
How To Calculate the Implied Volatility Formula (IV) of a Stock. In plain terms, we calculate IV by taking the price of an option and putting it into a pricing model called Black-Scholes. Luckily, the video above goes over its importance when trading options.
How do you calculate IV in options trading?
With volatility, trading volume is critical. Options trading volume is typically highest for at-the-money (ATM) option contracts; thus, they are generally used to calculate IV. Once the price of the ATM options has been determined, an options pricing model can be used to determine IV.
What does IV indicate in stocks?
Keeping in mind that IV indicates the swing of movement, but not the direction, the longer the period of time before expiration, the longer the stock needs to move either in or out of the trader’s favor, making it riskier but also offering greater potential to prove profitable eventually.
How do you calculate the implied volatility Formula (IV) of a stock?
How Do You Calculate the Implied Volatility Formula (IV) of a Stock? The implied volatility formula is found by taking the price of an option and putting it into a pricing model called the Black-Scholes. Volatility measures the magnitude of change.
Does iv affect the price of options?
The answer to this question is NO. The impact of IV as explained earlier on both call options and put options is the same i.e. directly proportionate. As the IV goes up, the option prices go up irrespective of the fact that it may be a call option or a put option. This is very well demonstrated in the SAMCO Option Calculator.

What is IV of a stock?
Implied Volatility (IV) uses an option price to determine and calculate what the current market is talking about, the future volatility of the option's underlying stock. Implied volatility is one of the six essential factors used in options pricing models.
How do you calculate daily implied volatility?
Fortunately, you can convert annual to daily volatility: You would divide the annualized figure by the square root of 252 (since there are 252 trading days in a year). Don't worry, you can estimate the daily figure and just divide by 16 (you can use 15.874 if you want to be more specific).
What does IV of 50% mean?
We usually look at a time frame of one year. For example, if an underlying had an IV low of 50% and an IV high of 150%, an IV rank of 50 would mean IV was currently at 100%. If that same underlying had an IV of 50% or lower, it would have an IV Rank of 0.
What is a good stock IV?
Around 20-30% IV is typically what you can expect from an ETF like SPY. While these numbers are on the lower end of possible implied volatility, there is still a 16% chance that the stock price moves further than the implied volatility range over the course of a year.
How do you calculate implied volatility in Excel?
First, you must set all the parameters that enter option price calculation:Enter 53.20 in cell C4 (Underlying Price)Enter 55 in cell C6 (Strike Price)Cell C8 contains volatility, which you don't know. ... Enter 1% in cell C10 (Interest Rate)Enter 2% in cell C12 (Dividend Yield) ?More items...
What is the rule of 16 in options?
THE RULE OF 16 tells us how options are pricing a stock. If implied volatility—that is what the options market thinks will happen in the future—is 16, it means the stock is priced to move 1% each day until expiration. At 32%, it means a 2% move and so on.
What is a good IV for selling options?
Think of it this way: Selling options with low IV is good, selling options with mid-IV is better, and selling options with high IV is best.
Is high IV good for options?
When you see options trading with high implied volatility levels, consider selling strategies. As option premiums become relatively expensive, they are less attractive to purchase and more desirable to sell. Such strategies include covered calls, naked puts, short straddles, and credit spreads.
How do you trade with IV rank?
2:3319:42How We Use IV Rank to Determine Our Strategy | Trading FoundationsYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOkay so in a real simple way you know you can think of it if IV rank is trading at 50 percent thatMoreOkay so in a real simple way you know you can think of it if IV rank is trading at 50 percent that means it's trading in its 50th.
What stocks have the highest IV?
Top 5 stocks with greatest IV change from yesterdayStock symbol (Company name)IV Index MeanIV Index Change, %XLE (Energy Select Sector SPDR Fund)37.88%22.63%BABA (Alibaba Group Holding Ltd)69.55%21.57%JD (JD com Inc)63.51%16.66%3 more rows
What is considered high IV?
