What does it mean to vest shares?
What Does It Mean To Vest Your Shares? Vesting of shares means that the shareholder has to earn their shares over time by staying with the company in some capacity. If a shareholder leaves the company and owns unvested shares, then the corporation has the option to repurchase the unvested shares typically at the original purchase price.
What does vested mean stock?
Types of Vesting Periods
- Cliff Vesting. Cliff vesting is the process that entitles an employee to their full benefits on a given date. ...
- Graded Vesting. Graded vesting is the vesting process that over time, the employee gains ownership of employer contributions.
- Immediate Vesting. Immediate vesting is the most straightforward. ...
What is an unvested stock?
- The granted quantity is how many shares the company promises you.
- Typically, however, those shares don’t get released to you all at once, because the company would like to use this as a tool to get you to stay with them ...
- Unvested shares are ones which the company has promised you, but which h
What does vested shares mean?
What Does Vested Shares Mean? Vested shares mean shares that you own, even if you're fired or you quit. They're a form of compensation. You most often hear about them as part of the reward for employees at hip startups, but that's not the only type of company that offers them.

How do vesting stocks work?
When a stock option vests, it means that it is actually available for you to exercise or buy. Unfortunately, you will not receive all of your options right when you join a company; rather, the options vest gradually, over a period of time known as the vesting period.
What happens after 4 years of vesting?
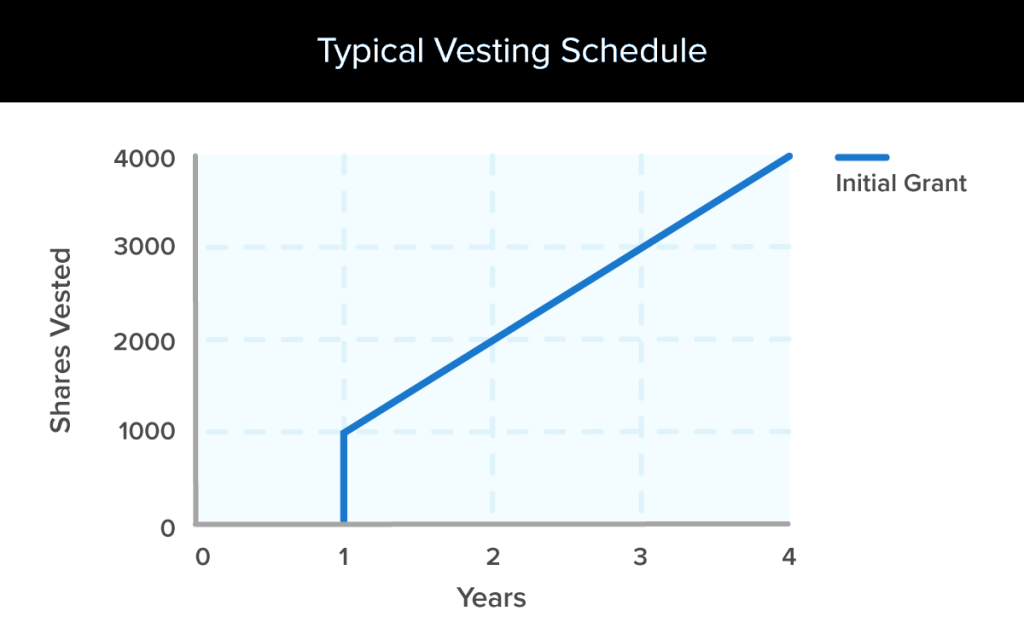
Under a standard four-year time-based vesting schedule with a one-year cliff, 1/4 of your shares vest after one year. After the cliff, 1/36 of the remaining granted shares (or 1/48 of the original grant) vest each month until the four-year vesting period is over. After four years, you are fully vested.
What does vesting after 3 years mean?
Let's say you have a plan that increases the amount you are vested in your plan each year by 20%—this is known as "graded vesting." You will be fully vested (i.e. the employer-matching funds will belong to you) after five years at your job, but if you leave your job after three years, you will be 60% vested, meaning ...
What does it mean to be vested after 5 years?
This typically means that if you leave the job in five years or less, you lose all pension benefits. But if you leave after five years, you get 100% of your promised benefits. Graded vesting. With this kind of vesting, at a minimum you're entitled to 20% of your benefit if you leave after three years.
Can you cash out vested stock?
Once they vest, an employee can exercise the right to buy the stock at that price, either paying with cash or doing a same-day sale, temporarily borrowing the money for the strike price and then immediately selling the stock for a profit. You often must utilize a stock option or forfeit it when you leave a company.
