How to Calculate The Cost of a Newly Issued Preferred Stock
- Convert the flotation cost percent to a decimal by dividing the number by 100. For example, a 5 percent flotation cost divided by 100 would be: 5/100=0.05
- Subtract the decimal of the flotation cost from 1. For the example: 1 – 0.05 = 0.95
- Multiply the market price for the preferred stock by one minus the flotation cost. ...
How to determine which preferred stock to buy?
Part 3 Part 3 of 3: Executing Your Trade
- Decide how many shares you want to buy. If you've followed the stock for a few weeks before making your purchase, you know the average price it's trading at ...
- Choose your order type. Since preferred stock is traded just like common stock, you have 4 ways you can place an order for the stock.
- Place your order with your broker. ...
What is the preferred stock formula?
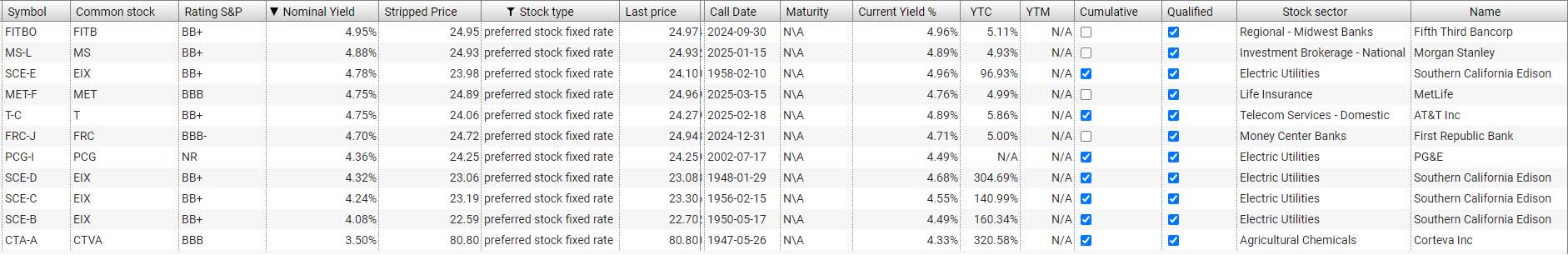
SAN FRANCISCO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--First Republic Bank (NYSE:FRC), a leading private bank and wealth management company, today announced that it has declared cash dividends on the following outstanding series of its perpetual preferred stock. A quarterly cash ...
How to find the best preferred stocks?
When looking for the best preferred stock ETFs, here are 3 key elements to keep an eye out for:
- Low expenses
- High dividend yield
- Sufficient liquidity
How much does preferred stock cost?
Generally, the dividend is fixed as a percentage of the share price or a dollar amount. This is usually a steady, predictable stream of income. If preferred stocks have a fixed dividend, then we can calculate the value by discounting each of these payments to the present day.
How to determine if you should invest in preferred stock?
If you're trying to determine whether to invest in preferred stock, compare its dividend yield to the company's bond yields and other stock issues.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stock is a type of ownership security or equity that differs from common stock in that it doesn't provide shareholders with voting rights. Preferred stock does pay a fixed dividend when the shares are issued that show up on the stock's prospectus, and that dividend must be paid before dividends from common stock.
What is the difference between common stock and preferred stock?
The main difference between common and preferred stock is that common stockholders usually have voting privileges at stockholders' meetings, while preferred stockholders do not. In most cases, owning common stock gives you one vote per the number of shares you own, although this figure varies by company.
Why are preferred stocks less risky?
Preferred stocks are less risky for investors because they're paid before common stocks if the company runs into financial trouble. As a result, preferred stockholders take priority over common shareholders, but they're still ranked behind bondholders. Even so, preferred stock is a smart investment.
How to figure out how much you make per quarter?
Once you have the decimal amount, multiply the rate by the stock's par value. To figure out how much you'll earn per quarter, simply divide the answer by four. You can then multiply the number by however many preferred stock shares you own. Although preferred stock might increase over time, this growth is limited.
Why are preferred stocks considered a stable investment?
They are considered a more stable investment because they provide a regular income stream. They can convert to a fixed number of common stock shares. How much you'll pay for a preferred stock depends on the company issuing the stock. In general, the cost is influenced by both the stock market and the preferred dividends.
