dividing the number of shares you own by the total number of shares outstanding and then multiplying that amount by 100. Owning stock in a company generally confers to the stock owner both corporate voting rights and income from any dividends paid.
What is GAAP earnings?
GAAP is shorthand for Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, and a company's GAAP earnings are those reported in compliance with them. A company's GAAP earnings are the amount of profit it generates on an unadjusted basis, meaning without regard for one-off or unusual events such as business unit purchases or tax incentives received. Most financial websites report P/E ratios that use GAAP-compliant earnings numbers.
Why do investors use adjusted earnings to calculate P/E?
Non-repeating events can cause significant increases or decreases in the amount of profits generated, which is why some investors prefer to calculate a company's P/E ratio using a per-share earnings number adjusted for the financial effects of one-time events. Adjusted earnings numbers tend to produce more accurate P/E ratios.
How to calculate forward P/E ratio?
The forward P/E ratio is simple to compute. Using the P/E ratio formula -- stock price divided by earnings per share -- the forward P/E ratio substitutes EPS from the trailing 12 months with the EPS projected for the company over the next fiscal year . Projected EPS numbers are provided by financial analysts and sometimes by the companies themselves.
Why should investors consider companies' strengths and weaknesses when gauging a stock's value?
Aside from metrics like the P/E ratio that are quantitatively computed, investors should consider companies' qualitative strengths and weaknesses when gauging a stock's value. A company with a defensible economic moat is better able to compete with new market participants, while companies with large user bases benefit from network effects. A company with a relative cost advantage is likely to be more profitable, and companies in industries with high switching costs can more easily retain customers. High-quality companies often have intangible assets (e.g., patents, regulations, and brand recognition) with considerable value.
How to evaluate a stock?
To evaluate a stock, review its performance against a benchmark. You may be satisfied with a stock that generated an 8% return over the past year, but what if the rest of the market is returning a few times that amount? Take the time to compare the stock’s performance with different market indexes, such as the Dow Jones Industrial Average, the S&P 500, or the NASDAQ Composite. These indexes can act as the benchmark against which to compare your own investments' performance. 1
How to calculate real return?
This is called a real return and can be done simply by subtracting inflation from the annual return of your investment.
What is the purpose of looking at the change in a stock price?
Looking at the change in a stock's price by itself is a naive way to evaluate the performance of a stock. Everything is relative, and so that return must be compared to make a proper evaluation. In addition to looking at a company’s total returns, comparing them to the market and weighing them relative to competitors within the company's industry, there are several other factors to consider in evaluating a stock’s performance.
Do dividends add to total return?
If the stock pays dividends, for instance, those cash flows must be added to the total return of the investment.
Is the S&P 500 a good yardstick?
If you invest in small speculative penny stocks, the S&P 500 will not be the right yardstick, as that contains only large-cap stocks listed on major stock exchanges. You may also want to look at how the economy has done during the same period, how inflation has risen, and other broader economic considerations.
Is a stock outperforming the market?
It could happen that a stock is outperforming the market but is nevertheless underperforming its own industry, so make sure to consider the stock’s performance relative to its primary competitors as well as companies of similar size in its industry.
