
What was the biggest drop in the stock market in 2008?
Nov 03, 2008 · The Dow declines 774 points (6.98%), at the time the largest point drop in history. 9 Oct. 3, 2008 A reworked $700 billion TARP plan, renamed the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008,...
When did the stock market crash of 2008 happen?
By Rob Bennett The S&P 500 experienced a loss of 37 percent in 2008. Was that loss real? Or was it a mirage? I believe it was mostly a mirage.
How much did the stock market fall in 2009?
Sep 14, 2018 · A trader works on the floor of the New York Stock Exchange on September 15, 2008 in New York City. In afternoon trading the Dow Jones Industrial Average fell over 500 points as U.S. stocks suffered...
What happened to the Dow in 2008?
On October 29, 1929, the stock market dropped 11.5%, bringing the Dow 39.6% off its high. After the crash, the stock market mounted a slow comeback. By the summer of 1930, the market was up 30% from the crash low. But by July 1932, the stock …
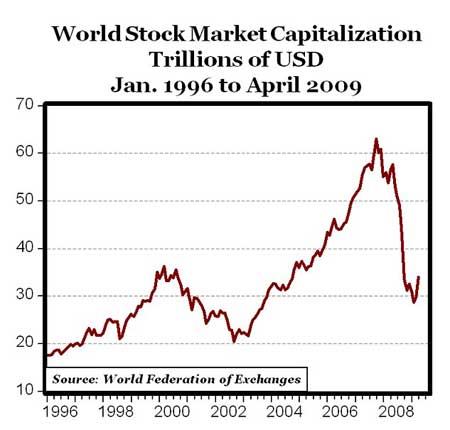
What percentage did the stock market drop in 2008?
On October 24, 2008, many of the world's stock exchanges experienced the worst declines in their history, with drops of around 10% in most indices. In the U.S., the DJIA fell 3.6%, although not as much as other markets.
How much did the stock market drop in 2008 and 2009?
From its local peak of 1,300.68 on August 28, 2008, the S&P 500 fell 48 percent in a little over six months to its low on March 9, 2009. This drop is similar to the decrease in much of the rest of the world (Bartram and Bodnar 2009).
How much did the stock market drop in 2008 daily?
On September 29, 2008, after Congress failed to pass a $700 billion bank bailout plan, the Dow Jones Industrial Average falls 777.68 points—at the time, the largest single-day point loss in its history.
How long did it take for stocks to recover after 2008?
2008: In response to the housing bubble and subprime mortgage crisis, the S&P 500 lost nearly half its value and took two years to recover. 2020: As COVID-19 spread globally in February 2020, the market fell by over 30% in a little over a month.
Who made the most money from the 2008 crash?
1. Warren Buffett. In October 2008, Warren Buffett published an article in the New York TimesOp-Ed section declaring he was buying American stocks during the equity downfall brought on by the credit crisis.
How long did the 2008 crash last?
The combination of banks unable to provide funds to businesses, and homeowners paying down debt rather than borrowing and spending, resulted in the Great Recession that began in the U.S. officially in December 2007 and lasted until June 2009, thus extending over 19 months.
How fast did the stock market crash in 2008?
The Great Recession saw the markets fall by 49% over a period of 16 months. In comparison, the Dow has fallen by about 28% over the Coronavirus crisis between February 11 and March 12, 2020.Mar 13, 2020
Why did the 2008 market crash?
The stock market and housing crash of 2008 had its origins in the unprecedented growth of the subprime mortgage market beginning in 1999. U.S. government-sponsored mortgage lenders Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac made home loans accessible to borrowers who had low credit scores and a higher risk of defaulting on loans.
What is the largest stock market loss in one-day?
"Facebook's $232 Billion Fall Sets Record for Largest One-Day Value Drop in Stock Market History." Accessed Feb. 4, 2022.Feb 9, 2022
How much has the stock market dropped in 2022?
For the first quarter of 2022, all major stock benchmarks saw their biggest quarterly losses in two years, ranging from a 4.6% decline for the S&P 500 to as much as 9% for the Nasdaq Composite.Apr 1, 2022
What was the worst stock market crash in history?
The Wall Street Crash of 1929. The stock market began right around 1600, and the first stock market crash was soon to follow. However, the Black Tuesday stock market crash that took place in 1929 remains the worst stock market crash in US history.
What was the biggest stock market crash?
1. The Great Crash Of 1929. The stock market crash of 1929, also referred to as the Great Crash or the Wall Street crash of 1929, saw both a sudden as well as a steep decline in stock prices in the United States during late October that year.Feb 9, 2022
How much did the Dow drop in 2008?
The Dow would plummet 3,600 points from its Sept. 19, 2008 intraday high of 11,483 to the Oct. 10, 2008 intraday low of 7,882. The following is a recap of the major U.S. events that unfolded during this historic three-week period.
What happened in 2008?
By the fall of 2008, borrowers were defaulting on subprime mortgages in high numbers, causing turmoil in the financial markets, the collapse of the stock market, and the ensuing global Great Recession.
