What past stock market declines can teach us?
Types of stock market declines. A look back at stock market history since 1951 shows that declines have varied widely in intensity, length and frequency. In the midst of a decline, it’s been nearly impossible to tell the difference between a slight dip and a more prolonged correction. The table below shows that declines in the Standard & Poor's 500 Index have been somewhat regular events.
What causes stock market drop?
Why Do Stock Prices Drop?
- Earnings Reports. Public companies release earnings reports four times a year (quarterly). ...
- Negative Corporate News. Negative corporate news ranges from product recalls to violations in accounting practices. ...
- Implicit Value. ...
- Explicit Value. ...
- Supply and Demand. ...
Are stocks about to crash?
Something is loading. As Jeremy Grantham continues to warn about the imminent threat of a stock market crash, the asset management firm he co-founded is making trades that partly reflect that view.
Is the stock market healthy or not?
Many strategists were concerned by the sharp move in stocks like AMC, including Matt Maley, chief market strategist for Miller Tabak + Co, who commented that “the action in AMC shows that today’s stock market is not a healthy one.”. The stock market was hit hard by the selling early Thursday, June 3.
How much was the S&P down in 2018?
When the S&P 500 plunged in 2018, it pulled back before hitting 20 percent. Stock market corrections — when stocks drop 10 percent from their latest peaks — are not uncommon. Nearly a dozen have taken place since 2000. But it's rare for a correction to turn into a bear market, a decline of 20 percent.
Was 2018 a bear market?
The next downturn during the financial crisis lasted about 18 months from peak to trough. Then came two near-bear markets, a decline of 19.4% in 2011 that lasted five months and 19.8% in 2018 that lasted three months. And finally, the most recent bear market in 2020 lasted just 33 days.
How much has the market grown since 2018?
The S&P 500's return can fluctuate widely year to yearYearS&P 500 annual return2018-4.4%201931.5%202018.4%202128.76 more rows•May 26, 2022
What happened to stock market in q4 2018?
The last quarter of 2018 was the worst quarterly performance for stocks since the third quarter of 2011, when the eurozone debt crisis saw stock markets tumble 17.1%. A large proportion of the quarter's losses in 2018 came in December, when global stocks fell 7.7%.
What caused 2018 crash?
The S&P 500 in December 2018 fell more than 9% as investors feared a central bank ready to tighten monetary policy, a slowing economy, and an intensifying trade war between the U.S. and China. It marked the worst December since 1931.
What caused the 2018 bear market?
The Bottom Line The most recent bear market was the result of a global health crisis compounded by fear, which initially triggered a wave of layoffs, corporate shutdowns, and financial disruptions.
How much has the stock market dropped in 2022?
Major indexes have notched big declines in 2022 as high inflation, rising interest rates and growing concerns about corporate profits and economic growth dent investors' appetite for risk. The blue-chips are down 18% this year, while the S&P 500 is down 23% and the tech-heavy Nasdaq Composite has fallen 32%.
How much is the market down year to date?
Performance5 Day-1.28%1 Month-5.48%3 Month-10.69%YTD-14.42%1 Year-10.60%
Will the stock market go up in 2021?
The S&P 500 stock index had a great run in 2021, rising more than 25 percent — on top of its 16 percent gain during the first year of the pandemic. The index hit 70 new closing highs in 2021, second only to 1995, when there were 77, said Howard Silverblatt, an analyst at S&P Dow Jones Indices.
Will the Stock Market Crash 2022?
Stocks in 2022 are off to a terrible start, with the S&P 500 down close to 20% since the start of the year as of May 23. Investors in Big Tech are growing more concerned about the economic growth outlook and are pulling back from risky parts of the market that are sensitive to inflation and rising interest rates.
Was 2018 a good year for the stock market?
2018 was not a good year for the stock market. Since the beginning of the year, the Dow Jones Industrial Average has lost about 10 percent of its value, as did the S&P 500. The Nasdaq dropped roughly 8 percent.
