
Exploring Option Profit Calculators
- As a first step, the investor should subtract the initial value of the asset in the contract from the current sale price of the asset. ...
- The next step involves multiplying this value by the total number of contracts purchased. ...
- As a final step, subtract the total price of the premium paid for the contracts from the prior calculation. ...
How to calculate probability of profit when trading options?
- Probability of the option expiring below the upper slider bar. If you set the upper slider bar to 145, it would equal 1 minus the probability of the option expiring ...
- Probability of earning a profit at expiration, if you purchase the 145 call option at 3.50. ...
- Probability of losing money at expiration, if you purchase the 145 call option at 3.50. ...
How to make money with options trading?
- Improve your portfolio returns
- Understand the pros and cons of a dividend investing approach
- Develop and craft your own dividend investing strategy
- Build wealth through a long-term compound interest plan
How do you calculate stock options?
You calculate the compensation element by subtracting the exercise price from the market value. The market value of the stock is the stock price on the day you exercise your options to buy the stock. You can use the average of the high and low prices that the stock trades for on that day.
How do you calculate option profit?
Using The Free Trade Calculator To Profit On Call And Put Spreads
- From there you can drop your price a little depending on how urgently you feel you need to get into the trade.
- And don’t worry, they’re not going to expire, so feel free to bookmark the page if you’d prefer.
- This typically happens to ITM options the day before the Dividend Ex-Date.
How much profit do you make from options?
How much money can you make trading options? It's realistic to make anywhere between 10% – $50% or more per trade. If you have at least $10,000 or more in an account, you could make $250 – $1,000 or more trading them. It's important to manage your risk properly trading them.
How do you calculate return on options?
The formula for calculating the expected return of a call option is projected stock price minus option strike price minus option premium. Each call option represents 100 shares, so to get the expected return in dollars, multiply the result of this formula by 100.
How can I calculate profit?
Profit is revenue minus expenses. For gross profit, you subtract some expenses. For net profit, you subtract all expenses.
How do you calculate profit on a buy call?
To calculate profits or losses on a call option use the following simple formula: Call Option Profit/Loss = Stock Price at Expiration – Breakeven Point.
What are the factors that affect the price of an option?
For example, the underlying stock moves favorably to enable high profits on an option position, but other factors, such as volatility, time decay, or dividend payment, may erode those gains in the short-term.
What is the worst strategy to follow in the case of losses in options trading?
Averaging down is one of the worst strategies to follow in the case of losses in options trading. Even though it may be very appealing, it should be avoided. Instead, it is better to close the current option position at a loss and start fresh with a new one with a longer time to expiry. Remember, options have expiry dates. After that date, they are worthless. Averaging down may suit stocks that can be held forever, but not options. Instead, averaging up may be a good strategy to explore for profit-making, provided there is sufficient time to expiry and a favorable outlook to the position continues.
What is partial profit?
Similar to the above scenario, partial profits are booked by traders at regular time intervals based on the remaining time to expiry, if the position is in profit. Options are decaying assets. A significant portion of an option premium consists of time decay value (with intrinsic value accounting for the rest). Most experienced option buyers keep a close eye on decaying time value and regularly square off positions as an option moves towards expiry to avoid further loss of time decay value while the position is in profit.
What happens if you hit the $100 target?
If the target of $100 is hit, the trailing target becomes $95 (5% lower). Suppose the uptrend continues with the price moving to $120, the new trailing stop becomes $114. A further uptrend to $150 changes the trailing stop to $142.5. Now, if the price turns around and starts going down from $150, the option can be sold off at $142.5.
Why do traders take long term positions?
Many traders also take long-term positions based on fundamentals analysis, in order to benefit from a low trading capital requirement. For example, assume you have a negative outlook about a stock leading to a long put position with two years to expiry and the target is achieved in nine months.
Is options trading volatile?
Options trading is a highly volatile game. No wonder countries like China are taking their time to open up their options market. 1 The highly volatile options market does provide enormous opportunity to profit, but attempting to do so without sufficient knowledge, clearly determined profit targets, and stop-loss methodologies will lead to failures and losses. Traders should thoroughly test their strategies on historical data, and enter the options trading world with real money with pre-decided methods on stop-losses and profit-taking.
Do options expire?
Unlike stocks that can be held for an infinite period, options have an expiry. Trade duration is limited and once missed, an opportunity may not come back again during the short lifespan of the option.
How do call option writers make profit?