What mortgages are lethal?
Among the most potentially lethal of the mortgages offered to subprime borrowers were the interest-only ARM and the payment option ARM, both adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs). Both of these mortgage types have the borrower making much lower initial payments than would be due under a fixed-rate mortgage. After a period of time, often only two or three years, these ARMs reset. The payments then fluctuate as frequently as monthly, often becoming much larger than the initial payments.
What is subprime mortgage?
Subprime mortgages are mortgages targeted at borrowers with less-than-perfect credit and less-than-adequate savings. An increase in subprime borrowing began in 1999 as the Federal National Mortgage Association (widely referred to as Fannie Mae) began a concerted effort to make home loans more accessible to those with lower credit and savings than lenders typically required. 1
What is the role of Fannie and Freddie?
2 . The role of Fannie and Freddie is to repurchase mortgages from the lenders who originated them and make money when mortgage notes are paid. Thus, ever-increasing mortgage default rates led to a crippling decrease in revenue for these two companies.
What is MBS in mortgage?
An MBS is a pool of mortgages grouped into a single security. Investors benefit from the premiums and interest payments on the individual mortgages the security contains. This market is highly profitable as long as home prices continue to rise and homeowners continue to make their mortgage payments.
Why did Bear Stearns fail?
By March 2007, with the failure of Bear Stearns due to huge losses resulting from its underwriting many of the investment vehicles linked to the subprime mortgage market, it became evident that the entire subprime lending market was in trouble.
To Date, Our Recession Articles Have Spoken To Main Street. 2008 Was About Mainstreet
I have written a few articles about my experience during the 2008 recession . Most of those have covered the potential loss of a job and reduced income. They also focused on the downfall of many of our neighbors and friends.
There Comes A Point Where There Is No Place to Hide
The reality is, 50% declines in the stock market are not abnormal. They are events that will probably happen a few times in each of our lives. You should expect and plan for such a decline. I am currently set-up for a risk tolerance to support a 60-70% decline in the market.
2008: Any Worse and The Market Would Be My Smallest Concern
That is also how I felt at the bottom of the trough in 2008. If the market dropped another 50% the faith of people in US currency would also collapse. So running to cash would be illogical. So where would you go?
Survival Trumps Retirement If the Market Fully Collapses
In essence in a world screwed up enough for the market to be worth 25% of today your concern is probably more on survival than retirement. Food and shelter would be my top concerns at that point. In essence, your portfolio has to support you to a certain level of risk. Beyond that point, we’re all just f##### anyway.
How did the banking crisis affect investors?
The banking crisis frightened investors. Their processing of all of the many negative information bits sent their way during those 12 months of time caused their belief about the future earning power of U.S. stocks to sour enough to justify slicing away one-third of the previous value of U.S. stocks.
How to avoid price crash?
Prices are always set properly, so there is no way to know what the future holds. The only way to avoid price crashes is to stay out of stocks, and it is not possible for most investors to finance comfortable retirements without investing heavily in stocks.
When was the P/E10 value improved?
The P/E10 value was dramatically improved in early 2009 compared to where it stood in early 2008. The P/E10 metric was telling all investors who would listen that stocks were a good buy, and that investors had overreacted in their decision to lop off one-third of the price of the market in a single year.
Will there be a mortgage crisis in the next 12 months?
First, there is always some chance that a mortgage crisis or a banking crisis will develop over the course of the next 12 months. According to the theory behind the Buy-and-Hold Model, it is only unanticipated negative economic developments that cause price drops.
Why did the stock market crash in 2008?
In all, the stock market crash 2008 as a result of a series of events that eventually led to the failure of some of the largest companies in the US.
What was the impact of the 2008 stock market crash?
There is no doubt behind the saying, that the crash pushed the banking system towards the edge of collapse.
What was the Dow value in September 2008?
The day was ended at the Dow value of 11,388.44. On September 20, 2008, the bank bailout bill was sent to Congress by Secretary Paulson and Federal Reserve Chair. The Dow fell to 777.68 points during the intraday trading that increased panic in the Global Market.
How many points did the Dow drop in 2008?
By September 17, 2008, the Dow fell by 446.92 points. By the end of the week on September 19, 2008, the Fed established the Asset-Backed Commercial Paper Money Market Mutual Fund Liquidity Facility that committed to offer loans to banks to buy Commerical paper from the money market funds.
How much did the Fed lose from Lehman Brothers?
By making $85 billion loans for 79.9% equity the Fed took ownership of the AIG. With the collapse of Lehman Brothers, there was a loss of $196 billion that increased the panic among many businesses. Bank has driven up the rates as they were afraid to lend money. By September 17, 2008, the Dow fell by 446.92 points.
What was the fourth cause of the 2008 financial crisis?
The fourth cause of the crash of 2008 was found to be the depression era Glass Steagall Act (1933) that allowed banks, securities firms and other insurance companies to enter into each other’s markets resulting in the formation of the bank that was too big to fail.
What were the causes of the Federal Reserve's crash?