What caused the 2016 stock market crash?
On January 20, 2016, due to crude oil falling below $27 a barrel, the DJIA closed down 249 points after falling 565 points intraday. The FTSE 100 fell 3.62% in a single day and entered bear market territory.
When did the stock market get boosted?
The market was further boosted at the end of 2017 and into the beginning of 2018 by the Republican tax cut package Trump signed into law at the end of last year.
How much has the Dow Jones lost?
Since the beginning of the year, the Dow Jones Industrial Average has lost about 10 percent of its value, as did the S&P 500. The Nasdaq dropped roughly 8 percent. The vast majority of losses have come since October, when the stock market, which was experiencing the longest bull run in history, took a turn for the worst.
What goods did Trump tariff?
The Trump administration’s tariffs on imported aluminum, steel, and other goods have introduced a large amount of uncertainty into the global economy.
Why is the Federal Reserve tightening its monetary policy?
That reduces liquidity in the market, creating obstacles for obtaining credit and loans — factors that could slow down the global economy.
What would happen if the Fed had another recession?
If another recession hits, the Fed would not have as much flexibility to try and revive the economy.
Will hiring be weak in 2019?
Hiring remains strong, but if it weakens in 2019, it would make investors more pessimistic and likely to sell stocks, potentially helping speed up an economic downturn.
Is the stock market an economy?
The stock market is not the economy. It’s worth remembering that there is a fundamental difference between economic indicators like the unemployment rate and the stock market. The economic indicators are backwards looking; they tell us what the unemployment rate was in the last few weeks or months.
What happened to the markets after Trump tweeted "I am a tariff man"?
Markets tumbled after Trump tweeted “I am a Tariff Man” and the Trump administration backed off earlier claims of a trade-war truce with China.
What is the Federal Reserve's interest rate increase?
Dec. 19, 2018. The Federal Reserve announced the interest rate would increase from 2.25 percent to 2.5 percent, the fourth increase this year. Higher rates mean higher borrowing costs but also tamp down inflation and aim to avert bubbles.
How many times has the Federal Reserve raised interest rates?
The Federal Reserve raised interest rates four times this year, increasing the rate a total of one point across the year. Nov. 20, 2018. All the year’s gains were erased on Nov. 20.
When did the dot com bubble burst?
It wasn’t long into 2000 that the dot-com bubble burst. Those who invested at the start of that decade wouldn’t have broken even until seven years later. And that would have been short lived, as the country plunged into the Great Recession shortly thereafter. Most of the gains since 2000 have only been in the past five years.
When did the S&P 500 hit its peak?
The housing market had already been dragging down stocks, but the S&P 500 reached its pre-Great Recession peak in October 2007. The markets boomed around news that interest rates would be cut by half a point, surpassing investor expectations.
When did the S&P 500 reach its all time high?
Better-than-expected earnings reports led the S&P 500 to an all-time high on Jan. 26, one of many record highs across the year culminating with a final peak on Sept. 20. March 21, 2018 June 13, 2018 Sept. 26, 2018 Dec. 19, 2018.
Is the stock market up after Trump?
Markets are still up overall since Trump entered office. Throughout his presidency, Trump has tied market gains to his administration, while pointing the finger elsewhere during its decline.
How much did the Dow drop at the closing bell?
Buyers charged back in and limited the damage, but at the closing bell the Dow was still down 1,175 points, by far its worst closing point decline on record. The drop amounted to 4.6% -- the biggest decline since August 2011, during the European debt crisis.
How many points did the Dow drop?
The Dow was down 800 points at 3 p.m. Within minutes, it was down 900, 1,000 -- and then 1,500 points. At its low, the Dow was down 1,597 points, before buyers rushed in and limited the decline.
What would happen if the economy got stronger?
If the economy gets much stronger, it could touch off inflation, which has been mysteriously missing for the nine years of the post-crisis recovery. That could force the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates faster than planned.
