You can calculate your preferred stock's annual dividend distribution per share by multiplying the dividend rate and the par value. If you want to determine how much your dividend will be on a quarterly basis (assuming your preferred stock pays quarterly), simply divide this result by four.
What are the dividends of preferred stocks?
The dividends of preferred stocks are different from and generally greater than those of common stock. When you buy a preferred stock, you will have an idea of when to expect a dividend because they are paid at regular intervals.
How do preferred stock preferences affect the value of common shareholders?
Doing so allows for the preferred shares’ respective dividend rate to affect the value attributed to each equity class. Consequently, common shareholders will be able to receive value after the preferred stockholders and convertible debt holders have received their preferences.
How are preferred shares paid out to shareholders?
It is paid out to shareholders in precedence over other types of dividends. i.e., dividends are paid out to shareholders before the common stock or equity dividends are issued. In case of liquidation of the company, shareholders with preferred shares are entitled to be paid from company assets first.
Can preferred stock be exchanged for common stock?
May be exchanged for common stock at a preagreed ratio (e.g., 3 shares of common for 1 share of preferred). A convertible preferred stock can effectively provide significant upside potential if the related common stock increases value. Intent to be bought back by the company (“mandatory redeemable”) on a certain future date.

How do you distribute dividends between preferred and common stock?
0:053:54Dividends per share preferred and common - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd how much go to the common stockholders. So preferred stock are told that we have promised themMoreAnd how much go to the common stockholders. So preferred stock are told that we have promised them when we give out a dividend. We will be given them out. Two percent and that we take that percentage.
Who gets dividends first preferred or common?
The main difference between preferred and common stock is that preferred stock gives no voting rights to shareholders while common stock does. Preferred shareholders have priority over a company's income, meaning they are paid dividends before common shareholders.
How do you allocate preferred stock?
2:139:51Preferred Stock and Common Stock Dividend Allocations - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd this is based off the interest rate on the preferred stock so in this case it's ten percentMoreAnd this is based off the interest rate on the preferred stock so in this case it's ten percent multiplied by the par. Value of the stock. Okay so if I take one hundred dollars.
How do you show allocation of dividends?
1:3014:09Dividend Allocation and Dividends per Share - Preferred vs. CommonYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo when we say entitled to we're gonna see how much that they should be getting those 50,000 shares.MoreSo when we say entitled to we're gonna see how much that they should be getting those 50,000 shares. So in order to do. That. We need to use a bit of a formula.
Why you should avoid preferred stocks?
A big risk of owning preferred stocks is that shares are often sensitive to changes in interest rates. Because preferred stocks often pay dividends at average fixed rates in the 5% to 6% range, share prices typically fall as prevailing interest rates increase.
Is preferred dividends the same as dividends paid?
Preferred dividends are the dividends that are accrued paid on a company's preferred stock. Any time a company pays dividends, preferred shareholders have priority over common shareholders, which means dividends must always be paid to preferred shareholders before they are paid to common shareholders.
Where do preferred stock dividends go on financial statements?
Dividends on common stock are not reported on the income statement since they are not expenses. However, dividends on preferred stock will appear on the income statement as a subtraction from net income in order to report the earnings available for common stock.
Where are preferred dividends on the balance sheet?
The amount received from issuing preferred stock is reported on the balance sheet within the stockholders' equity section. Only the annual preferred dividend is reported on the income statement.
Do preferred dividends go on income statement?
Preferred stock dividends are deducted on the income statement. The reason is that preferred stockholders have a higher claim to dividends than common stockholders do.
Do preferred stock dividends affect retained earnings?
If a company pays stock dividends, the dividends reduce the company's retained earnings and increase the common stock account. Stock dividends do not result in asset changes to the balance sheet but rather affect only the equity side by reallocating part of the retained earnings to the common stock account.
How do you calculate preferred and common stock?
Here's an easy formula for calculating the value of preferred stock: Cost of Preferred Stock = Preferred Stock Dividend (D) / Preferred Stock Price (P). Par value of one share of preferred stock equals the amount upon which the dividend is calculated. In other words, par value is the face value of one share of stock.
Is preferred stock recorded at par value?
To comply with state regulations, the par value of preferred stock is recorded in its own paid-in capital account Preferred Stock. If the corporation receives more than the par amount, the amount greater than par will be recorded in another account such as Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par - Preferred Stock.
What is the difference between common stock and preferred stock?
The main difference between common and preferred stock is that common stockholders usually have voting privileges at stockholders' meetings, while preferred stockholders do not. In most cases, owning common stock gives you one vote per the number of shares you own, although this figure varies by company.
How to determine if you should invest in preferred stock?
If you're trying to determine whether to invest in preferred stock, compare its dividend yield to the company's bond yields and other stock issues.
Why are preferred stocks less risky?
