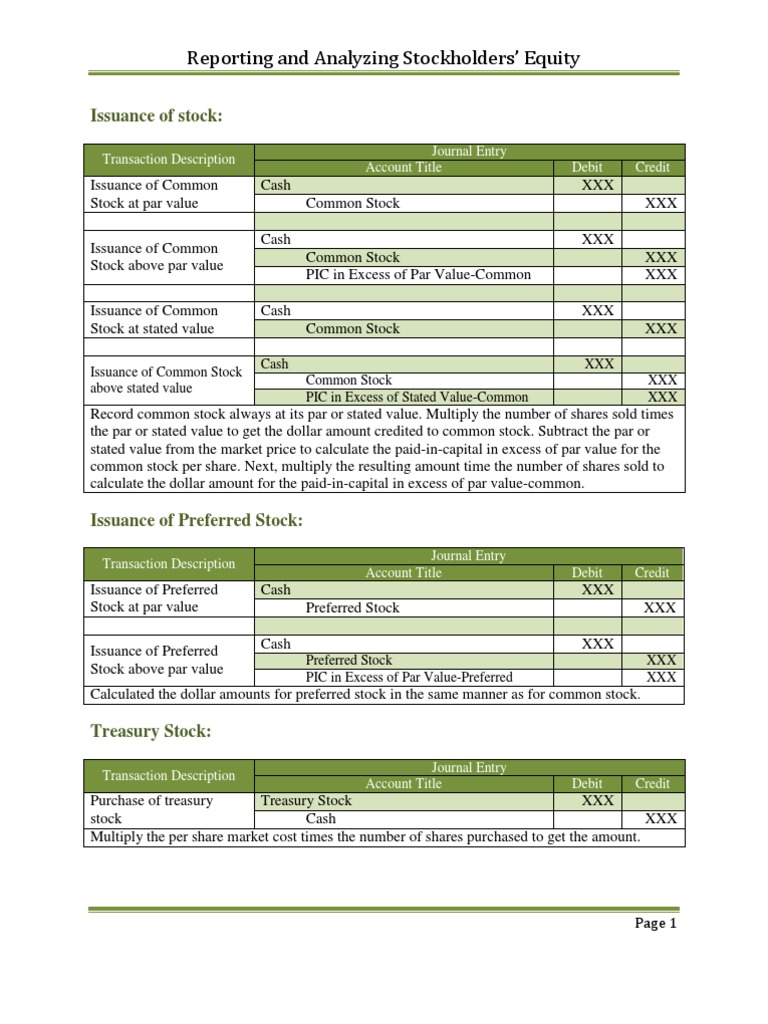
- Common stock at par = par value * number of shares issued
- Additional paid-in capital = number of shares* (amount at which shares issued – par value)
- Retained earning = Net Income – dividend
How do you calculate common stock value?
Oct 24, 2016 · Par value of common stock = (Par value per share) x (Number of issued shares) The par value of issued shares often appears on the balance sheet as a line item named "common stock." (Your broker may...
Why would a stock have no par value?
Apr 19, 2022 · Take the institution's total par value and divide that by the overall number of shares issued. The result of that calculation should be a small, even number, such as $1 or even $0.01, which is the par value. Advertisement Consider also: How to Calculate Preferred Dividends From the Balance Sheet How to Calculate Par Value
What is the formula to calculate price per share?
Book Value = Par Value + Additional Paid in Capital +Retained Earning Where, Common stock Common Stock Common stocks are the number of shares of a company and are found in the balance sheet. It is calculated by subtracting retained earnings from total equity. read more at par = par value * number of shares issued
How to calculate common stock outstanding from a balance sheet?
Dec 26, 2019 · The formula for calculating the book value per share of common stock is: Book value per share = Stockholder’s equity / Total number of outstanding common stock. For example, if there are 10,000 outstanding common shares of a company and each share has a par value of $10, then the value of outstanding share amounts to $100,000.

What is the formula in finding par value?
How is par value of common stock determined?
What does $10 par value mean?
How do you change the par value of a stock?
Step 1
Look through the company's financial statements for the balance sheet. It should have three sections: assets, liabilities and shareholders' equity. Go to the shareholders' equity section of the balance sheet. Sometimes the company uses the term "stockholders' equity," which means the same thing.
Step 2
Identify the line referring to the company's issuance of common stock. It will say something such as "book value of common shares outstanding" or "book value of common shares." This line will also provide the number of shares outstanding and the par value of the common stock, if any.
Step 3
If the par value is not explicitly stated, divide the book value of the common shares outstanding by the number of common shares outstanding. The result is the par value for one share of that company's common stock.
What is par value of shares?
What is Par value of Share? Par value of shares also known as the stated value per share is the minimal shares value as decided by the company which is issuing such shares to the public and the companies then will not sell such type of shares to the public below the decided value.
What does "no par value" mean?
