- Find the company's annual dividends using MarketBeat.
- If a company's dividends aren't annual, multiply the dividend per period by the number of payments in a year in order to find the annual dividends.
- Use MarketBeat to determine the share price.
- Use the formula, Dividend Yield = Current Annual Dividend Per Share/Current Stock Price, to get the dividend yield. What can the dividend yield tell ...
How to calculate the performance of stock that has dividends?
- Final Value ($): The value of the investment on the 'Ending Date'.
- Annual Return: Our estimate to the annual percentage return by the investment, including dollar cost averaging. (Also see our compound annual growth calculator)
- Graph: The value of the stock investment over time. ...
What is the average dividend yield?
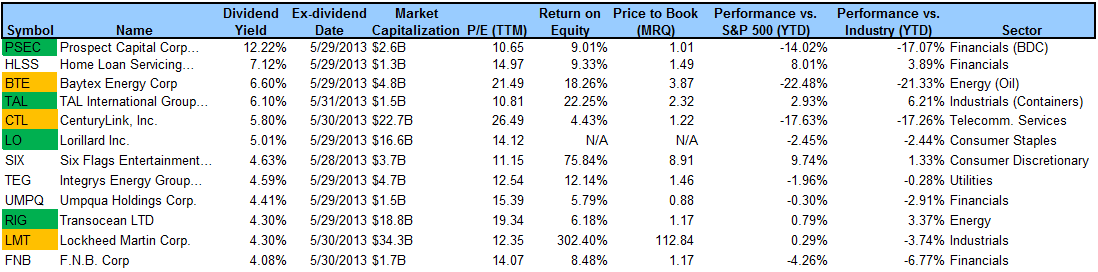
Moreover, the dividend yield at this level is probably unsustainable. Morningstar shows that in the trailing 12 months (TTM), the average dividend yield has been 5.71%. If we divide the ongoing ...
What is the formula for dividend yield ratio?
The average dividend yield for several industries is as follows:
- Basic materials industry: 4.92%
- Financial services industry: 4.17%
- Healthcare industry: 2.28%
- Industrial industry: 1.76%
- Services industry: 2.37%
- Technology industry: 3.2%
- Utility industry: 3.96%
How to calculate CAGR of stocks?
To calculate the CAGR of an investment:
- Divide the value of an investment at the end of the period by its value at the beginning of that period.
- Raise the result to an exponent of one divided by the number of years.
- Subtract one from the subsequent result.

What is a good dividend yield for a stock?
2% to 4%What is a good dividend yield? In general, dividend yields of 2% to 4% are considered strong, and anything above 4% can be a great buy—but also a risky one. When comparing stocks, it's important to look at more than just the dividend yield.
What is the formula to calculate dividends?
Here is the formula for calculating dividends: Annual net income minus net change in retained earnings = dividends paid.
What is dividend yield example?
The dividend yield is a financial ratio that tells you the percentage of a company's share price that it pays out in dividends each year. For example, if a company has a $20 share price and pays a dividend of $1 per year, its dividend yield would be 5%.
What is dividend yield calculator?
In short, dividend yield calculates the rupee amount of a company's current annual dividend per share divided by its current stock price. For example, a company with a stock price of Rs. 100 and paying dividend of Rs. 4 per share, has a dividend yield of 4%.
How to calculate dividend yield?
To calculate dividend yield, all you have to do is divide the annual dividends paid per share by the price per share. Dividend Yield = Annual Dividends Paid Per Share / Price Per Share. For example, if a company paid out $5 in dividends per share and its shares currently cost $150, its dividend yield would be 3.33%.
What is dividend in stock?
What Is a Dividend? A dividend is a portion of a company’s profits that it distributes to shareholders. Dividends are paid out in addition to any gains in the value of the company’s shares and reward shareholders for holding a stock.
Why is absolute dividend a less helpful metric?
The absolute dividend amount you receive per share is a less helpful metric because companies have widely varying stock prices.
How often do companies pay dividends?
Companies might pay special, one-time dividends, or they may pay dividends at regular intervals, such as every quarter or once a year. One of the big advantages of preferred stock is that it dependably pays regular dividends, although common stock may also pay out regular dividends.
Do dividends fluctuate?
Companies generally pay out dividends based on the number of shares you own, not the value of shares you own, though. Because of this, dividend yields fluctuate based on current stock prices. Many stock research tools list recent dividend yields for you, but you can also calculate dividend yield yourself.
What is dividend in stocks?
A dividend is a portion of a company’s profit that is paid back to shareholders. In most cases, companies that issue a dividend are financially stable. Many of these companies are in mature industries and have stable, predictable revenue and earnings. Utility stocks and consumer discretionary stocks are good examples of companies ...
Why is dividend yield a trap?
