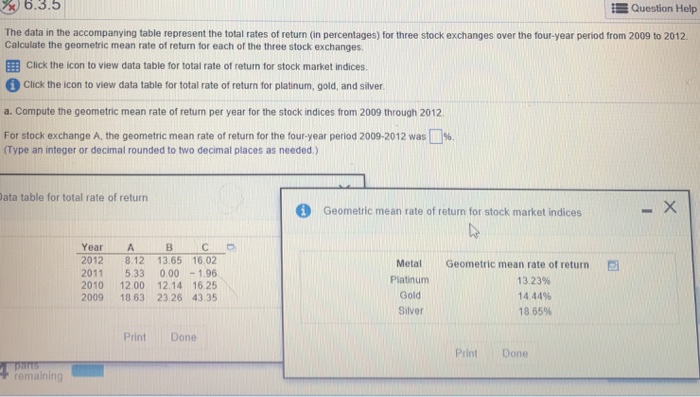
Total geometric return = (1 + Period 1) * (1 + Period 2) - 1 Geometric returns are best for analyzing periods when looking back. And because you know the time frame, and the order of returns, you can calculate a return that matches the investor's experience.
How do you calculate minimum required rate of return?
- Where RR is the required rate of return
- RFR is the risk-free rate of return
- B is the beta coefficient of the stock or asset
- RM is the expected return of the market
How to calculate the rate of return with a formula?
where:
- A = Amount (or Return) after a particular period of calculation
- P = Principal
- R = Rate of Interest
- n = Interest payment frequency
- T = Period of calculation
How do I calculate the simple rate of return?
- Time value of money. The method does not use discounting to reduce the incremental amount of net income to its present value. ...
- Cash flow. The method uses net income in the numerator of the calculation, rather than cash flows. ...
- Constant profit stream. ...
- Constraint analysis. ...
How to calculate your average annual rate of return?
What is the Annual Return Formula?
- Examples of Annual Return Formula (With Excel Template) Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of the Annual Return in a better manner. ...
- Explanation. ...
- Relevance and Use of Annual Return Formula. ...
- Annual Return Formula Calculator
- Recommended Articles. ...
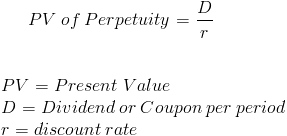
How do you calculate geometric mean growth rate?
The geometric mean is the average growth of an investment computed by multiplying n variables and then taking the nth –root....Future value = E*(1+r)^n Present value = FV*(1/(1+r)^n)E = Initial equity.r = interest rate.FV = Future value.n = number of years.
How do you calculate geometric rate of return in Excel?
For example, given two numbers, 4 and 9, the long-hand calculation for the geometric mean is 6:=(4*9)^(1/2) =(36)^(1/2) =6.=GEOMEAN(4,9) // returns 6.=(4+9)/2=6.5.=GEOMEAN(D6:D10)-1.
What is the formula for calculating geometric mean?
Basically, we multiply the numbers altogether and take the nth root of the multiplied numbers, where n is the total number of data values. For example: for a given set of two numbers such as 3 and 1, the geometric mean is equal to √(3×1) = √3 = 1.732.
What is the geometric rate?
Geometric growth rates may take the form of annual growth rates, quarter-on-previous quarter growth rates or month-on-previous month growth rates. The geometric growth rate is applicable to compound growth over discrete periods, such as the payment and reinvestment of interest or dividends.
What is geometric return?
The geometric mean return formula is used to calculate the average rate per period on an investment that is compounded over multiple periods. The geometric mean return may also be referred to as the geometric average return.
Is CAGR the same as geometric mean?
In finance, geometric mean is used to calculate the rates of annual growth of an asset. The compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) is the same as the geometric mean of the growth of an asset over time.
How do you do geometric?
0:006:32Geometric Sequence Formula - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBut what makes it geometric is that you're multiplying by the same ratio. The same number to get toMoreBut what makes it geometric is that you're multiplying by the same ratio. The same number to get to the next term.
How do you calculate GM of a ship?
GM - Metacentric Height: This measurement is calculated by subtracting KG from KM (GM = KM - KG). GM is a measure of the ship's initial stability.
How are weighted and geometric mean calculated?
You apply an exponent to each element in the data set that equals the weight of the element. You then multiply these values together and raise to a power equal to one divided by the sum of the weights.
What is a Geometric Average Return?
The Geometric Average Return is a rate of return that is calculated by taking the product of all rates and then setting it to the 1/nth power. This...
Why is Geometric Average Return useful?
The Geometric Average Return is useful for comparing different investment options without the need to know the value of each. It also provides an “...
What are the differences between the arithmetic mean return and Geometric Average Return?
The main difference is that the arithmetic mean return will overstate the average rate of return when compounding occurs. This means that it does n...
When should I use the Geometric Average Return?
The Geometric Average Return is best used over several years where there are periods of compounding. It’s not suitable for short-term investment pr...