Can you calculate dividends with preferred stock?
With preferred stock, you can calculate your dividends and know how much to expect at regular intervals, which isn't the case with common stock. With common stocks, the company's board of directors decide when and whether to pay out dividends. Other characteristics worth noting about preferred stocks include:
How do corporations calculate the cost of preferred stock?
They calculate the cost of preferred stock by dividing the annual preferred dividend by the market price per share. Once they have determined that rate, ...
What is Preferred Stock?
Preferred stock is a form of equity that may be used to fund expansion projects or developments that firms seek to engage in. Like other equity capital, selling preferred stock enables companies to raise funds. Preferred stock has the benefit of not diluting the ownership stake of common shareholders, as preferred shares do not hold the same voting rights that common shares do.
What is the term for the first cash flow payment after a liquidation?
Because of the nature of preferred stock dividends, it is also sometimes known as a perpetuity. Perpetuity Perpetuity is a cash flow payment which continues indefinitely.
What is unlevered cost of capital?
Unlevered Cost of Capital Unlevered cost of capital is the theoretical cost of a company financing itself for implementation of a capital project, assuming no debt. Formula, examples. The unlevered cost of capital is the implied rate of return a company expects to earn on its assets, without the effect of debt. WACC assumes the current capital
Does common equity have a par value?
However, preferred stock also shares a few characteristics of bonds, such as having a par value. Common equity does not have a par value.
Is preferred stock more valuable than common stock?
In theory, preferred stock may be seen as more valuable than common stock, as it has a greater likelihood of paying a dividend and offers a greater amount of security if the company folds.
How to find value of preferred stock?
If preferred stocks have a fixed dividend, then we can calculate the value by discounting each of these payments to the present day. This fixed dividend is not guaranteed in common shares. If you take these payments and calculate the sum of the present values into perpetuity, you will find the value of the stock.
What is preferred stock?
The owners of preferred shares are part owners of the company in proportion to the held stocks, just like common shareholders. Preferred shares are hybrid securities that combine some of the features of common stock with that of corporate bonds.
What happens to preferred shares when interest rate rises?
When the market interest rate rises, then the value of preferred shares will fall. This is to account for other investment opportunities and is reflected in the discount rate used.
What is call provision in preferred stock?
Something else to note is whether shares have a call provision, which essentially allows a company to take the shares off the market at a predetermined price. If the preferred shares are callable, then purchasers should pay less than they would if there was no call provision. That's because it's a benefit to the issuing company because they can essentially issue new shares at a lower dividend payment.
How do preferred shares differ from common shares?
Preferred shares differ from common shares in that they have a preferential claim on the assets of the company. That means in the event of a bankruptcy, the preferred shareholders get paid before common shareholders. 1
What is preferred shareholder?
In addition, preferred shareholders receive a fixed payment that's similar to a bond issued by the company. The payment is in the form of a quarterly, monthly, or yearly dividend, depending on the company's policy, and is the basis of the valuation method for a preferred share.
What is call provision in stock market?
Something else to note is whether shares have a call provision, which essentially allows a company to take the shares off the market at a predetermined price. If the preferred shares are callable, then purchasers should pay less than they would if there was no call provision.
How to calculate preferred stock value?
Here’s an easy formula for calculating the value of preferred stock: Cost of Preferred Stock = Preferred Stock Dividend (D) / Preferred Stock Price (P).
How to Calculate Par Value of Preferred Stock?
Par value of one share of preferred stock equals the amount upon which the dividend is calculated. In other words, par value is the face value of one share of stock.
What is Startup Preferred Stock?
Stock, or equity, is often one of the most critical assets in a startup. Equity can help a startup attract top talent as well as early-stage investors. In a new business, two types of stock are typically offered: common and preferred. Common stock is a share of ownership in the startup, typically accompanied by voting rights. Although preferred stock also represents ownership, it differs from common stock in two significant ways: no voting rights and preferential claims.
What is the Difference Between Common Stock and Preferred Stock?
As stated above, a common stock owner has purchased ownership in the startup along with voting rights, enabling them to vote on issues such as who will serve on the board of directors or on specific management decisions. The more ownership you have, the more significant impact your vote holds.
