How to Calculate The Cost of a Newly Issued Preferred Stock
- Convert the flotation cost percent to a decimal by dividing the number by 100. For example, a 5 percent flotation cost divided by 100 would be: 5/100=0.05
- Subtract the decimal of the flotation cost from 1. For the example: 1 – 0.05 = 0.95
- Multiply the market price for the preferred stock by one minus the flotation cost. For the example, a market price of $100 would yield: 100x (0.95) = 95.
- Divide the dividend paid by the preferred stock by this number. For the example, a dividend for the stock of $5 would result in: 5/95 = 0.053
- Multiply this result by 100 to find the cost of the newly issued preferred stock as a percent. For the example: 0.053 x 100 = 5.3 percent.
How do you calculate the cost of a stock flotation?
Subtract the decimal of the flotation cost from 1. For the example: 1 – 0.05 = 0.95 Multiply the market price for the preferred stock by one minus the flotation cost. For the example, a market price of $100 would yield: 100x (0.95) = 95.
Is the cost of capital overstated by the percentage of flotation expenses?
Nevertheless, the abovementioned approach is not accurate because the incorporation of flotation expenses does not depict the actual picture. In such a scenario, the cost of capital is overstated by the percentage of flotation expenses incurred.
What is the cost of preferred stock?
The cost of preferred stock is also used to calculate the Weighted Average Cost of Capital. WACC WACC is a firm’s Weighted Average Cost of Capital and represents its blended cost of capital including equity and debt. What is Preferred Stock?
How much does it cost to float common shares?
Flotation costs for issuing common shares typically fall in the range of 2 percent to 8 percent of the final price of the newly issued securities. A company's total cost of capital represents the smallest rate of return a company must make before generating a profit.
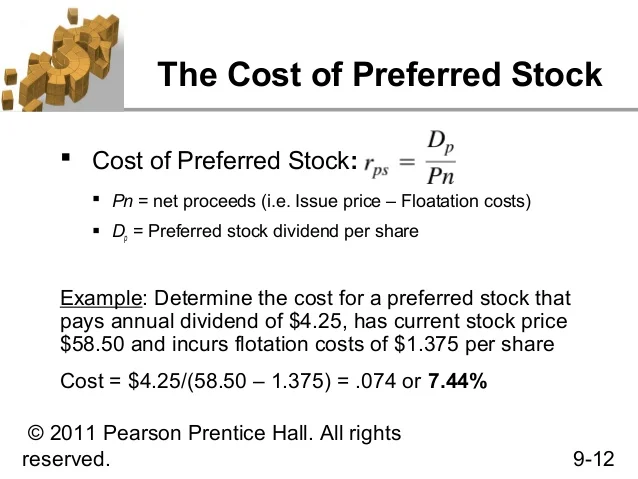
How do you calculate cost of preferred stock?
They calculate the cost of preferred stock by dividing the annual preferred dividend by the market price per share. Once they have determined that rate, they can compare it to other financing options. The cost of preferred stock is also used to calculate the Weighted Average Cost of Capital.
How do you calculate flotation cost of preferred stock?
The difference between the cost of existing equity and the cost of new equity is the flotation cost. The flotation cost is expressed as a percentage of the issue price and is incorporated into the price of new shares as a reduction.
What is the cost of preferred stock in WACC?
WACC Part 2 – Cost of Debt and Preferred Stock The cost of debt is the yield to maturity on the firm's debt and similarly, the cost of preferred stock is the yield on the company's preferred stock.
How do you add floatation costs?
#1 – Inclusion of Flotation Costs into the Cost of CapitalCost of Equity = (D1/P0) + g.Cost of Equity = (D1/ P0 [1-F]) + g.Example.= 0.64%.It results in an increase in the cost of new equity by 0.64%.Example.NPV = [($4,500,000 / 1.1146) + ($4,500,000 / 1.11462) + ($4,500,000 / 1.11463)] – ($10,000,000) = $909,300.More items...
How do you calculate floatation?
We estimate the buoyancy needed for an object using the formula B = ρ × V × g, where ρ and V are the object's density and volume, respectively, and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
What is flotation cost?
Flotation costs are the costs that are incurred by a company when issuing new securities. The costs can be various expenses including, but not limited to, underwriting, legal, registration, and audit fees. Flotation expenses are expressed as a percentage of the issue price.
Does the component cost of preferred stock include or exclude flotation costs explain?
Verified Answer. Flotation cost is included in the cost of preferred stock. The issue of new preferred stock incurs flotation cost that is adjusted in the selling price of the stock, so that effect of flotation cost is incorporated in the cost of preferred stock.
How do corporations calculate the cost of preferred stock?
They calculate the cost of preferred stock by dividing the annual preferred dividend by the market price per share. Once they have determined that rate, ...
Why is preferred stock sold?
Like other equity capital, selling preferred stock enables companies to raise funds. Preferred stock has the benefit of not diluting the ownership stake of common shareholders, as preferred shares do not hold the same voting rights that common shares do. Preferred stock lies in between common equity and debt instruments, in terms of flexibility.
What is the term for the first cash flow payment after a liquidation?
Because of the nature of preferred stock dividends, it is also sometimes known as a perpetuity. Perpetuity Perpetuity is a cash flow payment which continues indefinitely.
What is perpetuity in finance?
Perpetuity Perpetuity is a cash flow payment which continues indefinitely. An example of a perpetuity is the UK’s government bond called a Consol. . For this reason, the cost of preferred stock formula mimics the perpetuity formula closely.
What is a CFI?