Preferred stocks are less risky for investors because they're paid before common stocks if the company runs into financial trouble. As a result, preferred stockholders take priority over common shareholders, but they're still ranked behind bondholders. Even so, preferred stock is a smart investment.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stock is a type of ownership security or equity that differs from common stock in that it doesn't provide shareholders with voting rights. Preferred stock does pay a fixed dividend when the shares are issued that show up on the stock's prospectus, and that dividend must be paid before dividends from common stock.
How to figure out how much you make per quarter?
Once you have the decimal amount, multiply the rate by the stock's par value. To figure out how much you'll earn per quarter, simply divide the answer by four. You can then multiply the number by however many preferred stock shares you own. Although preferred stock might increase over time, this growth is limited.
Why are preferred stocks considered a stable investment?
They are considered a more stable investment because they provide a regular income stream. They can convert to a fixed number of common stock shares. How much you'll pay for a preferred stock depends on the company issuing the stock. In general, the cost is influenced by both the stock market and the preferred dividends.
Can you calculate dividends with preferred stock?
With preferred stock, you can calculate your dividends and know how much to expect at regular intervals, which isn't the case with common stock. With common stocks, the company's board of directors decide when and whether to pay out dividends. Other characteristics worth noting about preferred stocks include:
How to calculate preferred stock dividend?
You can calculate your preferred stock's annual dividend distribution per share by multiplying the dividend rate and the par value. If you want to determine how much your dividend will be on a quarterly basis (assuming your preferred stock pays quarterly), simply divide this result by four.
Where to find preferred stock dividend rate?
Your preferred stock's dividend rate and par value can be found in the issuing company's preferred stock prospectus, so the first step is to locate this information.
How are preferred stocks and bonds similar?
Another similarity between preferred stocks and bonds is that while the market value of preferred shares can fluctuate, the dividends don't. Preferred stocks have a set dividend rate that's based on the "par value" of the stock -- usually $25, but other amounts do exist. In other words, calculating preferred stock dividends is a fairly straightforward process, and you can expect the same dividend amount to continue, quarter after quarter and year after year.
Why are preferred stocks bought?
Like a bond, preferred stocks are bought primarily for their income potential and not for growth. Also as with a bond, preferred shareholders are ahead of common shareholders (but behind bondholders) in times of bankruptcy.
Is preferred stock a good investment?
Preferred stock can be a good income investment. Here's how to calculate your preferred stocks' dividend distribution. Preferred stock is a special type of stock that trades on an exchange but works more like a bond than common stock. Like a bond, preferred stocks are bought primarily for their income potential and not for growth.
How do common stock and preferred stock gain access to capital?
While common stock is the most typical, another way to gain access to capital is by issuing preferred stock. The customary features of common and preferred stock differ, providing some advantages and disadvantages for each.
How to determine if a company has to pay dividends?
To pay a dividend the company must have sufficient cash and a positive balance in retained earnings (companies with a “deficit” (negative) Retained Earnings account would not pay a dividend unless it is part of a corporate liquidation action). Many companies pride themselves in having a long-standing history of regular and increasing dividends, a feature that many investors find appealing. Other companies view their objective as one of continual growth via reinvestment of all earnings; their investors seem content relying on the notion that their investment value will gradually increase due to this earnings reinvestment activity. Whatever the case, a company has no obligation to pay a dividend, and there is no “liability” for dividends until such time as they are actually declared. A “declaration” is a formal action by the board of directors to indicate that a dividend will be paid at some stipulated future date. On the date of declaration, the following entry is needed on the corporate accounts:
How much is $100 par stock?
The preferred stock description makes it clear that the $100 par stock is 8% cumulative. This means that each share will receive $8 per year in dividends, and any “missed” dividends become dividends in arrears.
What is the right to vote on certain general governance matters?
The right to vote on certain general governance matters like election of the board of directors, employee stock award plans, mergers, and similar corporate matters. Proceeds from liquidation. Receives proceeds of liquidation after creditors and other priority claims are settled. Periodic financial reports.
What are the different types of stock?
For example, some companies have multiple classes of common stock. A “family business” that has grown very large and become a public company may be accompanied by the creation of Class A stock (held by the family members) and Class B stock (held by the public), where only the Class A stock can vote. This enables raising needed capital but preserves the ability to control and direct the company. While common stock is the most typical, another way to gain access to capital is by issuing preferred stock. The customary features of common and preferred stock differ, providing some advantages and disadvantages for each. The following tables reveal general features that can be modified on a company by company basis.
When can a shareholder expect a dividend?
But, if the shareholder sells the stock before the ex-dividend date, the new shareholder can expect the dividend. In the illustrated time line, if one were to own stock on the date of declaration, that person must hold the stock at least until the “green period” to be entitled to receive payment.
Why do companies issue preferred?
For instance, a company can issue preferred that is much like debt (cumulative, mandatory redeemable), because a fixed periodic payment must occur each period with a fixed amount due at maturity.
How to calculate preferred dividend per share?
