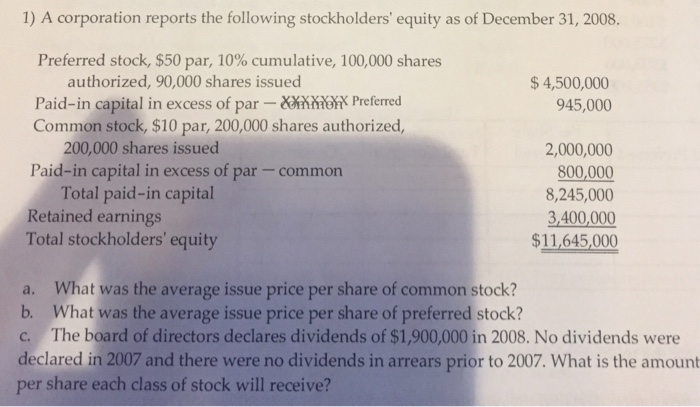
The par value of common stock for the company is simply: Par value of common stock = (Par value per share) x (Number of issued shares) The par value of issued shares often appears on the balance sheet as a line item named "common stock."
How do you calculate common stock value?
- Outstanding shares – Oustanding shares are the number of shares available to the company owners who hold a portion of the business. ...
- Treasury Shares – Treasury Shares the shares bought back by the company.
- Issued Shares – Issued shares are the total number of shares issued by the company out of the overall pool of authorized shares.
Why would a stock have no par value?
What is No-Par-Value Stock?
- Reasons for Issuing No-Par-Value Stocks. Initial Public Offering (IPO) An Initial Public Offering (IPO) is the first sale of stocks issued by a company to the public.
- Accounting Entry of Par Value and No-Par-Value Stocks. State laws may or may not require corporations to have a par value on the issued common stocks. ...
- More Resources. ...
What is the formula to calculate price per share?
- List the various prices at which you bought the stock, along with the number of shares you acquired in each transaction.
- Multiply each transaction price by the corresponding number of shares.
- Add the results from step 2 together.
- Divide by the total number of shares purchased.
How to calculate common stock outstanding from a balance sheet?
You can calculate outstanding shares by:
- Finding the company’s total number of preferred stock, common stock outstanding, and treasury stock.
- Add the number of preferred stock and common stock outstanding, then subtract the number of treasury shares from that total.
- Alternatively, you can calculate the weighted average of outstanding shares.
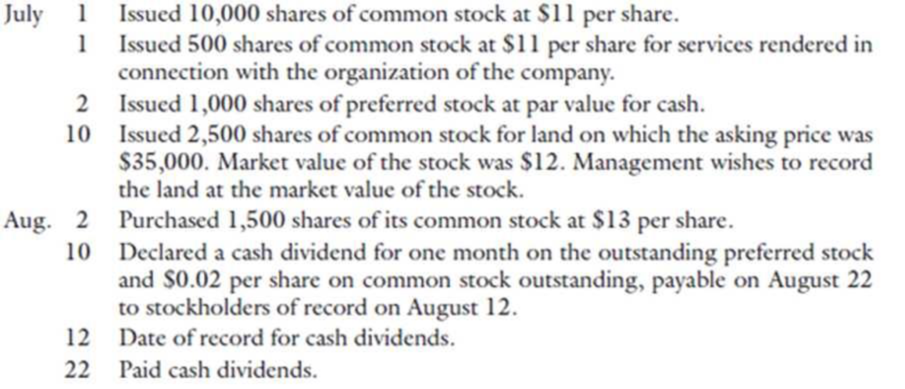
What is the par value per share of common stock?
Par Value Definition Par value of a stock refers to the face value, par or nominal value of common stock, according to Financial Dictionary. Par value of common stock formula refers to the value written on the face of the common stock certificate or in the corporation's organization or operating documents.
What is the formula to calculate par?
How do you calculate PAR inventory levels? To calculate PAR inventory levels, use the following formula: PAR level = (amount of inventory used each week + safety stock) ÷ (number of deliveries each week)
How do you find the par value on a balance sheet?