How is the Geometric Average Return calculated?
The Geometric Average Return can be found using a specific calculator or Excel spreadsheet. The calculation requires that the term values are multi...
Geometric Mean Return
The geometric mean return, also called the geometric average return, is a way to calculate the average compounding rate of return on the investments. It considers the compound interests multiplied by the interest over the number of periods.
Geometric Average Return Formula
The most commonly used formula to calculate the Geometric Average Return is −
Geometric Average Return Analysis
The geometric mean is called by many names, such as the compounded annual growth rate (CAGR), the geometric average, or the time-weighted rate of return (TWRR). It represents the rate of the average return for a set of values.
Understanding Geometric Average Return
In statistical and business terms, a geometric average return (a.k.a. geometric mean return) represents the rate of return on investment per year, averaged over a specified time period.
Geometric Average vs. Arithmetic Average
Imagine you put $500 into zero-coupon bonds for one year with 6% interest. You take this profit and reinvest at 14% for the next year. How can you calculate what your average return is for the two years together?
Recognizing the Difference
The gap between geometric average and arithmetic average may appear negligible in this example (but 8 basis points can sometimes be very significant). Actually, the two outcomes would be identical if r 1 = r 2 = ... r n.
How to calculate the average rate of return using geometric mean return?
Geometric mean return is a more complicated method of calculating the average rate, but it’s more accurate than the arithmetic one. It is calculated as:
Geometric mean return and arithmetic mean return
Geometric mean return will always be a bit lower than the arithmetic one. Arithmetic mean return is a simpler and less accurate method because it doesn’t take compounding into account. It’s calculated by dividing the sum of returns for each period by the total number of periods.
Why is geometric mean return important?
Geometric mean return is a method that allows us to calculate the average rate of return on investment (or portfolio). The main advantage of this method is the fact, that we don’t have to know the original principal amount, geometric mean return method is completely focused on the rate of return.
What is geometric mean?
Geometric mean, sometimes referred to as compounded annual growth rate or time-weighted rate of return, is the average rate of return of a set of values calculated using the products of the terms. What does that mean? Geometric mean takes several values and multiplies them together and sets them to the 1/nth power.
Why is geometric mean important?
Geometric mean is an important tool for calculating portfolio performance for many reasons, but one of the most significant is it takes into account the effects of compounding .
Can the arithmetic mean be used as a quick and dirty estimate of the actual annual return?
First, if the return variance is small from year to year, then the arithmetic mean can be used as a quick and dirty estimate of the actual average annual return. Second, if there is great variation each year, then the arithmetic average will overstate the actual average annual return by a large amount.
Is the geometric mean easy to use?
Arithmetic mean is easy to use, quick to calculate, and can be useful when trying to find the average for many things in life. However, it is an inappropriate metric to use to determine the actual average return of an investment . The geometric mean is a more difficult metric to use and understand. However, it is an exceedingly more useful tool ...
What is rate of return?
What is a Rate of Return? A Rate of Return (ROR) is the gain or loss of an investment over a certain period of time. In other words, the rate of return is the gain. Capital Gains Yield Capital gains yield (CGY) is the price appreciation on an investment or a security expressed as a percentage. Because the calculation of Capital Gain Yield involves ...
What is the basis point of interest rate?
It only takes into account its assets. Basis Points (bps) Basis Points (BPS) Basis Points (BPS) are the commonly used metric to gauge changes in interest rates . A basis point is 1 hundredth of one percent.
How to find geometric mean?
To calculate the geometric mean return, we follow the steps outlined below: 1 First, add 1 to each return. The trick is to avoid problems posed by negative values. 2 Multiply all the returns in the sequence. 3 Raise the product to the power of 1 divided by the number of returns ‘n’. 4 Finally, subtract 1 from the final result
Is geometric return better than arithmetic return?
In conclusion, the geometric return is always a better measure of investment performance when compared to the arithmetic return, unless there is no volatility of returns. Then, the difference between the arithmetic mean return and the geometric mean return increases as the volatility increases. Reading 7 LOS 7m.
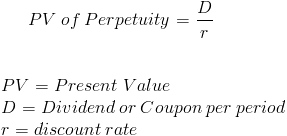
Understanding Geometric Average Return
Geometric Average vs. Arithmetic Average
- Imagine you put $500 into zero-coupon bonds for one year with 6% interest. You take this profit and reinvest at 14% for the next year. How can you calculate what your average return is for the two years together? The simple way of doing this is to average out the interest rates for the two years, i.e. 6% + 14% = 20%, divided by two years = 10%. How...
Recognizing The Difference
- The gap between geometric average and arithmetic average may appear negligible in this example (but 8 basis points can sometimes be very significant). Actually, the two outcomes would be identical if r1 = r2 = ... rn. Nevertheless, should r1 and rnbe substantially different, we can get substantial variations in the results produced by the two methods.