A dividend yield trap occurs when the stock of a company falls faster than its earnings. This will make its yield look more attractive than it really is. Here’s why it’s a trap. Let’s say you buy the stock at its low price and then the company cuts its dividend. Now, investors may start to sell off even more, lowering the share price which means you’ve lost capital growth and are looking at a lower yield.
What is the dividend yield of Company B?
However, Company B was able to increase its annual dividend from $1.50 to $1.75. Now its dividend yield is 3.5%. This means investors will have to look at other factors to decide which company’s stock is better to own. For example, maybe analysts are projecting that Company A will raise its dividend later in the year.
What is dividend payout ratio?
The payout ratio is the amount of a company’s net income that goes towards dividends.
What does it mean when a company projects a dividend increase?
If the company is expecting growth in earnings and revenue, they may project a dividend increase. If the company is expecting slowing and/or declining earnings and revenue, they may project keeping the dividend the same.
How often do companies pay dividends?
Companies typically pay dividends quarterly (i.e. four times per year) or annually (once a year). When a company delivers its earnings report to shareholders, it usually provides guidance about the direction of the dividend. If the company is expecting growth in earnings and revenue, they may project a dividend increase.
Can dividend stocks grow in a bull market?
However, although dividend stocks are traditionally lumped into the “value” category, many of these companies can generate significant capital growth, particularly in a bull market. One of the distinctions, however, is the ability of these companies to pay a dividend in a bear market.
Dividend Yield: A Critical Measure of Income Investing
First, we will look at what is a dividend, and some of the advantages of buying stocks for dividends, then we will take a close look at the Dividend Yield and how to calculate it.
What is a Dividend?
Of the 6000+ stocks currently available to purchase on the major U.S. indexes, circa 2800 companies currently offer a dividend payout.
What is Dividend Yield?
The dividend yield is essentially the “Percentage Payment you will receive from the company whose shares you hold in relation to the price you paid for the stock.”
Example: How to Calculate Dividend Yield?
Here is an example of the Dividend Yield. I own 1000 shares of ABC Company at the cost of $10 per share; this equals $10,000 invested.
5 Critical Lessons on the Inverse Relationship of Dividend Yield vs. Stock Price
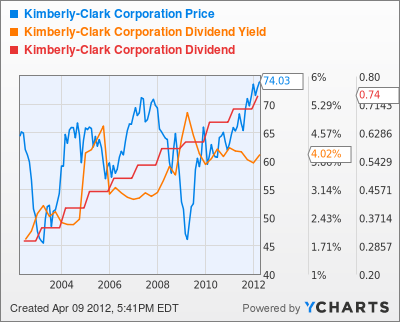
What most people do not understand is the inverse relationship between dividend yield and the stock price. As a stock price goes down, the dividend yield goes up.
How to Get the Best Yields on Great Stocks
As we have seen, during the last 13 years, the dividend yield on MSFT has varied between 1% in 2005 and over 3% in 2013. That is a dividend income difference of 300%.
3 Bonus Rules of Dividend Payments on Long-Term Investments in Successful Companies
The historical benefit of dividend yield should not be underestimated.
How to calculate dividend yield?
Dividend yield is shown as a percentage and calculated by dividing the dollar value of dividends paid per share in a particular year by the dollar value of one share of stock. 2
What is dividend yield?
Dividend yield is a method used to measure the amount of cash flow you're getting back for each dollar you invest in an equity position. In other words, it's a measurement of how much bang for your buck you're getting from dividends. The dividend yield is essentially the return on investment for a stock without any capital gains.
Do technology stocks turn up on stock screens?
If you're looking for high-growth technology stocks, they're not likely to turn up in any stock screens you might run looking for dividend-paying characteristics. However, if you're a value investor or looking for dividend income, a couple of measurements are specific to you.
Is dividend yield good?
A good dividend yield can be a good measure when evaluating stocks for investment purposes. But it doesn't always mean a strong company. Look beyond the number at just one moment in time and be sure to look at the industry and the company's dividend yield over an extended period.
What is dividend yield?
The dividend yield formula is used to determine the cash flows attributed to an investor from owning stocks or shares in a company. Therefore, the ratio shows the percentage of dividends for every dollar of stock.
What is dividend per share?
Dividend per share#N#Dividend Per Share (DPS) Dividend Per Share (DPS) is the total amount of dividends attributed to each individual share outstanding of a company. Calculating the dividend per share#N#is the company’s total annual dividend payment, divided by the total number of shares outstanding
Is a high yield ratio good or bad?
Therefore, the yield ratio does not necessarily indicate a good or bad company.
What does dividend yield mean?
A stock's dividend yield tells you how much dividend income you receive, compared to the current price of the stock. Buying stocks with a high dividend yield can provide a good source of income, but there are other factors to take into account.