Can I sell vested stock?
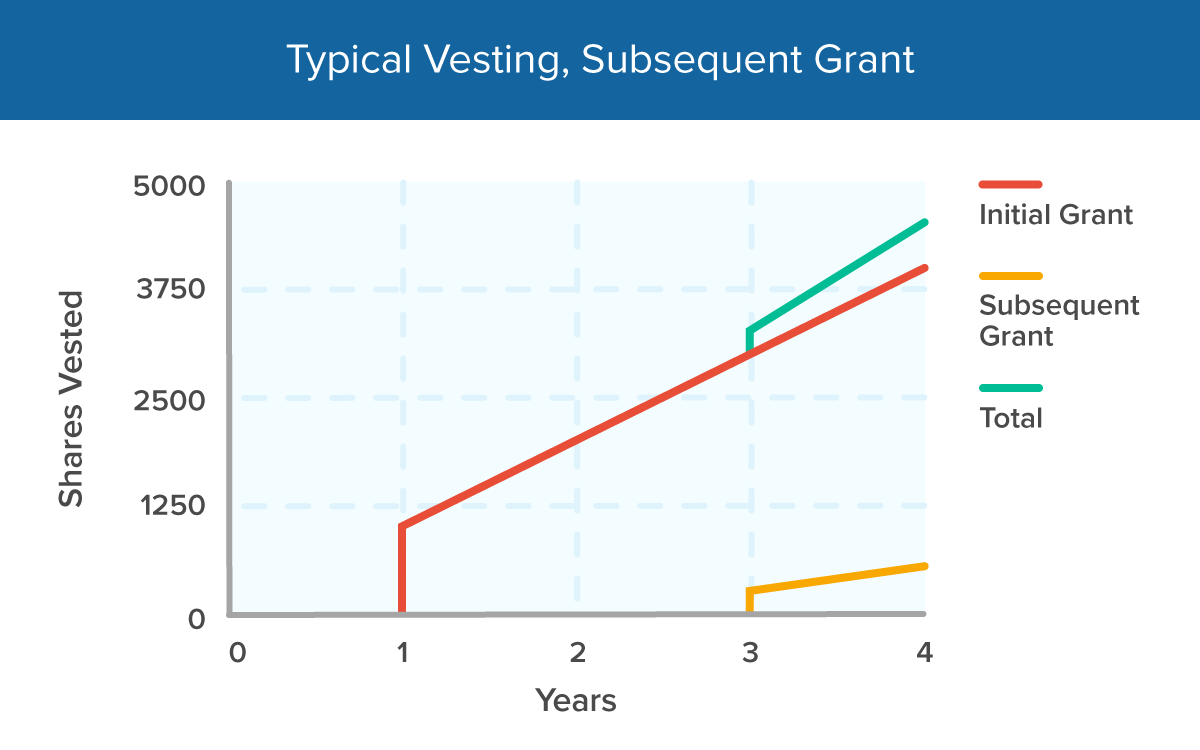
Your graded vesting schedule spans four years, and 25% of the grant vests each year. At the first anniversary of your grant date and on the same date over the subsequent three years, 1,250 shares vest. Once each portion vests, you can sell the shares.
What is a 2 year vesting period?
What will happen to my benefits if I've met the two year vesting period? If you've met the two year vesting period the amount held in your active pension account up to your date of leaving is transferred to a deferred pension account and you then have what are known as deferred benefits.
How is vesting calculated?
Service for vesting can be calculated in two ways: hours of service or elapsed time. With the hours of service method, an employer can define 1,000 hours of service as a year of service so that an employee can earn a year of vesting service in as little as five or six months (assuming 190 hours worked per month).
What happens if you leave before vested?
Typically, if you leave your employer before you are fully vested, you will forfeit all or a portion of the employer-provided contributions to your account.
What are the benefits of being vested?
Key Takeaways A vested benefit is a financial package granted to employees who have met the requirements to receive a full, instead of partial, benefit. Vested benefits include cash, employee stock options (ESO), health insurance, 401(k) plans, retirement plans, and pensions.
What is a 4 year vesting schedule?
It is common to see a four-year vesting schedule tied to stock options with a one-year cliff. This simply means an employee needs to stay for a minimum of one year to earn any shares, and will have fully vested shares after four years of service.
What happens after vesting period?
Once vesting occurs, the benefits of the plan or stock cannot be revoked. This is true even if the employee no longer works for the company, so long as the vesting period has been met. A vested benefit is a financial incentive offered by an employer to an employee.
