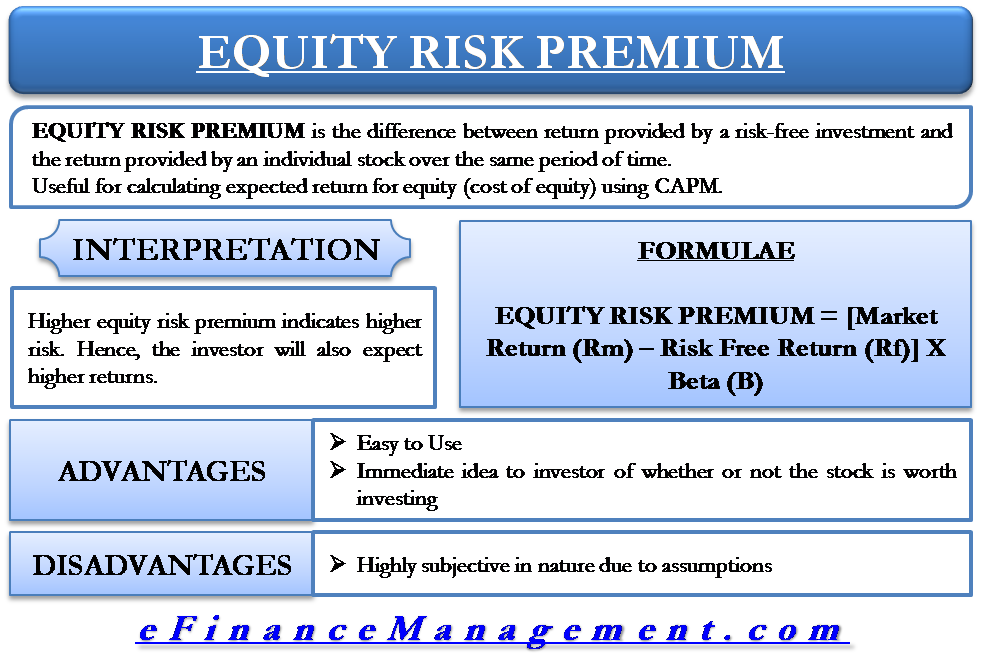
To find the expected return, plug the variables into the CAPM
Capital asset pricing model
In finance, the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) is an empirical model used to determine a theoretically appropriate required rate of return of an asset, if that asset is to be added to an already well-diversified portfolio, given that asset's non-diversifiable risk.
How do you calculate beta from market rate of return?
Multiply the beta value by the difference between the market rate of return and the risk-free rate. For this example, we'll use a beta value of 1.5. Using 2 percent for the risk-free rate and 8 percent for the market rate of return, this works out to 8 - 2, or 6 percent.
How to calculate the expected rate of return on a stock?
To calculate the expected rate of return on a stock, you need to think about the different scenarios in which the stock could see a gain or loss. For each scenario, multiple that amount of gain or loss (return) by the probability of it happening.
How does beta affect a stock's returns?
A stock with a low beta won't lose as much as the S&P when it falls, but it won't gain as much as the S&P when it posts gains. On the other hand, a stock with a beta over 1 will lose more than the S&P when it falls but will also gain more than the S&P when it posts a gain. For example, pretend Vermeer's Venom Extraction has a beta of .5.
How risky is a stock with a beta of 1?
If you make your beta calculations and find out the stock you're analyzing has a beta of 1, it won't be any more or less risky than the index you used as a benchmark. The market goes up 2%, your stock goes up 2%; the market goes down 8%, your stock goes down 8%.

How do you calculate the expected return of a stock?
An expected return is calculated by multiplying potential outcomes by the odds of them occurring and then totaling these results. Expected returns cannot be guaranteed. The expected return for a portfolio containing multiple investments is the weighted average of the expected return of each of the investments.
How do you calculate beta with market return and risk-free rate?
Subtract the risk-free rate from the market (or index) rate of return. If the market or index rate of return is 8% and the risk-free rate is again 2%, the difference would be 6%. Divide the first difference above by the second difference above. This fraction is the beta figure, typically expressed as a decimal value.