What did Trump say about the economy?
The statement cited strengthening economic growth, low unemployment and increasing wages for workers.
Is the Russell 2000 a negative index?
The Russell 2000, an index of smaller stocks that have heavy exposure to the U.S. economy, turned negative for 2018 for the first time.
Is the Dow up 40%?
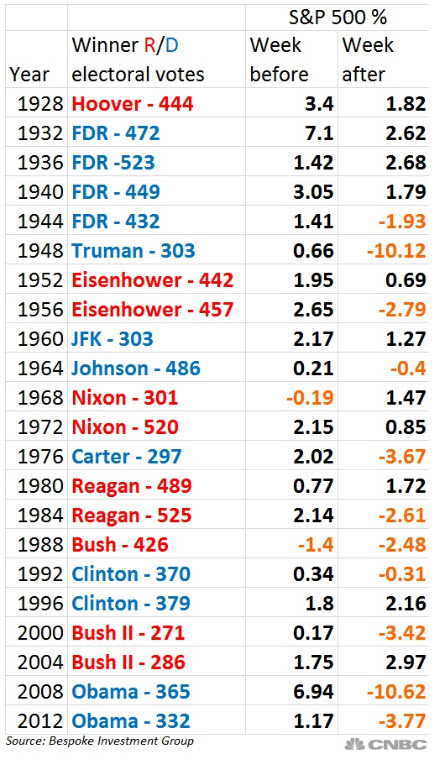
Despite the recent turmoil, the Dow remains up almost 40% since President Trump's election. The robust performance has been driven by strong corporate profits, healthy economic growth and excitement about the Republican tax cut for businesses. Analysts at Bespoke Investment Group urged calm.
Why did the stock market go into turmoil in February?
But the early February nosedive may have been exacerbated by the implosion of little-known investments used to bet that markets will stay calm .
What caused the Dow and S&P 500 to decline?
Inflation fears have caused the Dow and S&P 500 to do something they haven't in 11 months: decline. Both indexes had their worst month in two years.
Why was the market insanity so startling?
The market insanity was even more startling because it followed a period of extreme calm. And it arrived during a roaring economy. "It's been a real roller-coaster. A wild ride," said Ed Yardeni, president of investment advisory Yardeni Research.
Why is Wall Street glued to the 10-year Treasury rate?
Wall Street is glued to the 10-year Treasury rate because it helps set the price on virtually all other assets. When rates are low, like they had been, it means bonds aren't returning much money, and it encourages investors to gamble on riskier assets like stocks.
Who said the market has seen its lows?
Yardeni said he thinks the market has seen its lows for now.
What happened in February?
In early February, the runaway train stock market ran smack into spiking bond rates that were pricing in the threat of inflation. Investors suddenly became worried the economy, boosted by huge tax cuts, could overheated and force the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates.
How much did the Nasdaq lose in 2018?
The Nasdaq Composite lost 3.9 percent in 2018, its worst year in a decade, when it dropped 40 percent. The S&P 500 and Dow fell for the first time in three years, while the Nasdaq snapped a six-year winning streak. 2018 was a year fraught with volatility, characterized by record highs and sharp reversals. This year also marks the first time ever ...
What was the Dow Jones Industrial Average down in 2018?
After solid gains on Monday, the and Dow Jones Industrial Average were down 6.2 percent and 5.6 percent, respectively, for 2018.
What is the best performing stock in 2018?
Merck shares rose more than 1 percent, ending the year as the best-performing Dow component of 2018. Pfizer, the second best performer on the Dow this year, also climbed 1.6 percent on Monday. Netflix jumped 4.5 percent while Amazon rose 1 percent after the popular FAANG trade (Facebook, Amazon, Apple, Netflix and Alphabet) took a beating recently.
How much was the S&P 500 down on Christmas Eve?
But that doesn’t explain just how wild a ride December was for investors. At its low price on Christmas Eve, the S&P 500 was down more than 20 percent from its record high on an intraday basis, briefly meeting the requirement for a bear market.