What is vesting stock?
What is vesting? When a company gives you equity as part of your compensation package, they’re offering you partial ownership of the company. However, your stock usually has to vest first, meaning you typically need to work for the company for a period of time if you want to become an owner.
What is a time based stock vesting cliff?
With time-based stock vesting, you earn options or shares over time. Most time-based vesting schedules have a vesting cliff. A cliff is when the first portion of your option grant vests. After the cliff, you usually gradually vest the remaining options each month or quarter. Many companies offer option grants with a one-year cliff.
What is milestone based vesting?
With milestone vesting, you get your options or shares after completing a specific project or when you and/or the company reach a business goal (e.g. the company hits a certain valuation). This type of vesting isn’t as common as time-based vesting.
How many shares of Sadie's stock are vested?
Over the next three years, an additional four shares vest every month. By November 1st, 2021, Sadie is completely vested and can exercise all 192 of the shares in her option grant if she chooses.
What is hybrid vesting?
Hybrid vesting. Hybrid vesting is a combination of time-based and milestone vesting. With hybrid vesting, you have to both work at the company for a certain amount of time and hit one or more milestones to receive your options or shares.
Do you have to buy RSUs to vest?
But unlike stock options, you don’t need to purchase them—you just need to wait for them to vest.
Can you exercise stock options?
With stock options, like ISOs or NSOs, you aren’t getting actual shares of stock—yet. Instead, you’re getting the right to exercise (buy) a set number of shares at a fixed price later on. You usually have to earn your options over time—a process called vesting. And you can only exercise vested stock options (unless your company allows early exercising).
What is vesting schedule?
In simple terms, the stock issued to a founder at incorporation is subject to a vesting schedule, meaning that incremental portions of the stock will vest over time as the founder’s involvement with the company continues (i.e., the founder continues to provide valuable services to the company).
What happens to stock after a cliff?
For example, a vesting schedule may provide that an initial portion of the stock will vest after a specified waiting period has been met (i.e., a “cliff”), and then the stock will continue to vest in equal incremental amounts thereafter for a specified period of time. If at any time the founder leaves the company or stops providing services to the company while the stock is still vesting, then the stock will stop vesting upon his or her termination from the company, and the company then will have the right to repurchase from the founder any stock that has not yet vested.
What happens when a founder jumps ship?
If a founder jumps ship, then the company can pull back some or all of their shares depending on the vesting schedule.
What happens to stock when founder leaves?
If at any time the founder leaves the company or stops providing services to the company while the stock is still vesting, then the stock will stop vesting upon his or her termination from the company, and the company then will have the right to repurchase from the founder any stock that has not yet vested.
Can co-founders buy back shares?
This situation would have been a lot better if the co-founders would have insisted on standard cliff vesting at incorporation, because four months later, they still would be able to buy back all of the technical co-founder’s shares at the low founder stock price. Instead, the company only has the right to buy back the unvested portion of the shares and he will continue to own a significant portion of the company (i.e., his vested shares at incorporation). Ironically, he will continue to hold shares for behavior that actually has harmed the company (and could jeopardize its existence).
What is a vesting plan?
To encourage employee loyalty, employers frequently make contributions to your retirement or stock-option account subject to a vesting plan. This incentive program set up by a company determines when you'll be fully "vested" in, or acquire full ownership of, employer contributions to the plan.
What to do if you are not sure about your vesting schedule?
If you're not sure about your vesting schedule, contact your human resources department or check your benefits manual to learn more about any vesting plans that your retirement or other benefit accounts may impose.
How long does a 401(k) cliff vest?
Federal law requires that cliff vesting schedules in qualified retirement plans, such as a 401 (k) or a 403 (b) plans, not exceed three years. 1 2.
What is 100% vested in a plan?
If you are 100% vested in a plan, the full balance of the plan account belongs to you, which means that your employer can't take the assets away from you for any reason.
What happens if you are not fully vested?
1. Until you are fully vested, your account balance is misleading;
Does vesting apply to your own money?
Vesting doesn't apply to any money you contribute yourself (it's your money, and you get to keep it even if you leave the company). Whenever you make a contribution to your retirement plan at work, you are 100% vested in your own contributions. Vesting schedules apply only to funds that employers contribute on your behalf.
Do stock options vest in retirement?
Because most stock options are not part of an employee's retirement plan, their vesting schedules are not limited by the same federal rules that govern matching contributions.
What is vesting money?