The company's par value is calculated by multiplying the par value per share by the total number of shares issued.
When common stock has a par value?
Key Takeaways. A par value for a stock is its per-share value assigned by the company that issues it and is often set at a very low amount such as one cent. A no-par stock is issued without any designated minimum value. Neither form has any relevance for the stock's actual value in the markets.
What is par value example?
For example, the par value for shares of Apple, Inc. is $0.00001 and the par value for Amazon stock is $0.01. Small corporations that intend to have only one or a few shareholders sometimes issue stock at $1 par value. If you have printed stock certificates, their par value should be printed on the certificate.
What is common stock formula?
Common Stock = Total Equity – Preferred Stock – Additional Paid-in Capital – Retained Earnings + Treasury Stock. However, in some of the cases where there is no preferred stock, additional paid-in capital, and treasury stock, then the formula for common stock becomes simply total equity minus retained earnings.
How do you find the par value in Excel?
2:173:43How To Calculate The Price Of A Bond In Excel - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe second method we'll explore involves using the present value function we type equals pv firstMoreThe second method we'll explore involves using the present value function we type equals pv first enter the rate which is 5 followed by the years to maturity.
Is par value the same as market value?
The entity that issues a financial instrument assigns a par value to it. When shares of stocks and bonds were printed on paper, their par values were printed on the faces of the shares. Market value, however, is the actual price that a financial instrument is worth at any given time for trade on the stock market.
Are face value and par value the same?
Par value refers to the "face value" of a security, and the terms are interchangeable. Par value and face value are most important with bonds, as they represent how much a bond will be worth at the time of the bond's maturity.
What does common stock $10 par mean?
Definition of Par Value (Par value can also refer to an amount that appears on bond certificates.) In the case of common stock the par value per share is usually a very small amount such as $0.10 or $0.01 and it has no connection to the market value of the share of stock.
Which best describes par value for stock?
The par value of a stock represents the market value of the stock on the date it is first issued.
What does par mean in par value?
face valuePar value, in finance and accounting, means stated value or face value. From this come the expressions at par (at the par value), over par (over par value) and under par (under par value).
What is par value in stock?
The par value of a share of common stock is its stated face value. The issuer assigns a par value when a stock is originated; it is usually quite low--$0.01 or even $0. The par value is different from the current market price of the stock. In theory, if the market price of a stock fell below the par value, the company could be liable for ...
What happens if the market price of a stock falls below the par value?
In theory, if the market price of a stock fell below the par value, the company could be liable for the difference. The shareholders' equity portion of a company's balance sheet gives information about the par value of common stock. Advertisement.
What are the sections of a balance sheet?
It should have three sections: assets, liabilities and shareholders' equity. Go to the shareholders' equity section of the balance sheet. Sometimes the company uses the term "stockholders' equity," which means the same thing.
How to calculate par value of shares?
The par value of common stock for the company is simply: Par value of common stock = (Par value per share) x (Number of issued shares)
What is par value?
The par value of a common share is an arbitrary value assigned to shares to fulfill state requirements. The par value is unrelated to the price at which the shares are first issued or their market price once they begin trading. The par value is stated in the company's articles of incorporation and figures on the paper stock certificates ...
Why do companies have a low par value?
Companies like to set a very low par value because it represents their legal capital, which must remain invested in the company and cannot be distributed to shareholders. Another reason for setting a low par value is that when a company issues shares, it cannot sell them to investors at less than par value. How does one calculate the par value of ...
Do bonds have a par value?
Bonds have a par value, of course – it's just the principal amount. However, stocks can also have a par value. Here you'll learn what that par value represents and how to calculate the company's par value of common stock for the purpose of financial accounting.
Why are common stocks listed in the equity section?
Common stocks are listed in the equity section because stocks are considered as an asset. From the total number of stocks, we can calculate the number of outstanding stocks. Outstanding stocks are stocks that are issued to the public and owned by stockholders, investors, and company members. If we deduct the number of treasury stocks ...
What is a claim on a company's assets?
The claims on a company’s assets are comprised of liability and equity. Liability includes the claims on the company’s assets by external firms or individuals. Mortgage and loans are examples of liabilities of a company.