A call option writer stands to make a profit if the underlying stock stays below the strike price.
How do options traders make money?
Options traders can profit by being an option buyer or an option writer. Options allow for potential profit during both volatile times, and when the market is quiet or less volatile. This is possible because the prices of assets like stocks, currencies, and commodities are always moving, and no matter what the market conditions are there is an options strategy that can take advantage of it.
Why are options important?
Options allow for potential profit during both volatile times, and when the market is quiet or less volatile. This is possible because the prices of assets like stocks, currencies, and commodities are always moving, and no matter what the market conditions are there is an options strategy that can take advantage of it.
How much does it cost to buy 10 call options?
If you buy 10 call option contracts, you pay $500 and that is the maximum loss that you can incur. However, your potential profit is theoretically limitless. So what’s the catch? The probability of the trade being profitable is not very high. While this probability depends on the implied volatility of the call option and the period of time remaining to expiration, let’s say it 25%.
What is a low risk option?
This is the most basic option strategy. It is a relatively low-risk strategy since the maximum loss is restricted to the premium paid to buy the call, while the maximum reward is potentially limitless. Although, as stated earlier, the odds of the trade being very profitable are typically fairly low. "Low risk" assumes that the total cost of the option represents a very small percentage of the trader's capital. Risking all capital on a single call option would make it a very risky trade because all the money could be lost if the option expires worthless.
What is P&L in options?
Options contracts and strategies using them have defined profit and loss—P&L—profiles for understanding how much money you stand to make or lose. When you sell an option, the most you can profit is the price of the premium collected, but often there is unlimited downside potential. When you purchase an option, your upside can be unlimited and ...
What happens when you buy options?
When you purchase an option, your upside can be unlimited and the most you can lose is the cost of the options premium. Depending on the options strategy employed, an individual stands to profit from any number of market conditions from bull and bear to sideways markets.
What factors determine the value of an option?
These include the current stock price, the intrinsic value, time to expiration or the time value, volatility, interest rates, and cash dividends paid.
What are the drivers of the price of an option?
Let's start with the primary drivers of the price of an option: current stock price, intrinsic value, time to expiration or time value, and volatility. The current stock price is fairly straightforward. The movement of the price of the stock up or down has a direct, though not equal, effect on the price of the option.
How to calculate Black Scholes model?
The model's formula is derived by multiplying the stock price by the cumulative standard normal probability distribution function. Thereafter, the net present value (NPV) of the strike price multiplied by the cumulative standard normal distribution is subtracted from the resulting value of the previous calculation.
Why does an option seller not expect to get a substantial premium?
An option seller of GE will not expect to get a substantial premium because the buyers do not expect the price of the stock to move significantly.
What are the models used to price options?
Options contracts can be priced using mathematical models such as the Black-Scholes or Binomial pricing models.
How does time value relate to options?
It is directly related to how much time an option has until it expires, as well as the volatility, or fluctuations, in the stock's price.
How much is a 30 call option?
For example, let's say General Electric (GE) stock is selling at $34.80. The GE 30 call option would have an intrinsic value of $4.80 ($34.80 - $30 = $4.80) because the option holder can exercise the option to buy GE shares at $30, then turn around and automatically sell them in the market for $34.80 for a profit of $4.80.