Why is preferred stock preferred?
Because preferred stock creates a more advantageous position for investors as it mitigates their investment risk by giving them a greater claim to the startup's assets. Investors today typically will not invest in your startup in exchange for common share ownership. They insist on preferred shares.
How does preferred stock differ from common stock?
Although preferred stock also represents ownership, it differs from common stock in two significant ways: no voting rights and preferential claims.
How does series seed financing differ from venture capital financing?
Essentially, “series seed financings differ from venture capital financings in that the special negotiated rights attached to the preferred stock sold are usually scaled back, and the documentation involved is condensed into fewer agreements.” These distinctions are important for founders to understand and use to their advantage when funding their startup.
How to calculate preferred stock price?
Divide the preferred dividend by the required rate of return. The result is the preferred stock price. This price is the highest amount you should pay per share. If you pay any more than this, you will be overpaying.
How is preferred stock calculated?
On the other hand, dividends from preferred shares are fixed and are usually larger than those from common stocks. Preferred payments are set when the shares are first issued. The price of preferred stock is calculated by using the dividend payment, par value and a required rate of return.
How to find preferred dividend?
Obtain the preferred dividend. The dividend can be found in the prospectus or provided by your stock broker. The prospectus may present the preferred dividend as a percentage rate of the par value; this is called a dividend rate. If so, multiply the rate times the par value. This will equal the preferred dividend.
Where to find the par value of preferred stock?
Obtain the original price at which the preferred stock was issued. This is called the par value and can be found in the stock's prospectus. The prospectus is located on the company website; if not, you can ask your broker to provide the information.
How to calculate preferred stock?
The following formula can be used to calculate the cost of preferred stock: Rps = Dps/Pnet. Where: Rps = cost of preferred stock. Dps = preferred dividends.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stock may also be callable or convertible, which means that the issuing company is given the option to purchase its shares back from holders (typically at a premium) or convert the shares to common stock. Calculating the cost of preferred stock. Preferred stocks are issued with a fixed par value, and they pay dividends to shareholders ...
Why do companies issue preferred stock?
Companies issue preferred stock to fund initiatives such as product development and expansion. Preferred stock is an attractive option for companies because it allows them to raise capital while limiting the control they give their shareholders.
What is stock ownership?
Stocks represent a share of ownership in a company and a right to part of the company's earnings. Companies can issue two types of stock: common stock and preferred stock.
Why is it important to understand the cost of preferred stock?
Understanding the cost of preferred stock helps companies make strategic decisions for raising capital. For example, if a company can raise money by issuing preferred stock and bonds with respective costs of 2.2% and 4.2%, then it might favor the preferred stock, which comes at a lower cost.
Do preferred stockholders get voting rights?
Unlike common stockholders, holders of preferred stock do not get voting rights, which means they have less influence over company decisions and activities. While preferred stockholders do get consistent dividend payments, companies have the right to defer those payments if they encounter financial hardships and find themselves cash-restricted.
How to calculate preferred stock price?
Multiply the market price for the preferred stock by one minus the flotation cost. For the example, a market price of $100 would yield: 100x (0.95) = 95.
How to find the cost of a newly issued preferred stock?
Multiply this result by 100 to find the cost of the newly issued preferred stock as a percent. For the example: 0.053 x 100 = 5.3 percent.
How does preferred stock differ from common stock?
Preferred stock differs from common stock since holders of preferred stock usually do not vote on company matters, but their dividends are paid to preferred investors before common shareholders'. Avoid confusing the cost of preferred stock with the price.
How to convert flotation cost to decimal?
Convert the flotation cost percent to a decimal by dividing the number by 100. For example, a 5 percent flotation cost divided by 100 would be: 5/100=0.05
What is the Cost of Preferred Stock?
The Cost of Preferred Stock represents the rate of return required by preferred shareholders and is calculated as the annual preferred dividend paid out (DPS) divided by the current market price.
Cost of Preferred Stock Overview
The recommended modeling best practice for hybrid securities such as preferred stock is to treat it as a separate component of the capital structure.
Cost of Preferred Stock Formula
The cost of preferred stock represents the dividend yield on the preferred equity securities issued.