How do you calculate risk-free expected return?
To calculate the real risk-free rate, subtract the inflation rate from the yield of the Treasury bond matching your investment duration.
How do you calculate expected return in CAPM?
The expected return, or cost of equity, is equal to the risk-free rate plus the product of beta and the equity risk premium.
How do you calculate expected return in beta?
Expected return = Risk Free Rate + [Beta x Market Return Premium] Expected return = 2.5% + [1.25 x 7.5%]
How is risk-free rate of return calculated using CAPM?
It is calculated by dividing the difference between two Consumer Price Indexes(CPI) by previous CPI and multiplying it by 100.
What will happen to the expected return on a stock with a beta of 1.5 and a market risk premium of 9% if the Treasury bill increases from 3% to 5%?
The S&P 500 would be expected to yield about 17.00%. What will happen to the expected return on a stock with a beta of 1.5 and a market risk premium of 9% if the Treasury bill yield increases from 3 to 5%? A. The expected return will remain unchanged.
What is the expected return of a zero beta security?
A zero-beta portfolio would have the same expected return as the risk-free rate. Such a portfolio would have zero correlation with market movements, given that its expected return equals the risk-free rate or a relatively low rate of return compared to higher-beta portfolios.
How do you use CAPM to value stock?
To calculate the value of a stock using CAPM, multiply the volatility, known as “beta“, by the additional compensation for incurring risk, known as the “Market Risk Premium”, then add the risk-free rate to that value.
Is CAPM expected return?
The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) describes the relationship between systematic risk and expected return for assets, particularly stocks. 1 CAPM is widely used throughout finance for pricing risky securities and generating expected returns for assets given the risk of those assets and cost of capital.
What is the relationship of risk and return as per CAPM?
The CAPM contends that the systematic risk-return relationship is positive (the higher the risk the higher the return) and linear. If we use our common sense, we probably agree that the risk-return relationship should be positive.
What is expected return theory?
that can take any values within a given range. The expected return is based on historical data, which may or may not provide reliable forecasting of future returns. Hence, the outcome is not guaranteed.
Is expected return a predictor of stock performance?
Although not a guaranteed predictor of stock performance, the expected return formula has proven to be an excellent analytical tool that helps investors forecast probable investment returns and assess portfolio risk and diversification.
How to calculate expected return on stock?
Follow these steps to calculate a stock’s expected rate of return in Excel: 1. In the first row, enter column labels: 2. In the second row, enter your investment name in B2, followed by its potential gains and probability of each gain in columns C2 – E2*. 3.
What is the rate of return?
The money that you earn on an investment is known as your return. The rate of return is the pace at which money is earned or lost on an investment. If you’re going to invest, you may want to consider how much money that investment is likely to earn you.
What is systemic risk?
All investments are subject to pressures in the market. These pressures, or sources of risk, can come in the form of systematic and unsystematic risk. Systematic risk affects an entire investment type. Within that investment category, it probably can’t be “diversified” away.
What is required rate of return?
The required rate of return is a concept in corporate finance. It’s the amount of money, or the proportion of money received back from the money invested, that a project needs to generate in order to be worth it for the investor or company doing it.
Why is compound annual growth rate useful?
This can be useful because it’s a way of comparing investments over annual timespans.
Why is the real rate of return negative?
This matters because the reason to invest in assets like stocks, bonds, property and so on is to generate money to buy things — and if the cost of things is going up faster than the rate of return on your investment, then the “real” rate of return is actually negative.
Is historical data predictive?
That said, investors may want to be leery of extrapolating past returns for the future. Historical data is a guide, it’s not necessarily predictive.
What is risk free rate?
Hence, the risk-free rate as well is required to be brought to the same real terms, which is basically inflation-adjusted for the economy. Since the rate is mostly the long term government bonds – they are adjusted to the rate of inflation factor and provided for further use.
Is the interest rate on a zero-coupon bond a proxy?
Therefore, the interest rate on zero-coupon government securities like Treasury Bonds, Bills, and Notes, are generally treated as proxies for the risk-free rate of return.
Is the rate of return higher in India?
