How to Calculate the Average Return on a Portfolio of Stocks
- Calculate Total Portfolio Value. Segregate your portfolio into different annual periods. You need the number of shares...
- Get First Year's Ending Value. Multiply the number of shares of each stock by the ending price for each year and then...
- Calculate First Year's Return. Subtract the portfolio's beginning...
How do you calculate stock market returns?
Part 1 Part 1 of 3: Calculating Stock Returns Download Article
- Determine a period in which to measure returns. The period is the timeframe in which your stock price varies.
- Choose a number of periods. The number of periods, n, represents how many periods you will be measuring within your calculation.
- Locate closing price information. ...
- Calculate returns. ...
How to calculate the average return on portfolio of stocks?
What is an Average Return?
- Annualized Return vs. Average Return. ...
- Calculating Average Return Using Arithmetic Mean. Simple arithmetic mean is one typical example of average return. ...
- Computing Return From Value Growth. ...
- Average Return vs. ...
- Limitations of Average Return. ...
- More Resources. ...
How do you calculate market return?
How do you calculate market rate of return? It compares the risk of an unlevered company to the risk of the market. It is calculated by taking equity beta and dividing it by 1 plus tax adjusted debt to equity. Basis Points (bps) A basis point is 1 hundredth of one percent.
How do you calculate average stock?
What is Average Formula?
- Examples of Average Formula (With Excel Template) Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of Average Formula in a better manner. ...
- Explanation. An average is a central number in the data which is used to answer the many types of question and doubt.
- Relevance and Uses of Average Formula. ...
- Average Formula Calculator
- Recommended Articles. ...

How do you calculate average annual return?
Calculating an average annual return is much simpler than the average annual rate of return, which uses a geometric average instead of a regular mean. The formula is: [(1+r1) x (1+r2) x (1+r3) x ... x (1+ri)] (1/n) - 1, where r is the annual rate of return and n is the number of years in the period.
What is average annual return of stock market?
The average stock market return is about 10% per year for nearly the last century. The S&P 500 is often considered the benchmark measure for annual stock market returns. Though 10% is the average stock market return, returns in any year are far from average.
How do you calculate average annual stock price?
If you do not have Excel, you can manually calculate the 52-week average selling price by calculating the sum of the adjusted daily closing prices for each trading day listed in the 52-week period. Then, take that amount and divide it by the number of trading days in the 52-week period.
What is the average stock market return over 3 years?
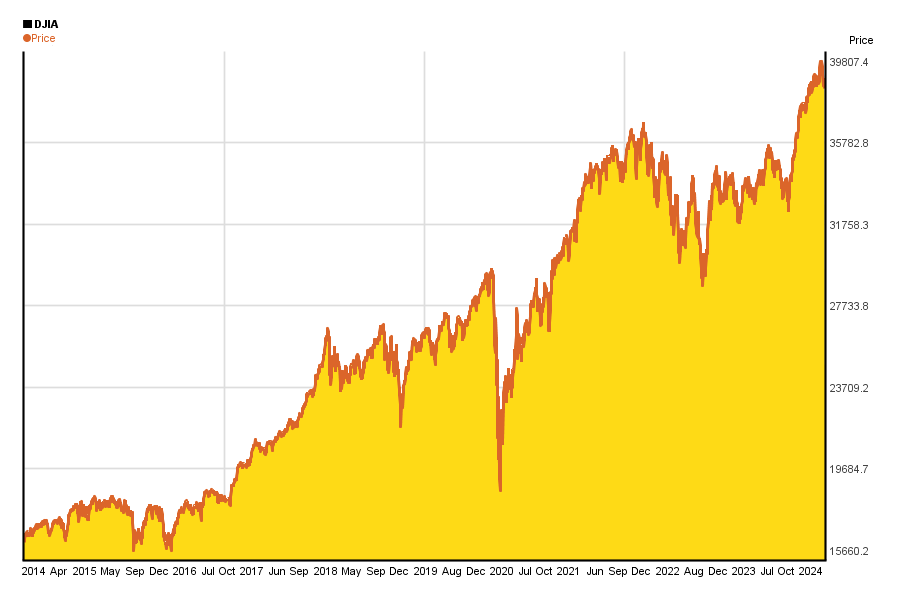
The S&P 500 index is a basket of 500 large US stocks, weighted by market cap, and is the most widely followed index representing the US stock market. S&P 500 3 Year Return is at 50.15%, compared to 40.26% last month and 55.40% last year. This is higher than the long term average of 22.50%.