Nuances to the Cost of Preferred Stock
Sometimes, preferred stock is issued with additional features that ultimately impact its yield and the cost of the financing.
Cost of Preferred Stock Excel Template
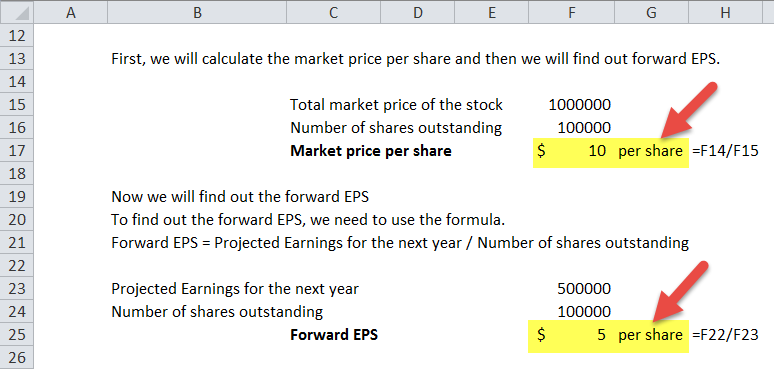
Now that we’ve defined the concept behind the cost of preferred equity, we can move on to an example modeling exercise in Excel. To access the model template, fill out the form below:
Cost of Preferred Stock Example Calculation
In our modeling exercise, we’ll be calculating the cost of preferred stock for two different dividend growth profiles:
How to calculate preferred dividend per share?
Once you know how to calculate the preferred dividend per share, you would just need to multiply the number of shares with the preferred dividend per share. And you would know how much you would get each year.
What is preferred dividend?
Preferred Dividends is a fixed dividend received from Preferred stocks. It means that if you’re a preferred shareholder, you will get a fixed percentage of dividends every year. And the most beneficial part of the preferred stock is that the preferred shareholders get a higher rate of dividend.
Why do preference shareholders have higher dividends?
The reason for this is because preference shareholders do not have ownership control over the company, hence to attract the investors, higher rates of dividends are offered to them.
What is non-cumulative preferred stock?
Non-cumulative Preferred Stocks Non-cumulative preference shares are the stocks which allow the investors to receive a fixed dividend at the pre-determined dividend rate every year. However, if any year's dividend remains unpaid, the preference shareholders are not liable to receive it in the future. read more.
What is dividends in arrears?
Dividends In Arrears Dividends in Arrears is the cumulative dividend amount that has not been paid to the cumulative preferred stockholders by the presumed date.
How much preferred dividend does Urusula get?
Urusula has invested in preferred stocks of a firm. As the prospectus says, she will get a preferred dividend of 8% of the par value of shares. The par value of each share is $100. Urusual has bought 1000 preferred stocks.
Why is preferred stock called perpetuity?
The preferred stock pays a fixed percentage of dividends. That’s why we can call it perpetuity because the dividend payment is equal and paid for an infinite period. However, a firm can choose to skip the equal payment of preferred dividends to preferred shareholders.

Unique Features of Preferred Shares
valuation Models
- If preferred stocks have a fixed dividend, then we can calculate the value by discounting each of these payments to the present day. This fixed dividend is not guaranteed in common shares. If you take these payments and calculate the sum of the present values into perpetuity, you will find the value of the stock. For example, if ABC Company pays a ...
Growing Dividends
- If the dividend has a history of predictable growth, or the company states a constant growth will occur, you need to account for this. The calculation is known as the Gordon Growth Model. V=D(r−g)V=\frac{D}{(r-g)}V=(r−g)D By subtracting the growth number, the cash flows are discounted by a lower number, which results in a higher value.
Considerations
- Although preferred shares offer a dividend, which is usually guaranteed, the payment can be cut if there are not enough earnings to accommodate a distribution; you need to account for this risk. The risk increases as the payout ratio (dividend payment compared to earnings) increases. Also, if the dividend has a chance of growing, then the value of the shares will be higher than the result …
The Bottom Line
- Preferred shares are a type of equityinvestment that provides a steady stream of income and potential appreciation. Both of these features need to be taken into account when attempting to determine their value. Calculations using the dividend discount model are difficult because of the assumptions involved, such as the required rate of return, growth, or length of higher returns. Th…