It is your money to keep regardless of how long you work for that company or if you choose to find employment elsewhere. Vesting only applies to the funds that an employer contributes.
Why is vesting schedule important?
It is important because it rewards those who work to make a company great, and keeps all parties committed to the success of the company. Vesting schedules also protect the employer from losing money on benefits for employees that do not stick around for the long haul.
What is cliff vesting?
Cliff vesting is the process that entitles an employee to their full benefits on a given date. For example, if a company has a two-year cliff vesting schedule, an employee will be 100% vested after 2 years of employment.
Why do employers vest their employees?
The reason that many employers have vesting policies is to encourage their employees to stay with their company. It provides employers with less turnover as many employees will stick with their positions until they are fully vested to get the most out of their benefits.
What is immediate vesting?
Immediate vesting is the most straightforward. An employee immediately owns the benefits upon their first day of employment.
How much vested is a 4 year contract?
For example, if a company has a 4-year graded vesting schedule, from the date of your hire to your first year of employment you will be 0% vested. After your first year of employment, you will be 25% vested.
How long is a vesting period?
There are different types of vesting periods, each with their own requirements. The most common is three to five years.
What is vesting shares?
Shares vesting refer to the grant of shares over a pre-decided tenure as the compensation package or contribution towards the pension scheme to the employees or to the founders of the company to reward them for their work performance and to retain them for longer years in the company.
What is share vesting?
Through share vesting, the company can keep its employees loyal to the company.
How long does a vesting share accrue?
Another disadvantage is that an employee does vesting on a long term basis. The benefit of vesting shares accrues to the employee only after four to five years, i.e., once he is fully vested. Recently hired employees may not receive the benefit of it as there exists a cliff period.
Why is share vesting beneficial?
It is also very beneficial to employees as it puts them in the position of receiving high value for their shares, as in the case of Facebook. When companies include share vesting as a part of the employee contract, it leads to improvement in the performance of the employee. As the employee’s performance is tied to shares offered for vesting, ...
What does vesting mean in a pension plan?
It means share awarded to employees or founders as a part of the compensation package. It could be a contribution to the pension plan and also as a way to reward and retain them. This shares by an individual is a process that happens over many years (usually four to five years). Through share vesting, the company can keep its employees loyal to ...
What are the disadvantages of vesting shares?
Besides the many benefits of vesting in shares, one major disadvantage is that tax consequences are depending on the types of shares vested, tax liability changes. Taxes may also apply depending on when you choose to buy and sell your share or stock option.
How long does it take to fully vested an employee?
Hence, only after four years, the employee is said to be fully vested. Fully Vested Fully vested refers to a situation where an investor enjoys full authority and control of every financial instrument (stock options, retirement benefits, profit sharing). It is often followed by a vesting schedule.
What is time based stock vesting?
Time-based vesting is probably the most common type of stock vesting. The way it works is the following: At some point in time (typically when you are hired or your contract is renewed), your company grants you a certain number of options, or other types of equity which vest over time. After that, for a fixed period of time, ...
What does vesting mean in equity?
It means that when you are given equity , you are not handed a part of the company in the very moment you sign your contract. Rather, what you’re signing is an agreement with the company that you are entitled to buy a certain number of shares in the company, for a pre-agreed upon price (called ‘the exercise price’), when certain conditions are met in the future. The fulfillment of those conditions is what we broadly refer to as vesting.
How long does equity vest?
Typically, your equity will vest cumulatively over fixed intervals of time after the vesting cliff. For example, you might be able to exercise 25% of your options after your first year at the company, 50% on the second, 75% on the third, and the full amount of equity on your fourth year with the business.
What is the expiration date of stock?
Very simply, the stock expiration date is the date marking the end of your exercise window, after which any unexercised vested equity you were previously entitled to returns to the company.
Why is time based vesting better than milestone based vesting?
However, it can sometimes be hard to measure certain milestones; or if these take to long to be materialised, employees might lose their hope and interest in actually claiming the value of their equity. This is why time-based vesting is often considered as a simpler solution by employers, and preferred over milestone-based vesting.
How long does it take to exercise vested equity?
This period is called an ‘exercise window’, and it typically lasts for 90 days (although this may vary from one company to the next, so make sure to check your grant agreement).
Can you exercise equity after a fixed period of time?
After that, for a fixed period of time, you will not be able to exercise (i.e. actually buy) any of the equity that has been granted to you. For example, many companies do not let you exercise your equity for the first year of employment - although this can vary vastly from one business to the next.