Put simply, IVP tells you the percentage of time that the IV in the past has been lower than current IV. It is a percentile number, so it varies between 0 and 100. A high IVP number, typically above 80, says that IV is high, and a low IVP, typically below 20, says that IV is low.
What makes IV go up?
IV typically gets high when the company has news or some event impending that could move the stock – I call it the event horizon – and I refer to this kind of volatility as event volatility. These stocks sometimes are called “situation” stocks.
What's implied volatility?
Implied volatility is the annual implied movement of a stock, presented on a one standard deviation (1 SD) basis. If XYZ stock has an implied volat...
Is high implied volatility good or bad?
Implied volatility being high or low is dependent on the product itself as well as whether a trader is buying option premium (with debit spreads) o...
What is a low implied volatility range?
Around 20-30% IV is typically what you can expect from an ETF like SPY. While these numbers are on the lower end of possible implied volatility, th...
How can I predict implied volatility?
Implied volatility is derived from the Black-Scholes model by entering relevant inputs and attempting to solve for IV by using options prices. One...
What does implied volatility measure?
Implied volatility measures the annual, one standard deviation range of a stock price with an accuracy of 68.2%. Since there are many expirations t...
How does implied volatility affect options prices?
Implied volatility is derived from options prices, so changes in options prices affect IV. High IV environments allow traders to collect more premi...
What is considered a low implied volatility?
Low implied volatility for a specific product depends on where the historical range has been, and we can use IV rank or IV percentile to get a bett...
What is implied volatility in stocks?
Implied volatility in stocks is the perceived price movement derived from the options market of that particular stock. Implied volatility is presen...
How does implied volatility affect delta?
Higher IV means wider expected ranges from the stock price, which means delta values are spread out much more than in a low IV environment. Think o...
Is implied volatility beneficial?
High implied volatility is beneficial to help traders determine if they want to buy or sell option premium. It also gives us an idea of how the mar...
When does IV decrease?
IV decreases when the market is bullish, and investors believe that prices will rise over time. Bearish markets are considered to be undesirable, hence riskier, to the majority of equity investors. Implied volatility does not predict the direction in which the price change will proceed.
How to determine implied volatility?
Implied volatility can be determined by using an option pricing model. It is the only factor in the model that isn't directly observable in the market. Instead, the mathematical option pricing model uses other factors to determine implied volatility and the option's premium .
What is VIX charting?
Traders and investors use charting to analyze implied volatility. One especially popular tool is the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) Volatility Index ( VIX ). Created by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), the VIX is a real-time market index. The index uses price data from near-dated, near-the-money S&P 500 index options to project expectations for volatility over the next 30 days. 1
What is implied volatility?
Implied volatility is the market's forecast of a likely movement in a security's price. Implied volatility is often used to price options contracts: High implied volatility results in options with higher premiums and vice versa. Supply/demand and time value are major determining factors for calculating implied volatility.
Why does the price of an option increase?
This is because an option's value is based on the likelihood that it will finish in-the-money (ITM).
What are the factors that affect implied volatility?
Factors Affecting Implied Volatility. Just as with the market as a whole, implied volatility is subject to unpredictable changes. Supply and demand are major determining factors for implied volatility. When an asset is in high demand, the price tends to rise.
Does the IV indicate direction of the movement?
However, as mentioned earlier, it does not indicate the direction of the movement. Option writers will use calculations, including implied volatility to price options contracts. Also, many investors will look at the IV when they choose an investment.
Determine Whether Implied Volatility Is High Or Low
Determine whether IV is high or low, rising or falling, by looking at a metrics that shows the IV rank.
Research Why Some Options Yield Higher Premiums
There will always be a reason why some options yield higher premiums due to high implied volatility. It could be a product approval, or news about a merger or acquisition.
Identifying Options With High Implied Volatility For Short Premium Strategies
After you’ve done your research, you could identify options with high implied volatility that you might consider selling. You can sell options and still be bullish or neutral.
Identifying Options With Low Implied Volatility For Long Premium Strategies
When the implied volatility is low and the premiums are low-priced, it’s typically a buyers’ market. In a low IV environment, you can consider options buying strategies such as:
What is implied volatility?