CFI is the official global provider of the Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)™. Become a Certified Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® CFI's Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® certification will help you gain the confidence you need in your finance career. Enroll today!
Does common equity have a par value?
However, preferred stock also shares a few characteristics of bonds, such as having a par value. Common equity does not have a par value.
Is preferred stock more valuable than common stock?
In theory, preferred stock may be seen as more valuable than common stock, as it has a greater likelihood of paying a dividend and offers a greater amount of security if the company folds.
Get Professional Assignment Help Cheaply
Are you busy and do not have time to handle your assignment? Are you scared that your paper will not make the grade? Do you have responsibilities that may hinder you from turning in your assignment on time? Are you tired and can barely handle your assignment? Are your grades inconsistent?
How It Works
You fill all the paper instructions in the order form. Make sure you include all the helpful materials so that our academic writers can deliver the perfect paper. It will also help to eliminate unnecessary revisions.
How to calculate cost of preferred stock?
Thus, the cost of preferred stock is calculated by dividing the annual preferred stock dividend by the net proceeds from the sales of preferred stock for the new issuance of preferred stock.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stock is one special type of stock that provides constant dividends similar to interest income. The preferred stockholders have a special right to receive their stated dividends before the earnings can be distributed to the common stockholders. In order to calculate the value of the preferred stock, we first need to know the cost ...
Is preferred stock convertible?
We assume that the preferred stock is not convertible. If the preferred stock is convertible, this model cannot be used.
What is the Cost of Preferred Stock?
The Cost of Preferred Stock represents the rate of return required by preferred shareholders and is calculated as the annual preferred dividend paid out (DPS) divided by the current market price.
Cost of Preferred Stock Overview
The recommended modeling best practice for hybrid securities such as preferred stock is to treat it as a separate component of the capital structure.
Cost of Preferred Stock Formula
The cost of preferred stock represents the dividend yield on the preferred equity securities issued.
Nuances to the Cost of Preferred Stock
Sometimes, preferred stock is issued with additional features that ultimately impact its yield and the cost of the financing.
Cost of Preferred Stock Excel Template
Now that we’ve defined the concept behind the cost of preferred equity, we can move on to an example modeling exercise in Excel. To access the model template, fill out the form below:
Cost of Preferred Stock Example Calculation
In our modeling exercise, we’ll be calculating the cost of preferred stock for two different dividend growth profiles:
What is the flotation cost of common stock?
Flotation costs for issuing common shares typically fall in the range of 2 percent to 8 percent of the final price of the newly issued securities. Advertisement.
What is flotation cost?
These fees are collectively called flotation costs, which are mathematically expressed as a percentage of the security's issue price.
How does flotation affect capital?
Flotation costs impact a company's total capital costs because the total of these fees increases the total capital costs and impacts the price of new securities. Companies recoup their flotation costs either by including the costs in the security's issuing price or by absorbing these costs into their future cash flows.
Why do companies pay flotation fees?
Because these fees can drive up the cost of new shares, which directly impacts how much capital a company can raise when it issues the shares, flotation costs are an essential part of the equation that determines the total cost a company fronts to issue new shares.
Do two companies have the same flotation cost?
No two companies have the same flotation cost totals when they issue new securities because these fees represent various expenses that are company-specific. Common fee categories, however, include legal fees, registration fees, audit fees and underwriting fees. A company must also pay a fee to a stock exchange to list its new shares.
Is flotation a one time fee?
This way, a company's capital costs are not overstated by nonrecurring flotation costs fees.
What is flotation cost?
What are Flotation Costs? Flotation costs are the costs that are incurred by a company when issuing new securities. The costs can be various expenses including, but not limited to, underwriting, legal, registration, and audit fees. Flotation expenses are expressed as a percentage of the issue price.
How do flotation costs affect cost of capital?
Recall that the cost of capital of a company consists of the cost of debt and cost of equity#N#Cost of Equity Cost of Equity is the rate of return a shareholder requires for investing in a business. The rate of return required is based on the level of risk associated with the investment#N#. Thus, expenses affect the cost of capital by changing either cost of debt or cost of equity, depending on a type of securities issued (e.g., issuance of common stock affects the cost of equity).
What is preferred stock?
Preferred Shares Preferred shares (preferred stock, preference shares) are the class of stock ownership in a corporation that has a priority claim on the company’s assets over common stock shares. The shares are more senior than common stock but are more junior relative to debt, such as bonds.
Is flotation expense one time?
The main idea behind the method is that the costs are only one-time expenses paid to third parties. The approach of deducting the flotation expenses from the company’s cash flows is more appropriate than the direct incorporation of the costs into a cost of capital because it considers the one-time nature of the expenses.
Does flotation affect capital?
Since flotation expenses affect the amount of capital that can be raised by issuing new securities, the costs must somehow impact a company’s cost of capital. There are two main views regarding the matter:
Step 1
Convert the flotation cost percent to a decimal by dividing the number by 100. For example, a 5 percent flotation cost divided by 100 would be: 5/100=0.05
Step 2
Subtract the decimal of the flotation cost from 1. For the example: 1 – 0.05 = 0.95
Step 3
Multiply the market price for the preferred stock by one minus the flotation cost. For the example, a market price of $100 would yield: 100x (0.95) = 95.
Step 4
Divide the dividend paid by the preferred stock by this number. For the example, a dividend for the stock of $5 would result in: 5/95 = 0.053
Step 5
Multiply this result by 100 to find the cost of the newly issued preferred stock as a percent. For the example: 0.053 x 100 = 5.3 percent.