How much does the S&P 500 return a year on average?
Key Takeaways. The S&P 500 index acts as a benchmark of the performance of the U.S. stock market overall, dating back to the 1920s (in its current form, to the 1950s). The index has returned a historic annualized average return of around 10.5% since its 1957 inception through 2021.
How do I calculate annual stock return in Excel?
Enter the number of years you held the stock in cell A4. If you held the stock for 3 years, enter 3. Enter the following formula into cell A5: =(((A3+A2)/A1)^(1/A4)-1)*100 and the spreadsheet will display the average annual return as a percentage.
How do you calculate the average return on a stock in Excel?
One of the best methods for calculating an average return for a stock investment is the XIRR function in Excel. The XIRR function calculates an annual return that would make the net present value of the cash flows equal to zero. You can think of it as an average annual return for your investment.
What is the average stock market return in 10 years?
Average Market Return for the Last 10 Years Looking at the S&P 500 from 2011 to 2020, the average S&P 500 return for the last 10 years is 13.95% (11.95% when adjusted for inflation), which is a little over the annual average return of 10%.
What is the average stock market return over 20 years?
From 2012 through 2021, the average stock market return was 14.8% annually for the S&P 500 index (SNPINDEX:^GSPC).
What is the 10 year average return on the Dow?
5, 10, 20, and 30-Year Return on the Stock MarketAverage Rate of ReturnInflation-Adjusted Return5-Year (2017-2021)18.55%15.19%10-Year (2012-2021)16.58%14.15%20-Year (2002-2021)9.51%7.04%30-Year (1992-2021)10.66%8.10%May 27, 2022
What is the average stock market return over 40 years?
This is a basic truth that is helpful for those who are beginning to invest; it's also what leads us to that long-term return of an annualized historical average return of 7%. The S&P 500 has gained in 40 of the last 50 years.
What is average return?
What is an Average Return? Average return is the mathematical average of a sequence of returns that have accrued over time. In its simplest terms, average return is the total return over a time period divided by the number of periods.
What is annualized total return?
Annualized Total Return An annualized total return is the return earned on an investment each year. It is computed as a geometric average of the returns of each year earned over a
Why do investors use money weighted returns?
Because of its several flaws when calculating the internal rate of returns, investors and analysts use money-weighted returns as alternative options.
What is the average growth rate?
The average growth rate is used to assess an increase or decrease in the value of an investment over a period of time. The growth rate is computed using the growth rate formula:
What is it called when you own stock?
An individual who owns stock in a company is called a shareholder and is eligible to claim part of the company’s residual assets and earnings (should the company ever be dissolved). The terms "stock", "shares", and "equity" are used interchangeably. or security.
When does computation apply to a comparison?
Computation only pays attention to the return values and applies a comparison concept when analyzing the performance of more than a single investment over multiple time periods.
Is the internal rate of return a high number?
This assumption is impractical, given that sometimes the internal rate of return can yield a high number, and the factors for such return may be limited or unavailable in the future. Due to these flaws, investors and analysts opt to use money-weighted return or geometric mean as the alternative metric for analysis.
Why should dividends be entered as positive numbers?
The dividends should be entered in as positive numbers, because they represent a cash inflow to you. Finally, I'll enter the share price as of the most recent trading day. On November 9, 2015, Microsoft shares traded for $54.10 per share.
Is IRR annual or monthly?
As one final reminder, remember that IRRs are annual. Thus, if you hold an investment for only a few days or weeks, the return will likely seem very high. A 10% gain in a month, for example, works out to an IRR of 207%, which tells you that a 10% return in a month will more than triple your investment in one year's time if you continue to earn that return.
What is average return?
Average return is defined as the mathematical average of a series of returns generated over a period of time. In regards to the calculator, average return for the first calculation is the rate in which the beginning balance concludes as the ending balance, based on deposits and withdrawals that are made in-between over time. The time value of money is accounted for, which is a theory that states that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow. For the second calculation, average return is the total return of the entire period (for all returns involved) divided by the number of periods. The time value of money is also accounted for here.
What is the ARR in accounting?
The average rate of return (ARR), also known as accounting rate of return, is the average amount (usually annualized) of cash flow generated over the life of an investment. ARR does not account for the time value of money. As a result, it is best to use ARR in conjunction with other metrics when considering large financial decisions.
What is cumulative return?
Cumulative return refers to the aggregate amount an investment gains or loses irrespective of time, and can be presented as either a numerical sum total or as a percentage rate. It is generally contrasted with annual return, which is the return (or loss) of an investment in a single year only.
What is the average annual return on the stock market?
Since 1926, the average annual stock market return has been roughly 10%. For this reason, it’s been considered a benchmark when assessing and targeting performance for long-term equity investments.
How long has the stock market been at 10%?
The stock market has returned a 10% average annual rate for almost 100 years.
How long do you have to hold investments to reduce taxes?
Depending on the type of account you have, as well as how long you hold individual investments, taxes can reduce the value of your return. If you have a taxable brokerage account, you will pay ordinary income tax rates on gains from investments you hold for less than a year—these are called short-term capital gains.
How does long term investing affect portfolio?
While how long you’ll be invested affects your portfolio’s asset allocation, so too does your risk tolerance, or how well you can handle large gains and losses. This is because realizing long-term gains depends on staying in the market, through the ups and downs, long term; in other words, not overreacting and selling when you’re losing money and then trying to time when to get back in.
How does inflation affect your return?
Management fees, expenses, and taxes will also affect your average return, while inflation will reduce your buying power and thereby reduce your effective return.
What is the average expense ratio of mutual funds?
In 2019, the average mutual fund expense ratio was 0.45%. 4.
Why did the S&P 500 drop in 2008?
This is because short-term stock market returns rarely match up with long-term averages. In 2008, for example, the S&P 500 dropped 39% due to the financial crisis. The next year, it was up 30%. In fact, had you been invested in the S&P 500 for five years from the beginning of 2004 through 2008, your portfolio would have lost an annualized 2.26% (each year). If you’d been in for the five years ending in 2009, you would have only gained 0.55% on average each year. 2
How to calculate average return on stock portfolio?
Calculating the average return on your stock portfolio first requires calculating the return for each period. Then you can add each period's return together and divide that value by how many periods there are to get the average return.
How to calculate average return?
Add each period's return and then divide by the number of periods to calculate the average return. Continuing with the example, suppose your portfolio experienced returns of 25 percent, -10 percent, 30 percent and -20 percent for the next four years.
How to calculate yearly return of 5 percent?
Then subtract the two years of losses -- a total of 30 percent -- to get a total gain of 25 percent. Divide 25 percent by 5 years to calculate the average yearly return of 5 percent.
How to calculate the first year's return?
Subtract the portfolio's beginning value from the ending value of each year and then divide by the beginning value. Doing so calculates each year's return. Continuing with the example, subtract $4,500 from $4,950 to get $450. Divide $450 by $4,500 to calculate the first year's return of 0.10, or 10 percent.
How to calculate ending price of stock?
Multiply the number of shares of each stock by the ending price for each year and then add each stock's total. The ending price in one year is the same as the beginning value in the next year.
What does the average return on a portfolio of stocks show?
The average return on a portfolio of stocks should show you how well your investments have worked over a period of time. This not only shows you how you performed, but it also helps to predict future returns.
How to segment a portfolio?
You need the number of shares of each stock and the beginning and ending prices for each year. Multiply the number of shares of each stock by its price at the beginning of each year and then add each stock's total for the year.
How much has the stock market returned in a year?
On average, as measured by the S&P 500, the stock market has returned roughly 10% per year. This can vary widely each year depending on a variety of market factors. 4
What are the average returns of the stock market long term?
On average, the stock market has returned roughly 10% per year. This can vary widely each year depending on a variety of market factors. 1
How Often Does the Stock Market Lose Money?
Negative stock market returns occur, but historical data shows that the positive years far outweigh the negative years.
What are some examples of securities with higher growth potential?
To do better than the stock market average, you have to invest in a more aggressive portfolio. International stocks, small- and mid-cap stocks, and growth stocks are examples of securities with higher growth potential, but these also bring higher risks. Discuss your investing goals with a financial advisor to help you decide the right mix for an aggressive growth strategy.
What is historical stock market returns?
Historical stock market returns provide a great way for you to see how much volatility and what return rates you can expect over time when investing in the stock market. In the table at the bottom of this article, you'll find historical stock market returns for the period of 1986 through 2019, listed on a calendar-year basis.
How does down year affect the market?
The market's down years have an impact, but the degree to which they impact you often gets determined by whether you decide to stay invested or get out. An investor with a long-term view may have great returns over time, while one with a short-term view who gets in and then gets out after a bad year may have a loss.
How is wealth built over time?
Wealth is built over the long run by staying in the market, investing in quality stocks, and adding more capital over time.
How to calculate ROI?
ROI is calculated by subtracting the initial value of the investment from the final value of the investment (which equals the net return), then dividing this new number (the net return) by the cost of the investment, then finally, multiplying it by 100.
How much of the ROI comes from capital gains?
Further dissecting the ROI into its component parts reveals that 23.75% came from capital gains and 5% came from dividends. This distinction is important because capital gains and dividends are taxed at different rates in most jurisdictions.
What does it mean when ROI is negative?
Alternatively, when ROI calculations yield a negative figure, it means that net returns are in the red because total costs exceed total returns. (In other words, this investment produces a loss.) Finally, to calculate ROI with the highest degree of accuracy, total returns and total costs should be considered. For an apples-to-apples comparison between competing investments, annualized ROI should be considered.
Why is ROI calculation so complicated?
This type of ROI calculation is more complicated because it involves using the internal rate of return (IRR) function in a spreadsheet or calculator.
Why is ROI expressed as a percentage?
First, ROI is typically expressed as a percentage because it is intuitively easier to understand (as opposed to when expressed as a ratio). Second, the ROI calculation includes the net return in the numerator because returns from an investment can be either positive or negative.
What is ROI in investing?
Return on investment (ROI) is an approximate measure of an investment's profitability. ROI has a wide range of applications; it can be used to measure the profitability of a stock investment, when deciding whether or not to invest in the purchase of a business, or evaluate the results of a real estate transaction.
How long is 0.5 years?
In the equation above, the numeral 0.5 years is equivalent to six months.
How to find average historical return?
Using a simple mean computation, the average historical return can be found by summing up all the returns and dividing the sum by the number of years (or periods). The calculation can be longer and more tedious, depending on the number of time periods used – e.g., 5 years or more.
How to calculate historical returns?
To begin calculating the historical returns, the difference between the most recent price and the past price needs to be computed and then divided by the past price multiplied by 100 to get the result as a percentage. The calculation can be done iteratively to cater for longer time periods – e.g., 5 years or more.
What is an ETF?
Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) An Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) is a popular investment vehicle where portfolios can be more flexible and diversified across a broad range of all the available asset classes. Learn about various types of ETFs by reading this guide.
What is the S&P 500 index?
S&P 500 Index The Standard and Poor’s 500 Index, abbreviated as S&P 500 index, is an index comprising the stocks of 500 publicly traded companies in the. , ETFs, mutual funds, commodities, stocks, real estate, etc.
Why is historical data used in financial analysis?
Historical data is commonly used in financial analysis to project future returns or determine what variables may impact future returns and the extent to which the variables may influence returns.
What is financial analysis?
Financial Analysts primarily carry out their work in Excel, using a spreadsheet to analyze historical data and make projections Types of Financial Analysis. to project future returns or determine what variables may impact future returns and the extent to which the variables may influence returns.
What is rate of return?
Rate of Return The Rate of Return (ROR) is the gain or loss of an investment over a period of time copmared to the initial cost of the investment expressed as a percentage. This guide teaches the most common formulas

Annualized Return vs. Average Return
Calculating Average Return Using Arithmetic Mean
- Simple arithmetic mean is one typical example of average return. Consider a mutual investment returns the following every year over six full years, as shown below. The average return for six years is computed by summing up the annual returns and divided by 6, that is, the annual average return is calculated as below: Annual Average Return = (15% +1...
Computing Return from Value Growth
- The average growth rate is used to assess an increase or decrease in the value of an investment over a period of time. The growth rate is computed using the growth rate formula: For example, assume that an investor invested $100,000 in an investment product, and the stock prices fluctuated from $100 to $250. Using the above formula to calculate the average return gives the …
Average Return vs. Geometric Average
- The geometric average proves to be ideal when analyzing average historical returns. What sets the geometric meanapart is that it assumes the actual value invested. Computation only pays attention to the return values and applies a comparison concept when analyzing the performance of more than a single investment over multiple time periods. The geometric average return take…
Limitations of Average Return
- Despite its preferences as an easy and effective measure for internal returns, the average return has several pitfalls. It does not account for different projects that might require different capital outlays. In the same vein, it ignores future costs that may affect profit; rather, it only focuses on projected cash flows resulting from a capital injection. Also, average return does not consider th…
More Resources
- Thank you for reading CFI’s guide on Average Return. To keep learning and developing your knowledge of financial analysis, we highly recommend the additional resources below: 1. Annualized Total Return 2. Return on Investment (ROI) 3. Average Annual Growth Rate 4. Annualized Rate of Return