That means corporations are not having any kind of legal obligations to their debt holders. Though the par value usually is so low that no par value also won’t provide much of the difference.
What is shareholder equity?
The broad classification Shareholder’s equity is that the first one is “ paid in capital. Paid In Capital Paid in Capital is the capital amount that a Company receives from investors in exchange for the stock sold in the primary market, including common or preferred stock.
Is equity a common stock?
Keep in mind that equity is not just comprised of common stocks. It also includes retained earnings, treasury stock, and preferred stocks. When you add up the liabilities and stockholder equity, their sum will always be equal to the total value of the company’s assets.
Why are common stocks listed in the equity section?
Common stocks are listed in the equity section because stocks are considered as an asset. From the total number of stocks, we can calculate the number of outstanding stocks. Outstanding stocks are stocks that are issued to the public and owned by stockholders, investors, and company members. If we deduct the number of treasury stocks ...
What is Treasury stock?
Treasury stocks are stocks that have been repurchased by the company that issued the stocks in the first place. These shares have no voting rights or dividend payments. Neither does this stock receive any assets after the company liquidates. To summarize the formula, Outstanding stocks = Issued stocks – Treasury stocks.
What happens when a company goes public?
When a company goes public from private, it offers an opportunity for investors to claim partial ownership in the company by buying its stocks. This initial offering is known as IPO and this is when the company becomes a publicly owned company.
What is a claim on a company's assets?
The claims on a company’s assets are comprised of liability and equity. Liability includes the claims on the company’s assets by external firms or individuals. Mortgage and loans are examples of liabilities of a company.
What is equity in a company?
Equity is the claim of shareholders claims on the company assets. By purchasing stocks of the company, they have the right to claim ownership in the company. Their ownership percentage is determined by the ratio of shares owned to the total number of outstanding shares.
What is a company's liability?
Liability includes the claims on the company’s assets by external firms or individuals. Mortgage and loans are examples of liabilities of a company. Equity is the claim of shareholders claims on the company assets. By purchasing stocks of the company, they have the right to claim ownership in the company.
What is par value?
Par value is the nominal or face value of a bond, share of stock, or coupon as indicated on a bond or stock certificate. The certificate is issued by the lender and given to a borrower or by a corporate issuer and given to an investor. It is a static value determined at the time of issuance and, unlike market value, it doesn’t fluctuate.
Why is par value important?
What is the Importance of Par Value? For a company issuing a bond, the par value serves as a benchmark for pricing. When the bond is traded, the market price of the bond may be above or below par value, depending on factors such as the level of interest rates.
What is an IPO?
In an initial public offering. Initial Public Offering (IPO) An Initial Public Offering (IPO) is the first sale of stocks issued by a company to the public. Prior to an IPO, a company is considered a private company, usually with a small number of investors (founders, friends, family, and business investors such as venture capitalists ...
What is interest rate?
Interest Rate An interest rate refers to the amount charged by a lender to a borrower for any form of debt given, generally expressed as a percentage of the principal. and the bond’s credit status. A bond that is trading above par is being sold at a premium and offers a coupon rate higher than the prevailing interest rates.
What is above par bond?
A bond that is trading above par is being sold at a premium and offers a coupon rate higher than the prevailing interest rates. Investors will pay more, as the yield or return is expected to be higher. On the other hand, a bond that is trading below par is on a discount trade, has a lower interest rate than the current market ...
What is market price?
Market Price The term market price refers to the amount of money for what an asset can be sold in a market. The market price of a given good is a point of convergence. of stocks has no effect on the books, par value has a legal bind on part of the company to its investors – no shares will be sold below that price.
What is a CFI?
CFI is the official provider of the global Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA) Become a Certified Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® CFI's Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® certification will help you gain the confidence you need in your finance career. Enroll today!
There's the easy way, and then there's the really easy way
The par value of a stock is an arbitrary number assigned to each share of stock when it is first sold to investors. The par value has no actual relation to the market value of each share; it's just an accounting requirement to create an initial point of reference for future accounting transactions.
Gather the needed information from balance sheet
Figuring out the par value requires a basic understanding of the balance sheet. Because par values represent legal capital, the information we need will be found in the equity section of the balance sheet, along with the other capital accounts.
Figuring out par value can be even easier than that
That math is pretty simple, but the accountants at these companies make figuring out par value even easier. They do the calculation for you.
How many ways can a stock be issued at par value?
The par value stock can be issued in three ways – at par, above par and below par. A brief explanation and journal entries for all the situations are given below:
What is par value stock?
Par value stock is a type of common or preferred stock having a nominal amount (known as par value) attached to each of its share. Par value is the per share legal capital of the company that is usually printed on the face of the stock certificate. It is also known as stated value and face value. A company is free to choose any amount as ...
What happens when stock is issued above par?