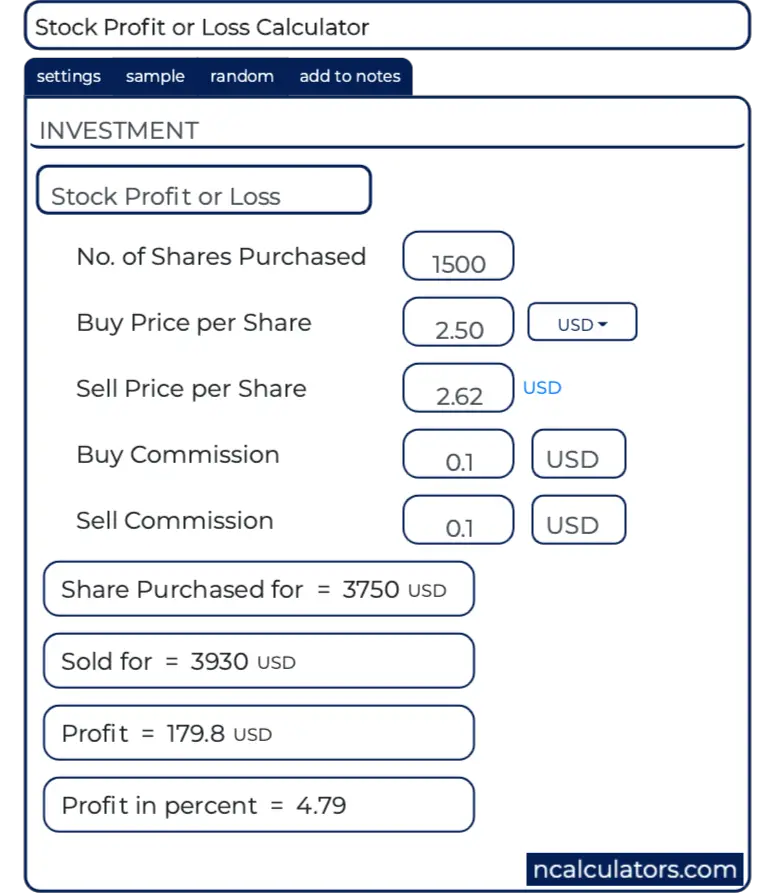
How Do You Calculate Profit on Stock?
If you want to calculate the profit on a stock, you'll need the total amount of money you used to purchase your stock and the total value of your shares at the current price. You'll also need to know any fees associated with your transactions So if you bought 10 shares of Company X at $10 each and sold them for $20 each and incurred fees of $10, you stand to walk away with a profit of $90. Put simply, $200- $100- $10 = $90. Remember that this is just the dollar value and not the percentage change.
How Do You Calculate Gain or Loss Percentage on Stock With a Calculator?
You'll need the original purchase price and the current value of your stock in order to make the calculation. Subtract the total purchase price from the current price of the stock then divide that by the original purchase price and multiply that figure by 100. This gives you the total percentage change.
What is the percentage return on a $10/share investment?
The per-share gain is $7 ($17 – $10). Thus, your percentage return on your $10/share investment is 70% ($7 gain / $10 cost).
How much is 70% return on investment?
By multiplying the percentage return on the investment (70%) by the total dollar amount invested, investors will know how much in dollar terms they have made on this investment (70% return on $1,000 is $1,700; providing a dollar gain of $700).
How to find net gain or loss in stock?
In order to find the net gain or loss of your stock holding, you will have to determine the difference between what you paid for it and ultimately what you sold it for on a percentage basis. To do so, subtract the purchase price from the current price and divide the difference by the purchase price of the stock.
Is it hard to predict a stock's gain or loss?
But it's not an exact science. There are many factors that are hard to predict, such as human emotions, overall market behavior, and global events. As such, a stock can either be a winner or a loser and depending on the outcome, an investor will have to determine the gains or losses in their portfolio. In order to find the net gain ...
How to calculate percentage of stock loss?
The calculation is simple. First, calculate gain, subtracting the purchase price from the price at which you sold your stock. Remember that if you took a loss, this number could be negative. Now, divide the gain by the original purchase price. Multiply by 100 to get a percentage that represents the change in your investment.
How to calculate capital gains?
You can subtract the cost basis from total proceeds to calculate what you’ve made. If the proceeds are greater than the cost basis , you’ve made a profit, also known as a capital gain. At this point, the government will take a slice of the pie—you’ll owe taxes on any capital gains you make.
What is a qualified dividend?
Qualified dividends that meet certain requirements are subject to the preferential capital gains tax rates. Taxpayers are responsible for identifying the type of dividends they receive and reporting that income on Form 1099-DIV.
What is capital gains tax?
Capital gains tax rates are the rates at which you’re taxed on the profit from selling your stock, in addition to other investments you may hold such as bonds and real estate. You are only taxed on a stock when you sell and realize a gain, and then you are taxed on net gain, which is the difference between gains and losses.
Why do investors want to sell stocks?
The investor may want to sell stocks and buy other investments to rebalance the portfolio, bringing it back in line with their goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
How to find out what your net gain is?
You could tally all the fees you paid and subtract that sum from your profit to find out what your net gain was. Note that your brokerage account may do these calculations for you, but you might want to know how to do them yourself to have a better understanding of how the process works.
How much tax do you pay on long term capital gains?
Long-term capital gains, on the other hand, are given preferential tax treatment. Depending on your income and your filing status, you could pay 0%, 15% or a maximum of 20% on gains from investments you’ve held for more than a year.