What is equity in a company?
Equity is the claim of shareholders claims on the company assets. By purchasing stocks of the company, they have the right to claim ownership in the company. Their ownership percentage is determined by the ratio of shares owned to the total number of outstanding shares.
What happens when a company goes public?
When a company goes public from private, it offers an opportunity for investors to claim partial ownership in the company by buying its stocks. This initial offering is known as IPO and this is when the company becomes a publicly owned company.
Is equity a common stock?
Keep in mind that equity is not just comprised of common stocks. It also includes retained earnings, treasury stock, and preferred stocks. When you add up the liabilities and stockholder equity, their sum will always be equal to the total value of the company’s assets.
What is par value in stock?
Par value is the legal capital of a share of stock which must remain in the company and cannot be paid out as dividends. A company determines the par value per share of stock and prints the amount on each stock certificate.
How to calculate preferred stock?
All you have to do now is run a simple calculation: Par value of preferred stock = (Number of issued shares) x (Par value per share). So, multiply the number of shares issued by the par value per share to calculate the par value of preferred stock. In this example, multiply 1,000 by $1 to get $1,000 in par value of preferred stock.
What is par value?
Par value is the nominal or face value of a bond, share of stock, or coupon as indicated on a bond or stock certificate. The certificate is issued by the lender and given to a borrower or by a corporate issuer and given to an investor. It is a static value determined at the time of issuance and, unlike market value, it doesn’t fluctuate.
Why is par value important?
What is the Importance of Par Value? For a company issuing a bond, the par value serves as a benchmark for pricing. When the bond is traded, the market price of the bond may be above or below par value, depending on factors such as the level of interest rates.
What is interest rate?
Interest Rate An interest rate refers to the amount charged by a lender to a borrower for any form of debt given, generally expressed as a percentage of the principal. and the bond’s credit status. A bond that is trading above par is being sold at a premium and offers a coupon rate higher than the prevailing interest rates.
What is market price?
Market Price The term market price refers to the amount of money for what an asset can be sold in a market. The market price of a given good is a point of convergence. of stocks has no effect on the books, par value has a legal bind on part of the company to its investors – no shares will be sold below that price.
Why do investors pay more for bonds?
Investors will pay more, as the yield or return is expected to be higher. On the other hand, a bond that is trading below par is on a discount trade, has a lower interest rate than the current market and it is sold at a lower price.
Why do people invest in common stocks?
Investors invest in common stocks to generate income at a high rate.The advantage associated with the common stocks that holders acquire a voting right. Single stock provides one vote. Dividends are also offered to them when left. In case of bankruptcy, all preferred stockholders, bondholders, creditors get their dividends before the common stockholders. If the company does not have any dividend left after paying off all other holders, the common stockholder will get nothing. In such situations, it becomes risky to invest in common stocks. Here you will get finance assignment help from our assignment finance experts.
Why do corporations sell their shares?
A corporation sells its shares in order to make money from the individuals so that it can invest this money in the further progress of the corporation. In replacement, the company provides voting rights to the stockholders and the dividends when it is issued. In simple words, stockholders are the partial owner of the company and get dividends ...
What is preferred stock?
Preferred Stocks– When a person invests in the Preferred stocks, he or she is preferred over common stock investors in terms of getting dividends from the company. The downside of the preferred stock is that preferred stockholders do not have a right to vote.
What is dividend in accounting?
What is dividends -Dividend is a reward, money, stocks which are distributed among the shareholders of that company. Dividends are decided by the board of directors and need the approval of shareholders. Common stocks are represented in the stockholder equity section on a balance sheet.
What are the two types of stocks?
Types of Stocks– There are two types of stocks. Common Stocks. Preferred Stocks. 1. Common Stocks – An investor can purchase both types of stocks when available as both have their own privileges. But common stocks are the share that most people invest in. One share allows one vote to the buyer.
What is total equity?
Total Equity: Total Equity is the total net worth or capital of the company. When the liabilities are deducted from the assets, it gives the total equity of the company.
Can issued shares be greater than authorized shares?