Implied volatility is one of the important parameters and a vital component of the Black-Scholes model which is an option pricing model that shall give the option’s market price or market value. Implied volatility formula shall depict where the volatility of the underlying in question should be in the future and how the marketplace sees them. ...
Can implied volatility be forecast?
However, it has to be not ed that the implied volatility will not forecast in which the direction an option is leaning towards. This implied volatility can be used to compare with historical volatility, and hence decisions can be made based on those cases. This could be the measure of risk that the trader is putting into.
Can interpolation be near implied volatility?
One can also do interpolation , which could be near to the implied volatility, and by doing this, one can get approximate nearby implied volatility. This is not simple to calculate as it requires care at every stage to compute the same.
What is implied volatility?
Implied Volatility is the expected volatility in a stock or security or asset. In simple terms, its an estimate of expected movement in a particular stock or security or asset.
What are the factors that affect the price of an option?
Implied volatility is a very important factor amongst the 5 factors which impact option prices, the others being the asset price, strike price, time to expiry for the contract and the prevalent interest rates.
What is IV in trading?
A trader can use IV to calculate an expected range for an option throughout its life. It points out the anticipated highs and lows for the option’s underlying stock and indicates potentially good entry and exit points for the trader.
What happens when the price and IV drop?
When the price and IV drop, the option is deemed more of a risk, and therefore the premium is lower. Time value is the other primary factor that affects IV. Time value is the length of time left before the option reaches its expiration date.
What is option pricing model?
Option Pricing Models Option Pricing Models are mathematical models that use certain variables to calculate the theoretical value of an option. The theoretical value of an. ; however, it can’t be calculated unless the remaining five factors are already known. Ultimately, implied volatility is important because it acts as a sort ...
How does implied volatility differ from historical volatility?
Implied volatility differs from historical volatility (HV) in that, as the latter’s name suggests, historical volatility gives insight about future movements based solely on past movements. While HV is helpful, traders typically find IV more useful because it takes into account past movements and all market expectations.
Why is implied volatility important?
It’s important to understand that for investors, implied volatility is important because it provides insight into what the market thinks about a stock’s price movement – whether the movements will be large, moderate, or small. However, IV doesn’t forecast the direction in which the movements will occur.
What are the factors that affect implied volatility?
Implied volatility is affected by many of the same factors that affect the general market. Two of the primary factors that affect IV are supply and demand. . Prices typically rise in response to assets that are in high demand. Also, prices typically fall when assets aren’t as desired.
What is VIX stock?
VIX. VIX The Chicago Board Options Exchange (C BOE) created the VIX (CBOE Volatility Index) to measure the 30-day expected volatility of the US stock market, sometimes called the "fear index". The VIX is based on the prices of options on the S&P 500 Index.
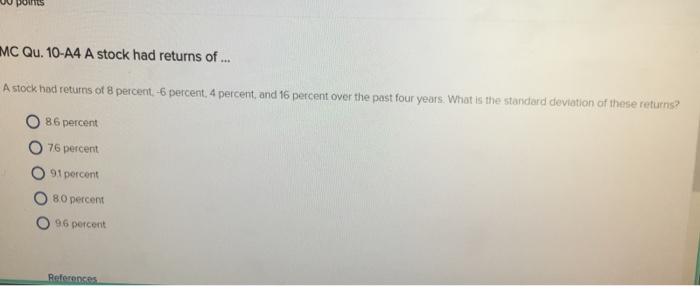
What is standard deviation in stock?
The standard deviation (volatility) of stock 1. The standard deviation of stock 2. The covariance, or relational movement, between the stock prices of stock 1 and stock 2. To calculate portfolio volatility, the logic underlying the equation is complicated, but the formula takes into account the weight of each stock in the portfolio, ...
What is portfolio volatility?
Portfolio volatility is a measure of portfolio risk, meaning a portfolio's tendency to deviate from its mean return. Remember that a portfolio is made up of individual positions, each with their own volatility measures. These individual variations, when combined, create a single measure of portfolio volatility.
Do stock prices fluctuate over time?