What is dividends?
A dividend is how a firm returns profits directly to its shareholders. 1 Companies aren't required to issue dividends, so there isn't a set rule about which will and which ones won't. Even if a company has issued dividends in the past, it may stop at any time.
Why do dividend stocks decrease in value?
During a recession or other times of hardship, dividend-paying stocks can quickly decrease in value, because there is a risk that the firm will reduce payouts in the future. If a company says that it's cutting its dividend, the stock price will react right away.
What to do if you don't want to study stocks?
If you don't want to study and purchase individual stocks, you can invest in a dividend income fund instead. These funds allow you to diversify your portfolio while letting experts make the hard choices about which stocks to buy and when to buy them.
Is a company required to pay dividends to the people who own its stock?
4 On the other hand, a company is not required to pay a dividend to the people who own its stock.
Why is trailing dividend yield used?
This figure is properly referred to as a trailing dividend yield because it uses historical dividend payments. However, it is more popular to quote a stock’s indicated dividend yield which uses the current dividend rate instead of the historical one.
Do dividend yields vary?
Usually the three different yields don’t vary much. But they can vary dramatically when the dividend has changed, or is expected to change, in a big way. For instance, a company might have recently announced that it will eliminate its dividend.
Can dividends go up or down?
Naturally, dividends can change with little notice. They may happily go up, or possibly go down, depending on the circumstances. It’s one of the risks, and potential rewards, investors face. The yield quoted today may not be the one investors actually receive.
What is dividend yield?
The dividend yield, expressed as a percentage, is a financial ratio (dividend/price) that shows how much a company pays out in dividends each year relative to its stock price. The reciprocal of the dividend yield is the price/dividend ratio.
Why is dividend yield increasing?
If a company’s dividend yield has been steadily increasing, this could be because they are increasing their dividend, because their share price is declining, or both. Depending on the circumstances, this may be seen as either a positive or a negative sign by investors.
What is dividend payout ratio?
However, the dividend payout ratio represents how much of a company's net earnings are paid out as dividends. While the dividend yield is the more commonly used term, many believe the dividend payout ratio is a better indicator of a company's ability to distribute dividends consistently in the future. The dividend payout ratio is highly connected ...
Why is a strong downtrend good for dividends?
Investors should exercise caution when evaluating a company that looks distressed and has a higher-than-average dividend yield. Because the stock's price is the denominator of the dividend yield equ ation, a strong downtrend can increase the quotient of the calculation dramatically.
Why are dividends so attractive?
While high dividend yields are attractive, it's possible they may be at the expense of the potential growth of the company. It can be assumed that every dollar a company is paying in dividends to its shareholders is a dollar that the company is not reinvesting to grow and generate more capital gains. Even without earning any dividends, shareholders have the potential to earn higher returns if the value of their stock increases while they hold it as a result of company growth.
Why do companies have a high yield?
Many companies have a very high yield as their stock is falling. If a company's stock experiences enough of a decline, it's possible that they may reduce the amount of their dividend, or eliminate it altogether.
Which companies pay higher dividends?
Companies in the utility and consumer staple industries often having higher dividend yields. Real estate investment trusts (REITs), master limited partnerships (MLPs), and business development companies ( BDCs) pay higher than average dividends; however, the dividends from these companies are taxed at a higher rate.
How to calculate dividend yield?
How to calculate the dividend yield on your portfolio: To calculate the current yield on your portfolio, you must follow these steps: Open a spreadsheet and write down all your holdings and the number of shares you own. Summarize the values.
Who sets the dividend rate?
The dividend is set by the board of directors (BoD), and the rate depends on things like net earnings, cash flow, short-term liquidity, etc. As a small shareholder, you practically have no control of the dividend rate. It’s all up to the BoD.
Can you reinvest dividends into the same stock?
Alternatively, the investor can reinvest the dividend into the same stock. When the dividend is distributed and paid out, the “principal” should keep up with the inflation rate. Thus, many investors are looking to allocate more capital to stocks with a higher dividend yield to get “income”.
Can you live off dividends?
This way, you can live off the dividend in perpetuity. At least that is the theory. We write “income” because a dividend is not really an income, it’s a distribution of shareholder’s equity. Make sure you don’t fool yourself into believing this is an “income” with no opportunity costs.
Do dividends have opportunity costs?
The current risk-free interest rates are low and make the alternatives better. Many investors (wrongly) believe dividends have no opportunity costs. Number one has been known for many decades. However, number two has really got a tailwind after the GFC in 2008/09.
Is dividend investing popular?
Dividend investing is popular. Dividend investing has become very popular . We believe this boils down to three factors: Dividends are a major source of the total returns. Research indicates dividends reinvested contribute to 40-50% of the total returns since WW2.