The issued share cannot be greater than the authorized shares. Treasury Stocks: These stocks are never issued to the public and always keep in a company’s treasury. Outstanding Shares: Outstanding shares are the shares that are distributed between all shareholders of a company.
What is the stated value of common stock?
The stated value is what amount is assigned to a company's stock for internal accounting when there isn't any par value for the stock. This means that it's stock that hasn't been assigned a value by the charter.
Why is no par stock given out?
Common stock is given out in an effort for the company to raise money. There is no par value with no-par common stock, and it's stock's legal capital that can't be paid out in the form of dividends. A business will report all the money they've gotten from giving out no-par common stock in one account on their balance sheet to disclose how much ...
What is outstanding stock?
The stock that's owned by the investors is outstanding stock . It's been issued, but a company may buy back their own stock which will become treasury stock. This decreases how many shares are outstanding overall. If you need help with knowing how to find stated value of common stock per share, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace.
What is authorized stock?
Authorized shares are defined as shares that the charter authorized when the corporation first formed. Issued shares have been sold to investors and are authorized stock. Unissued and issued shares make up all the stock that's authorized. The stock that's owned by the investors is outstanding stock.
Is market price a stated value?
Market price and a stated value have no relation to each other. A company can decide to issue no par value stock, but need to give it a stated value for their records so they can follow the minimum requirement that the state has where it's incorporated. Since states have a law referring to par value when figuring out what ...
Is it legal to rebuy shares?
Since it's not legal for a company to rebuy shares or pay dividends if the legal capital gets impaired, having a stated value assists with giving shareholders protection of some sort.
How to calculate common stock?
The formula for common stock can be derived by using the following steps: Step 1: Firstly , determine the value of the total equity of the company which can be either in the form of owner’s equity or stockholder’s equity. Step 2: Next, determine the number of outstanding preferred stocks and the value of each preferred stock.
What is the formula for common stock?
However, in some of the cases where there is no preferred stock, additional paid-in capital, and treasury stock, then the formula for common stock becomes simply total equity minus retained earnings. It is the case with most of the smaller companies that have only one class of stock.
What is common stock?
The term “common stock” refers to the type of security for ownership of a corporation such that the holder of such securities has voting rights that can be exercised for various corporate events. Examples of such events include a selection of the board of directors or other major corporate decision.
Why is common stock important?
The common stock is very important for an equity investor as it gives them voting rights which is one of the most prominent characteristics of common stock. The common stockholders are entitled to vote on various corporate subjects which may include acquisition of another company, who should constitute the board and other similar big decisions. Usually, each common stockholder gets one vote for every share. Another striking feature of common stock is that these stocks usually outperform another form of securities, like bonds and preferred stocks, in the long run. However, common stock comes with a strong downside, that in case a company goes into bankruptcy, then the common stockholders get nothing until the creditors are fully paid off. In other words, when the company has to sell off its assets, then the cash generated from the sale will first go to the lenders, creditors, and other stakeholders, then the common stockholders are paid if anything is left. As such, common stock is another appropriate example of the trade-off between risk and returns, such that these stocks offer a higher return as they are riskier than another form of securities.
How to determine if a company has issued common stock as well as preferred stock?
If company has issued common as well as preferred stock: If a company has issued common as well as preferred stock, the amount of preferred stock and any dividends in arrears thereon are deducted from the total stockholders equity, the resulting figure is divided by the number of shares of common stock outstanding for the period.
What is book value per share?
What is book value? Book value per share of common stock is the amount of net assets that each share of common stock represents. Some stockholders have keen interest in knowing the book value of the shares they own. This article is focused on its calculation.
What is the difference between net assets and equity?
We know that: Net assets = Assets – Liabilities. Equity = Assets – Liabilities. Net assets = Equity. So an alternative and equally acceptable approach is to replace the numerator of the formula by the stockholders’ equity.
Is book value for common stock only?
Mostly, the book value is calculated for common stock only. The presence of preferred stock in the total stockholders equity, however, has a significant impact on the calculation. The formulas and examples for calculating book value per share with and without preferred stock are given below:
