Part 2 of 3: Calculating Stock Volatility Download Article
- Find the mean return. Take all of your calculated returns and add them together. ...
- Calculate the deviations from the mean. For every return, Rn, a deviation, Dn, from the mean return, m, can be found.
- Find the variance. ...
- Calculate the volatility. ...
How to calculate CAGR of stocks?
Oct 20, 2016 · To present this volatility in annualized terms, we simply need to multiply our daily standard deviation by the square root of 252. This assumes there are …
What is the formula for price volatility?
Jul 05, 2021 · Find the annualized standard deviation — annual volatility — of the the S&P 500 by multiplying the daily volatility by square root of the number of trading days in a year, which is 252.
How to calculate volatility correctly?
Mar 17, 2019 · The formula for the volatility of a particular stock can be derived by using the following steps: Firstly, gather daily stock price and then determine the mean of the stock price. Let us assume the daily stock price on... Next, compute the difference between each day’s stock price and the mean ...
What does high volatility mean in stocks?
Feb 10, 2015 · Calculating Historical Volatility in Excel. Step 1: Timeframe. Volatility is a time-bound measurement, meaning that it measures the price swings of an asset or security over a particular period. Step 2: Enter Price Information. Step 3: Compute Returns. Step 4: Calculate Standard Deviations. Step 5: ...
How do you calculate annual volatility in Excel?
What is Annualised volatility?
How do you calculate annualized volatility from monthly return?
How do you convert daily volatility to annual?
How is volatility measured?
How do you calculate volatility of a portfolio in Excel?
How do you calculate monthly volatility from daily volatility?
How is monthly volatility calculated?
How do you calculate the beta of a stock?
How do you calculate weekly volatility of a stock?
What is a good volatility percentage?
What are volatility indicators?
How to calculate volatility of a portfolio?
To calculate the volatility of a two-stock portfolio, you need: 1 The weight of stock 1 in the portfolio 2 The weight of stock 2 in the portfolio 3 The standard deviation (volatility) of stock 1 4 The standard deviation of stock 2 5 The covariance, or relational movement, between the stock prices of stock 1 and stock 2
What is portfolio volatility?
Portfolio volatility is a measure of portfolio risk, meaning a portfolio's tendency to deviate from its mean return. Remember that a portfolio is made up of individual positions, each with their own volatility measures. These individual variations, when combined, create a single measure of portfolio volatility.
What is standard deviation in stock?
The standard deviation (volatility) of stock 1. The standard deviation of stock 2. The covariance, or relational movement, between the stock prices of stock 1 and stock 2. To calculate portfolio volatility, the logic underlying the equation is complicated, but the formula takes into account the weight of each stock in the portfolio, ...
Why is historical data important?
Computing historical data can still be useful because this information can predict how a security's price will move in the future. With price fluctuations normally distributed, the stock's price tends to stay within one standard deviation — its implied volatility — of the stock's current price for 68% of price changes.
How to calculate volatility of a stock?
The formula for the volatility of a particular stock can be derived by using the following steps: 1 Firstly, gather daily stock price and then determine the mean of the stock price. Let us assume the daily stock price on an ith day as Pi and the mean price as Pav. 2 Next, compute the difference between each day’s stock price and the mean price, i.e., Pi – P. 3 Next, compute the square of all the deviations, i.e. (Pav – Pi)2. 4 Next, find the summation of all the squared deviations, i.e. ∑ (Pav – Pi)2. 5 Next, divide the summation of all the squared deviations by the number of daily stock prices, say n. It is called the variance of the stock price.#N#Variance = ∑ (Pav – Pi)2 / n 6 Next, compute the daily volatility or standard deviation by calculating the square root of the variance of the stock.#N#Daily volatility = √ (∑ (Pav – Pi)2 / n) 7 Next, the annualized volatility formula is calculated by multiplying the daily volatility by the square root of 252. Here, 252 is the number of trading days in a year.#N#Annualized volatility = = √252 * √ (∑ (Pav – Pi)2 / n)
What is volatility in stock market?
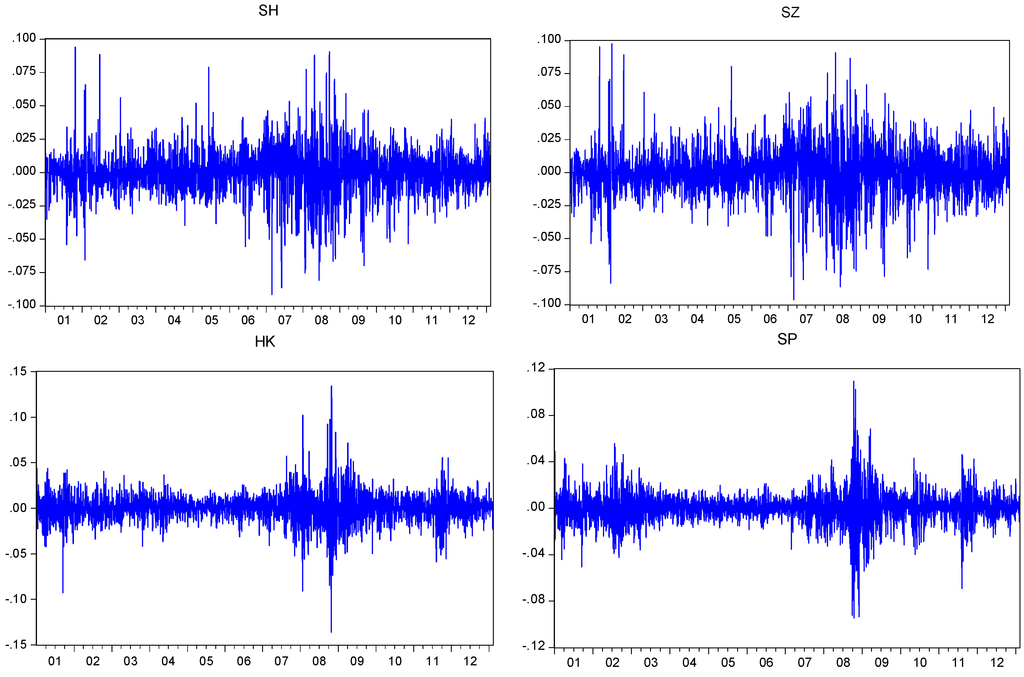
The term “volatility” refers to the statistical measure of the dispersion of returns during a certain period of time for stocks, security, or market index. The volatility can be calculated either using the standard deviation or the variance of the security or stock.
Why is volatility important?
From the point of view of an investor, it is essential to understand the concept of volatility because it refers to the measure of risk or uncertainty pertaining to the quantum of changes in the value of a security or stock. Higher volatility indicates that the value of the stock can be spread out over a larger range of values, ...
What does higher volatility mean?
Higher volatility indicates that the value of the stock can be spread out over a larger range of values, which eventually means that the value of the stock can potentially move in either direction significantly over a short period.
What is VIX stock?
VIX is a measure of the 30-day expected volatility of the U.S. stock market computed based on real-time quote prices of S&P 500 call and put options.
What is the VIX index?
VIX is a measure of the 30-day expected volatility of the U.S. stock market computed based on real-time quote prices of S&P 500 call and put options.
What is historical volatility?
Historical volatility is a measure of past performance; it is a statistical measure of the dispersion of returns for a given security over a given period of time. For a given security, in general, the higher the historical volatility value, the riskier the security is. However, some traders and investors actually seek out higher volatility ...
Why is volatility important?
Why Volatility Is Important For Investors. While volatility in a stock can sometimes have a bad connotation, many traders and investors actually seek out higher volatility investments. They do this in the hopes of eventually making higher profits. If a stock or other security does not move, it has low volatility.
What is volatility in stocks?
A stock whose price varies wildly (meaning a wide variation in returns) will have a large volatility compared to a stock whose returns have a small variation. By way of comparison, for money in a bank account with a fixed interest rate, every return equals the mean (i.e., there's no deviation) and the volatility is 0.
Who is Marcus Raiyat?
This article was co-authored by Marcus Raiyat. Marcus Raiyat is a U.K. Foreign Exchange Trader and Instructor and the Founder/CEO of Logikfx. With nearly 10 years of experience, Marcus is well versed in actively trading forex, stocks, and crypto, and specializes in CFD trading, portfolio management, and quantitative analysis. Marcus holds a BS in Mathematics from Aston University. His work at Logikfx led to their nomination as the "Best Forex Education & Training U.K. 2021" by Global Banking and Finance Review. This article has been viewed 102,114 times.
What is implied volatility?
There can be two types of volatility depending on its usage – Implied Volatility which is a forward-looking estimate and is used in the option pricing strategy. The other is the Regular Volatility which is more common and used a backward-looking real figure.
What is standard deviation in stock market?
It is the measure of the risk and the standard deviation is the typical measure used to measure the volatility of any given stock, while the other method can simply be the variance between returns from the same security or market index. One common measure of the volatility of given security with respect to the market index or ...
How to find standard deviation?
How to calculate the Standard Deviation 1 Calculate the average of the data set. 2 Subtract the average from the actual observation, to arrive the deviation. 3 Square up all the deviations and add them up, to arrive the Variance. 4 Calculate the square root of the variance, to arrive the Standard Deviation.
What is investment performance?
First, investment performance is typically skewed, which means that return distributions are typically asymmetrical. As a result, investors tend to experience abnormally high and low periods of performance. Second, investment performance typically exhibits a property known as kurtosis, which means that investment performance exhibits an abnormally ...
What is standard deviation in statistics?
Most investors know that standard deviation is the typical statistic used to measure volatility. Standard deviation is simply defined as the square root of the average variance of the data from its mean.
What is standard deviation?
Standard deviation is simply defined as the square root of the average variance of the data from its mean. While this statistic is relatively easy to calculate, the assumptions behind its interpretation are more complex, which in turn raises concern about its accuracy.
What is heteroskedasticity in statistics?
Heteroskedasticity simply means that the variance of the sample investment performance data is not constant over time. As a result, standard deviation tends to fluctuate based on the length of the time period used to make the calculation, or the period of time selected to make the calculation.
What are the advantages of using the historical method?
First, the historical method does not require that investment performance be normally distributed.
Why use histograms?
In practical terms, the utilization of a histogram should allow investors to examine the risk of their investments in a manner that will help them gauge the amount of money they stand to make or lose on an annual basis. Given this type of real-world applicability, investors should be less surprised when the markets fluctuate dramatically, and therefore they should feel much more content with their investment exposure during all economic environments.
Who is Charlene Rhinehart?
Charlene Rhinehart is the Founder and Editor-in-Chief of The Dividend InvestHER. She’s been a CPA for over a decade and has served as the Chair of the Illinois CPA Society Individual Tax Committee. Article Reviewed on May 31, 2021. Learn about our Financial Review Board. Charlene Rhinehart.
How to calculate volatility?
The following steps can be followed when calculating volatility through determining the standard deviation over time: 1 Collect the historical prices for the asset. 2 Compute the expected price (mean) of the historical prices. 3 Work out the difference between the average price and each price in the series. 4 Square the differences from the previous step. 5 Determine the sum of the squared differences. 6 Divide the differences by the total number of prices (find variance). 7 Compute the square root of the variance computed in the previous step.
What is volatility in investment?
Volatility is generally a measure of the riskiness of an investment. Increased volatility serves as an indication of increased uncertainty and risk. The opposite is also true; decreased volatility serves as an indication for lowered uncertainty and risk.
What is volatility in financials?
Volatility is a measurement of the frequency of financial asset price variations over time. This shows the potential risk levels associated with the price fluctuations of a security. The volatility of an asset is measured by investors and traders to analyze historical price fluctuations and forecast their possible movements.
What is implied volatility?
Implied volatility refers to the volatility of an underlying asset, which will return the theoretical value of an option equal to the option’s current market price. Implied volatility is a key parameter in option pricing. It provides a forward-looking aspect of possible future price fluctuations.
What is VIX stock?
VIX. VIX The Chicago Board Options Exchange (C BOE) created the VIX (CBOE Volatility Index) to measure the 30-day expected volatility of the US stock market, sometimes called the "fear index". The VIX is based on the prices of options on the S&P 500 Index.
What is the VIX index?
VIX The Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) created the VIX (CBOE Volatility Index) to measure the 30-day expected volatility of the US stock market, sometimes called the "fear index". The VIX is based on the prices of options on the S&P 500 Index.
What is mean mean in statistics?
Mean Mean is an essential concept in mathematics and statistics. In general, a mean refers to the average or the most common value in a collection of. Volume Price Trend Indicator (VPT) The Volume Price Trend Indicator (VPT) is a stock market indicator that helps traders relate a stock's price and trading volume.