Once you know how to calculate the preferred dividend per share, you would just need to multiply the number of shares with the preferred dividend per share. And you would know how much you would get each year.
What is preferred dividend?
Preferred Dividends is a fixed dividend received from Preferred stocks. It means that if you’re a preferred shareholder, you will get a fixed percentage of dividends every year. And the most beneficial part of the preferred stock is that the preferred shareholders get a higher rate of dividend.
Why do preference shareholders have higher dividends?
The reason for this is because preference shareholders do not have ownership control over the company, hence to attract the investors, higher rates of dividends are offered to them.
What is non-cumulative preferred stock?
Non-cumulative Preferred Stocks Non-cumulative preference shares are the stocks which allow the investors to receive a fixed dividend at the pre-determined dividend rate every year. However, if any year's dividend remains unpaid, the preference shareholders are not liable to receive it in the future. read more.
What is dividends in arrears?
Dividends In Arrears Dividends in Arrears is the cumulative dividend amount that has not been paid to the cumulative preferred stockholders by the presumed date.
How much preferred dividend does Urusula get?
Urusula has invested in preferred stocks of a firm. As the prospectus says, she will get a preferred dividend of 8% of the par value of shares. The par value of each share is $100. Urusual has bought 1000 preferred stocks.
Why is preferred stock called perpetuity?
The preferred stock pays a fixed percentage of dividends. That’s why we can call it perpetuity because the dividend payment is equal and paid for an infinite period. However, a firm can choose to skip the equal payment of preferred dividends to preferred shareholders.
How to calculate preferred stock dividend?
This is often based on the par value before a preferred stock is offered. It's commonly calculated as a percentage of the current market price after it begins trading. This is different from common stock, which has variable dividends that are declared by the board of directors and never guaranteed. In fact, many companies do not pay out dividends to common stock at all.
What is the difference between common stock and preferred stock?
The main difference is that preferred stock usually does not give shareholders voting rights, while common stock does, usually at one vote per share owned. 1 Many investors know more about common stock than they do about preferred stock.
How does preferred stock work?
In fact, preferred stock functions similarly to bonds since with preferred shares, investors are usually guaranteed a fixed dividend in perpetuity. The dividend yield of a preferred stock is calculated as the dollar amount of a dividend divided by the price of the stock.
What is preferred shareholder?
Preferred shareholders have priority over a company's income, meaning they are paid dividends before common shareholders. Common stockholders are last in line when it comes to company assets, which means they will be paid out after creditors, bondholders, and preferred shareholders.
What is preferred stock in liquidation?
In a liquidation, preferred stockholders have a greater claim to a company's assets and earnings.
What happens if a company misses a dividend?
If a company misses a dividend, the common stockholder gets bumped back for a preferred stockholder, meaning paying the latter is a higher priority for the company. The claim over a company's income and earnings is most important during times of insolvency.
What is common stock?
Common Stock. Common stock represents shares of ownership in a corporation and the type of stock in which most people invest. When people talk about stocks, they are usually referring to common stock. In fact, the great majority of stock is issued in this form.

Possible Preferred Stock Features
What Is Par?
- In the preceding discussion, there were several references to par value. Many states require that stock have a designated par value (or in some cases “stated value”). Thus, par value is said to represent the “legal capital” of the firm. In theory, original purchasers of stock are contingently liable to the company for the difference between the issue price and par value if the stock is issu…
A Closer Look at Cash Dividends
- Begin by assuming that a company has only common shares outstanding. There is no mandatory dividend requirement, and the dividends are a matter of discretion for the board of directors to consider. To pay a dividend the company must have sufficient cash and a positive balance in retained earnings (companies with a “deficit” (negative) Retained Earnings account would not pa…
Dividend Dates
- In observing the preceding entry, it is imperative to note that the declaration on July 1 establishes a liability to the shareholders that is legally enforceable. Therefore, a liability is recorded on the books at the time of declaration. Recall (from earlier chapters) that the Dividends account will directly reduce retained earnings (it is not an expense in calculating income; it is a distribution o…
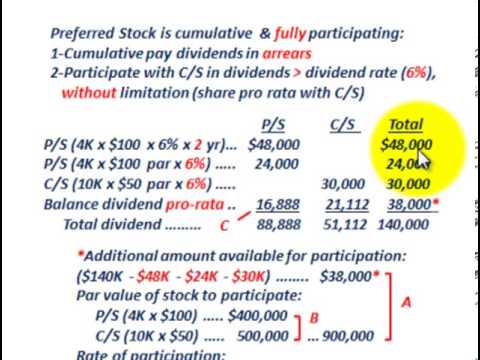
The Presence of Preferred Stock
- Recall that preferred dividends are expected to be paid before common dividends, and those dividends are usually a fixed amount (e.g., a percentage of the preferred’s par value). In addition, recall that cumulative preferred requires that unpaid dividends become “dividends in arrears.” Dividends in arrearsmust also be paid before any distributions ...