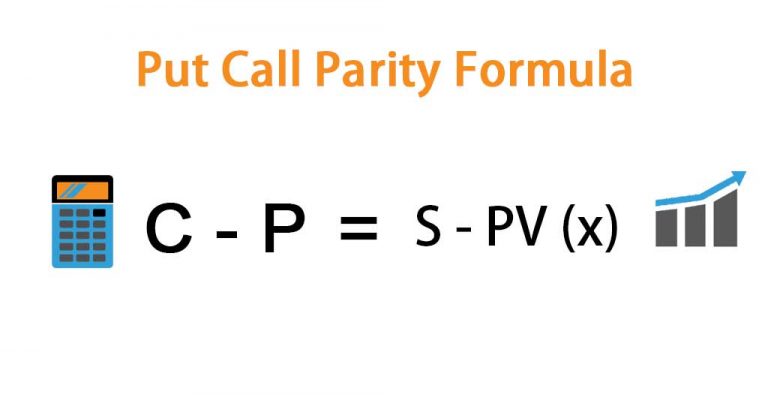How To Calculate Profit In Call Options To calculate profits or losses on a call option use the following simple formula: Call Option Profit/Loss = Stock Price at Expiration – Breakeven Point For every dollar the stock price rises once the $53.10 breakeven barrier has been surpassed, there is a dollar for dollar profit for the options contract.
How to calculate probability of profit when trading options?
- Probability of the option expiring below the upper slider bar. If you set the upper slider bar to 145, it would equal 1 minus the probability of the option expiring ...
- Probability of earning a profit at expiration, if you purchase the 145 call option at 3.50. ...
- Probability of losing money at expiration, if you purchase the 145 call option at 3.50. ...
What is the value of a call or put option?
When you sell a put option, three things can happen on expiry:
- Market Price > Strike Price = Out of Money put option = Gains / Profits
- Market Price < Strike Price = In the Money put option = Loss
- Market Price = Strike Price = At the Money call option = Profit in the form of premium.
When and how to take profits on options?
- Unlike stocks that can be held for an infinite period, options have an expiry. ...
- Long-term strategies like “ averaging down ” (i.e., repeated buying on dips) are not suitable for options due to its limited life.
- Margin requirements can severely impact trading capital requirements.
How do you calculate call option price?
- When the strike and stock prices are the same, the option is at-the-money.
- When the strike of a call is below the stock price, it is in-the-money (reverse for a put).
- When the strike of a call is above the stock price (reverse for a put), it is out-of-the-money.

How is option selling profit calculated?
Do bear in mind this formula is applicable on positions held till expiry.P&L = Premium Recieved – [Max (0, Strike Price – Spot Price)] ... @16510 (spot below strike, position has to be loss making) ... = – 1575.@19660 (spot above strike, position has to be profitable, restricted to premium paid) ... = 315.More items...
How do you calculate call options?
You can calculate the value of a call option and the profit by subtracting the strike price plus premium from the market price. For example, say a call stock option has a strike price of $30/share with a $1 premium, and you buy the option when the market price is also $30. You invest $1/share to pay the premium.
How is call price calculated?
Calculate the call price by calculating the cost of the option. The bond has a par value of $1,000, and a current market price of $1050. This is the price the company would pay to bondholders. The difference between the market price of the bond and the par value is the price of the call option, in this case $50.
How accurate is option profit calculator?
While OptionStrat is pretty accurate, it can't predict the future. One of the biggest unknowns about the future is implied volatility. Implied volatility represents the expected volatility of the option, and is affected by the supply and demand of it.
What is call option?
What Are Call Options? A call option is a contract between a buyer and seller. The contract will be for the right to purchase a certain stock at a certain price, up until a certain date (called the expiration date). Up until the contract expires, the buyer of a call has the right to purchase the stock at the agreed price.
What happens to a call option when the contract expires?
Up until the contract expires, the buyer of a call has the right to purchase the stock at the agreed price. On the other hand, the seller of a call option has an obligation to sell the stock if the buyer exercises the option.
Why is the profit scenario reversed?
The profit scenario is reversed for the call option seller because the maximum profit they can achieve is equal to the premium received and the potential losses are unlimited. The breakeven price for the call seller is also $24 and anything above that level will see them suffer losses on a one to one basis.
Do call option buyers have to pay premiums?
For receiving the right to buy the underlying shares, the call option buyer must pay to the seller a premium. This is the seller’s to keep no matter what happens. When determining the profit for the call option buyer we need to take into account to cost of the premium.
What happens if you lose a $6 premium on options?
While premiums are usually modest, they can impact value when using call options.
What happens if the strike price is $43?
So, if the current asset price is $47 and the strike price is set at $43, the option looks profitable indeed. However, if the premium is $6, then you lose.
Who is obliged to convey a stock?
The seller , on the other hand, is obliged to convey the stock if the buyer exercises the option. This relationship contrasts with that of a put option, where the right to exercise lands on the seller. When the purchaser holds the right, that person must determine whether going through with the deal makes sense.
What factors determine the value of an option?
These include the current stock price, the intrinsic value, time to expiration or the time value, volatility, interest rates, and cash dividends paid.
What are the drivers of the price of an option?
Let's start with the primary drivers of the price of an option: current stock price, intrinsic value, time to expiration or time value, and volatility. The current stock price is fairly straightforward. The movement of the price of the stock up or down has a direct, though not equal, effect on the price of the option.
Why do I get a higher premium on an AMZN option?
On the one hand, the seller of an AMZN option can expect to receive a higher premium due to the volatile nature of the AMZN stock. Basically, when the market believes a stock will be very volatile, the time value of the option rises.
How does time value relate to options?
It is directly related to how much time an option has until it expires, as well as the volatility, or fluctuations, in the stock's price.
What is the most widely used model of options?
Of these, the Black-Scholes model is the most widely known. 1 In many ways, options are just like any other investment—you need to understand what determines their price to use them effectively. Other models are also commonly used, such as the binomial model and trinomial model .
How does time decay in an option?
The time component of an option decays exponentially. The actual derivation of the time value of an option is a fairly complex equation. As a general rule, an option will lose one-third of its value during the first half of its life and two-thirds during the second half of its life.
How to calculate call option price?
In general, call option value (not profit or loss) at expiration at a given underlying price is equal to the greater of: 1 underlying price minus strike price (if the option expires in the money) 2 zero (if it doesn’t)
What is option payoff formula?
Before we start building the actual formulas in Excel, let’s make sure we understand what an option payoff formula is: It is a function that calculates how much money we make or lose at a particular underlying price.
What is the formula for the MAX function in Excel?
In our example, the formula in cell C8 will be: =MAX (C6-C4,0) … where cells C4 and C6 are strike price and underlying price, respectively.