In actuality, stock prices and index values often have asymmetrical distributions and can stay unusually high or low for long periods of time. In addition, a stock's or index's volatility tends to change over time, which challenges the assumption of an unchanging statistical distribution of returns. While performing historical volatility ...
What is book value?
The book value usually includes equipment, buildings, land and anything else that can be sold, including stock holdings and bonds. With purely financial firms, the book value can fluctuate with the market as these stocks tend to have a portfolio of assets that goes up and down in value.
Why do stocks have high P/E?
The reason stocks tend to have high P/E ratios is that investors try to predict which stocks will enjoy progressively larger earnings. An investor may buy a stock with a P/E ratio of 30 if they think it will double its earnings every year (shortening the payoff period significantly).
Why do investors use the PEG ratio?
Because the P/E ratio isn't enough in and of itself, many investors use the price to earnings growth (PEG) ratio. Instead of merely looking at the price and earnings, the PEG ratio incorporates the historical growth rate of the company's earnings. This ratio also tells you how company A's stock stacks up against company B's stock.
Why are dividend stocks attractive?
It's always nice to have a back-up when a stock's growth falters. This is why dividend-paying stocks are attractive to many investors—even when prices drop, you get a paycheck. The dividend yield shows how much of a payday you're getting for your money. By dividing the stock's annual dividend by the stock's price, you get a percentage. You can think of that percentage as the interest on your money, with the additional chance at growth through the appreciation of the stock.
What does a PEG ratio mean?
A PEG of 1 means you're breaking even if growth continues as it has in the past.
What is the P/B ratio?
Made for glass-half-empty people, the price-to-book (P/B) ratio represents the value of the company if it is torn up and sold today. This is useful to know because many companies in mature industries falter in terms of growth, but they can still be a good value based on their assets. The book value usually includes equipment, buildings, land and anything else that can be sold, including stock holdings and bonds.
Can a stock go up without earnings?
A stock can go up in value without significant earnings increases, but the P/E ratio is what decides if it can stay up. Without earnings to back up the price, a stock will eventually fall back down. An important point to note is that one should only compare P/E ratios among companies in similar industries and markets.
What Is Implied Volatility (IV)?
How Implied Volatility (IV) Works
- Implied volatility is the market's forecast of a likely movement in a security's price. It is a metric used by investors to estimate future fluctuations (volatility) of a security's price based on certain predictive factors. Implied volatility is denoted by the symbol σ (sigma). It can often be thought to be a proxy of market risk. It is commonly e...
Implied Volatility and Options
- Implied volatility is one of the deciding factors in the pricing of options. Buying options contracts allow the holder to buy or sell an assetat a specific price during a pre-determined period. Implied volatility approximates the future value of the option, and the option's current value is also taken into consideration. Options with high implied volatility have higher premiums and vice versa. Kee…
Implied Volatility and Option Pricing Models
- Implied volatility can be determined by using an option pricing model. It is the only factor in the model that isn't directly observable in the market. Instead, the mathematical option pricing model uses other factors to determine implied volatility and the option's premium.
Factors Affecting Implied Volatility
- Just as with the market as a whole, implied volatility is subject to unpredictable changes. Supply and demandare major determining factors for implied volatility. When an asset is in high demand, the price tends to rise. So does the implied volatility, which leads to a higher option premium due to the risky nature of the option. The opposite is also true. When there is plenty of supply but no…
Pros and Cons of Using Implied Volatility
- Implied volatility helps to quantify market sentiment. It estimates the size of the movement an asset may take. However, as mentioned earlier, it does not indicate the direction of the movement. Option writers will use calculations, including implied volatility, to price options contracts. Also, many investors will look at the IV when they choose an investment. During perio…
Real-World Example
- Traders and investors use charting to analyze implied volatility. One especially popular tool is the Cboe Volatility Index (VIX). Created by the Cboe Global Markets, the VIX is a real-time market index. The index uses price data from near-dated, near-the-money S&P 500 index options to project expectations for volatility over the next 30 days.4 Investors can use the VIX to compare …