When stock is issued at a price higher than its par value, it is said to have been issued above par. When stock is issued above par, the cash account is debited with the total amount of cash received , capital stock account is credited with the total par value of shares issued and an account known as additional paid-in capital or capital in excess of par is credited with the difference between cash received and the par value of shares issued. This information is summarized in the form of the following journal entry:
What does it mean when a stock is issued below par?
When stock is issued at a price lower than its par value, it is said to have been issued below par. In such an issue, the cash account is debited with the total amount of cash received, discount on issue of capital stock account is debited with the difference between amount received and the par value of shares issued and the common stock account is credited with the par value of the shares issued. The journal entry for such an issue is given below:
What is par value in stocks?
Par value is the face value of a security. Both stocks and bonds have a par value, which is set by the issuer of the security. Par value remains fixed for the life of a security, unlike market value, which fluctuates regularly. Because it influences interest and dividend payments, it’s a key factor for understanding your return on investment in ...
What is preferred stock par value?
Par Value for Preferred Stock. It’s helpful to think of preferred stock as a hybrid of bonds and common stock. Preferred stock represents equity in a company—a portion of ownership, like common stock. In addition, though, you are entitled to fixed dividend payments, like a bond’s fixed interest payments.
Why is par value important?
Par value remains fixed for the life of a security, unlike market value, which fluctuates regularly. Because it influences interest and dividend payments, it’s a key factor for understanding your return on investment in bonds and preferred stock.
What happens when you buy a bond?
When you buy bonds, you’re lending money for a set amount of time to an issuer, like a government, municipality or corporation. The issuer promises to repay your initial investment—known as the principal—once the term is over, as well as pay you a set rate of interest over the life of the bond. The principal in a bond investment may ...
What is YTM in bond?
YTM factors in the market price of a bond, its par value as well as any interest you may earn along the way. The YTM rate is often presented as a percentage. For example, a bond’s YTM may be 10%, meaning you can expect your money to grow by 10% when you consider the interest you’ll earn as well as the return of the par value.
What is preferred stock?
It’s helpful to think of preferred stock as a hybrid of bonds and common stock. Preferred stock represents equity in a company—a portion of ownership, like common stock. In addition, though, you are entitled to fixed dividend payments, like a bond’s fixed interest payments.
Does common stock pay dividends?
In addition, common stock’s par value has no relationship to its dividend payment rate. Instead, common stock dividends are generally paid as a certain dollar value per share you own. Many people will then divide this value by the cost of a share to create its dividend yield.
What is the stated value of common stock?
The stated value is what amount is assigned to a company's stock for internal accounting when there isn't any par value for the stock. This means that it's stock that hasn't been assigned a value by the charter.
What is an unissued stock?
Unissued and issued shares make up all the stock that's authorized. The stock that's owned by the investors is outstanding stock. It's been issued, but a company may buy back their own stock which will become treasury stock. This decreases how many shares are outstanding overall. If you need help with knowing how to find stated value ...
What is outstanding stock?
The stock that's owned by the investors is outstanding stock . It's been issued, but a company may buy back their own stock which will become treasury stock. This decreases how many shares are outstanding overall. If you need help with knowing how to find stated value of common stock per share, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace.
What is authorized stock?
Authorized shares are defined as shares that the charter authorized when the corporation first formed. Issued shares have been sold to investors and are authorized stock. Unissued and issued shares make up all the stock that's authorized. The stock that's owned by the investors is outstanding stock.
What is par value?
Par value is the face value of a bond. Par value is important for a bond or fixed-income instrument because it determines its maturity value as well as the dollar value of coupon payments. The market price of a bond may be above or below par, depending on factors such as the level of interest rates and the bond’s credit status.
What is par value in equity?
In the case of equity, the par value has very little relation to the shares' market price. Some states require that companies set a par value below which shares cannot be sold. To comply with state regulations, most companies set a par value for their stocks to a minimal amount.
Why is par value important?
Par value is important for a bond or fixed- income instrument because it determines its maturity value as well as the dollar value of coupon payments. The market price of a bond may be above or below par, depending on factors such as the level of interest rates and the bond’s credit status. Par value for a bond is typically $1,000 or $100 ...
What is discount bond?
When interest rates are high, a larger proportion of bonds will trade at a discount. For example, a bond with a face value of $1,000 that is currently trading at $1,020 will be said to be trading at a premium, while another bond trading at $950 is considered a discount bond.
What is the coupon rate of a bond?
The coupon rate is the interest payments that are made to bondholders, annually or semi-annually, as compensation for loaning the issuer a given amount of money.
Is a bond a premium or discount?
They could also be issued at a premium or at a discount depending on the level of interest rates in the economy. A bond that is trading above par is said to be trading at a premium, while a bond trading below par is trading at a discount.
What is above par bond?
A bond that is trading above par is said to be trading at a premium, while a bond trading below par is trading at a discount. During periods when interest rates are low or have been trending lower, a larger proportion of bonds will trade above par or at a premium.