The rate of return in India for the government securities is much higher than compared to the U.S. rates for the U.S. Treasury. The availability of such securities is easily accessible as well. It is factored by the growth rate of each economy and the stage of development at which each stand.
Is risk free rate inflation adjusted?
The various applications of the risk-free rate use the cash flows that are in real terms. Hence, the risk-free rate as well is required to be brought to the same real terms, which is basically inflation-adjusted for the economy. Since the rate is mostly the long term government bonds – they are adjusted to the rate of inflation factor ...
What is beta coefficient?
The Beta coefficient is a measure of sensitivity or correlation of a security. Marketable Securities Marketable securities are unrestricted short-term financial instruments that are issued either for equity securities or for debt securities of a publicly listed company. The issuing company creates these instruments for the express purpose ...
What are the drawbacks of beta?
The largest drawback of using Beta is that it relies solely on past returns and does not account for new information that may impact returns in the future. Furthermore, as more return data is gathered over time, the measure of Beta changes, and subsequently, so does the cost of equity.
What is the benefit of using beta coefficient?
Advantages of using Beta Coefficient. One of the most popular uses of Beta is to estimate the cost of equity (Re) in valuation models. The CAPM estimates an asset’s Beta based on a single factor, which is the systematic risk of the market.
What is systematic risk?
Systematic Risk Systematic risk is that part of the total risk that is caused by factors beyond the control of a specific company or individual. Systematic risk is caused by factors that are external to the organization. All investments or securities are subject to systematic risk and therefore, it is a non-diversifiable risk.
What is beta in stock market?
Learn more... Beta is the volatility or risk of a particular stock relative to the volatility of the entire stock market. Beta is an indicator of how risky a particular stock is, and it is used to evaluate its expected rate of return.
How to calculate the return of a stock?
Begin calculating returns for the stock market index. 1 Since return is a calculation over time, you won't put anything in your first cell; leave it blank. You need at least two data points to calculate returns, which is why you'll start on the second cell of your index-returns column. 2 What you're doing is subtracting the more recent value from the older value and then dividing the result by the older value. This just gives you the percent of loss or gain for that period. 3 Your equation for the returns column might look something like this: = (B4-B3)/B3
What does it mean when the beta is lower than 1?
The risk of an index is fixed at 1. A beta of lower than 1 means that the stock is less risky than the index to which it's being compared. A beta of higher than 1 means the stock is more risky than the index to which it's being compared.
How to interpret beta?
Know how to interpret beta. Beta is the risk, relative to the stock market as a whole, an investor assumes by owning a particular stock. That's why you need to compare the returns of a single stock against the returns of an index. The index is the benchmark against which the stock is judged. The risk of an index is fixed at 1. A beta of lower than 1 means that the stock is less risky than the index to which it's being compared. A beta of higher than 1 means the stock is more risky than the index to which it's being compared.
What is beta analysis?
Beta analyzes a stock's volatility over a set period of time, without regard to whether the market was on an upswing or downswing. As with other stock fundamentals, the past performance it analyzes is not a guarantee of how the stock will perform in the future. Thanks!
What does it mean when the beta is negative?
Usually the rates of return are figured over several months. Either or both of these values may be negative, meaning that investing in the stock or the market (index) as a whole would mean a loss during the period. If only one of the two rates is negative, the beta will be negative.
How many data points do you need to calculate returns?
You need at least two data points to calculate returns, which is why you'll start on the second cell of your index-returns column. What you're doing is subtracting the more recent value from the older value and then dividing the result by the older value.
Is expected return a prediction?
Expected return is just that: expected. It is not guaranteed, as it is based on historical returns and used to generate expectations, but it is not a prediction.
Do expected returns take volatility into account?
For instance, expected returns do not take volatility into account. Securities that range from high gains to losses from year to year can have the same expected returns as steady ones that stay in a lower range.
Can expected returns be dangerous?
So it could cause inaccuracy in the resultant expected return of the overall portfolio. Expected returns do not paint a complete picture, so making investment decisions based on them alone can be dangerous. For instance, expected returns do not take volatility into account.