What was the worst stock market crash in history?
The worst stock market crash in history started in 1929 and was one of the catalysts of the Great Depression. The crash abruptly ended a period known as the Roaring Twenties, during which the economy expanded significantly and the stock market boomed.
Why did the stock market recover from Black Monday?
Because the Black Monday crash was caused primarily by programmatic trading rather than an economic problem, the stock market recovered relatively quickly. The Dow started rebounding in November, 1987, and recouped all its losses by September of 1989.
Why did the Dow drop in 1929?
The Dow didn't regain its pre-crash value until 1954. The primary cause of the 1929 stock market crash was excessive leverage. Many individual investors and investment trusts had begun buying stocks on margin, meaning that they paid only 10% of the value of a stock to acquire it under the terms of a margin loan.
What was the cause of the 1929 stock market crash?
The primary cause of the 1929 stock market crash was excessive leverage. Many individual investors and investment trusts had begun buying stocks on margin, meaning that they paid only 10% of the value of a stock to acquire it under the terms of a margin loan.
When did the Dow Jones Industrial Average rise?
The Dow Jones Industrial Average ( DJINDICES:^DJI) rose from 63 points in August, 1921, to 381 points by September of 1929 -- a six-fold increase. It started to descend from its peak on Sept. 3, before accelerating during a two-day crash on Monday, Oct. 28, and Tuesday, Oct. 29.
When did the Dow lose its value?
The stock market was bearish, meaning that its value had declined by more than 20%. The Dow continued to lose value until the summer of 1932, when it bottomed out at 41 points, a stomach-churning 89% below its peak. The Dow didn't regain its pre-crash value until 1954.
Can a stock market crash happen quickly?
While a crash of the stock market can occur quickly, many of the market's biggest crashes have had effects that were long-lasting and deep. Here's a brief look at some of the market's most notable crashes.
How much did stocks fall during the Great Depression?
During the Great Depression, after peaking, stocks fell 48% in two months, recouped half of its losses by mid-April 1930, then fell to its ultimate bottom July 8, 1932, a little over two years later. The total loss was 89.2% and it took until November 23, 1954, 25 years later, to surpass its September 3, 1929 peak.
How much were stocks overvalued in the recession?
About a year before the recession began, stocks were 49% overvalued, which was a record high. When the recession began, due to the bursting of the tech bubble, this overvaluation had fallen to 9.5%. A year after the recession, stocks were about 33% undervalued, setting the stage for the longest economic expansion and bull market in U.S. history.
How much is the VIX overvalued?
On January 26, 2018, stocks were 49.4% overvalued, breaking the previous record. Two short years later, February 19, 2020, another record was set when stocks became 58.9% overvalued. Although the VIX spiked to 43.74% during this recession, it rose even higher after it ended (B-3).
What is the shaded grey on the Dow Jones Industrial Average?
A note on the graphs below: Recessions are shaded grey, the Dow Jones Industrial Average is used for stocks , and dividends are excluded.
How much did stocks fall in the 2000s?
From its peak January 14, 2000 to its ultimate bottom October 9, 2002, stocks fell about 38% . About a year before the recession began, stocks were 49% overvalued, which was a record high. When the recession began, due to the bursting of the tech bubble, this overvaluation had fallen to 9.5%.
What was the longest recession in history?
The 1973-75 Recession: November 1, 1973 to February 28, 1975. This recession was one of the longest. Sparked by the OPEC embargo against the U.S., it was also one of the worst for stocks. Stocks lost about 43% from the start of the recession to the bottom and dropped 49% if you begin January 11 that year.
When did the 1990 recession end?
End: February 28, 1991. The 1990 recession lasted the same length of time as the 2001 recession but was more severe. Stocks trended higher in the eight years prior and peaked two weeks after the recession began. Early in the recession, stock declined, losing 26% until bottoming October 11, 1990 (C-1).