Some of the top reasons for the crash are: Mild Recession in the Federal Reserve. Federal Reserve the Central Bank was facing a mild recession since 2001. The recession period resulted in the reduction of the federal funds rate from 6.5 to 1.75 from May 2000 to December 2001.
What was the financial crisis of 2008?
The 2008 financial crisis had its origins in the housing market, for generations the symbolic cornerstone of American prosperity. Federal policy conspicuously supported the American dream of homeownership since at least the 1930s, when the U.S. government began to back the mortgage market. It went further after WWII, offering veterans cheap home loans through the G.I. Bill. Policymakers reasoned they could avoid a return to prewar slump conditions so long as the undeveloped lands around cities could fill up with new houses, and the new houses with new appliances, and the new driveways with new cars. All this new buying meant new jobs, and security for generations to come.
What was the Commodity Futures Modernization Act of 2000?
Congress gave them one way to do so in 2000, with the Commodity Futures Modernization Act, deregulating over-the-counter derivatives—securities that were essentially bets that two parties could privately make on the future price of an asset. Like, for example, bundled mortgages.
Why did the mortgage salesmen make these deals without investigating a borrower's fitness or a property's
The salesmen could make these deals without investigating a borrower's fitness or a property's value because the lenders they represented had no intention of keeping the loans. Lenders would sell these mortgages onward; bankers would bundle them into securities and peddle them to institutional investors eager for the returns the American housing market had yielded so consistently since the 1930s. The ultimate mortgage owners would often be thousands of miles away and unaware of what they had bought. They knew only that the rating agencies said it was as safe as houses always had been, at least since the Depression.
What did Jim Bunning call the bailouts?
Senator Jim Bunning of Kentucky called the bailouts "a calamity for our free-market system" and, essentially, "socialism"—albeit the sort of socialism that favored Wall Street, rather than workers. Earlier in the year, Paulson had identified Lehman as a potential problem and spoke privately to its chief executive, Richard Fuld.
What did the Glass-Steagall Act do?
the Glass-Steagall Act ), they separated these newly secure institutions from the investment banks that engaged in riskier financial endeavors.
What was the financial environment like in the early 21st century?
The financial environment of the early 21st century looked more like the United States before the Depression than after: a country on the brink of a crash. pinterest-pin-it. An employee of Lehman Brothers Holdings Inc. carrying a box out of the company's headquarters after it filed for bankruptcy.
When did Paulson say the government would not rescue Lehman?
By the weekend of September 13-14, 2008, Lehman was clearly finished, with perhaps tens of billions of dollars in overvalued assets on its balance sheets.
What happened to the stock market after the 1929 crash?
After the crash, the stock market mounted a slow comeback. By the summer of 1930, the market was up 30% from the crash low. But by July 1932, the stock market hit a low that made the 1929 crash. By the summer of 1932, the Dow had lost almost 89% of its value and traded more than 50% below the low it had reached on October 29, 1929.
How much did the Dow drop in 1987?
On October 19, 1987, the stock market crashed. The Dow dropped 508 points or 22.6% in a single trading day. This was a drop of 36.7% from its high on August 25, 1987.
How much wealth was lost in the 2000 crash?
The Crash of 2000. A total of 8 trillion dollars of wealth was lost in the crash of 2000. From 1992-2000, the markets and the economy experienced a period of record expansion. On September 1, 2000, the NASDAQ traded at 4234.33. From September 2000 to January 2, 2001, the NASDAQ dropped 45.9%.
What happened in 1987?
The Crash of 1987. During this crash, 1/2 trillion dollars of wealth were erased. The markets hit a new high on August 25, 1987 when the Dow hit a record 2722.44 points. Then, the Dow started to head down. On October 19, 1987, the stock market crashed. The Dow dropped 508 points or 22.6% in a single trading day.
What is a weak technical position on the bull side?
"A market (or a stock) is said to be in a weak technical position on the bull side when the buying power has been exhausted, either in a small or a large way. A campaign of distribution exhausts buying power in a large way because much of the floating supply of stocks is then in the hands of traders and the public. Sponsors and large operators have sold. Those of the public who still hold these stocks are potentially bearish factors because, having bought, they must sooner or later sell, and their selling will bring pressure upon the market.
Why did large institutional investment companies use computers?
Large institutional investment companies used computers to execute large stock trades automatically when certain market conditions prevailed. Some analysts claim that the program trading of index futures and derivatives securities was also to blame.
How much wealth was lost in the 1929 stock market crash?
The Crash of 1929. In total, 14 billion dollars of wealth were lost during the market crash. On September 4, 1929, the stock market hit an all-time high. Banks were heavily invested in stocks, and individual investors borrowed on margin to invest in stocks.
Worse Than 2008 or Even The Great Depression
Euro Pacific Capital CEO and chief strategist Peter Schiff predicted this market crash in September 2018. And he nailed the timing. He told the New York Post it would hit within the next two years, near the end of Donald Trump’s first term. When the rally came crashing down in February, his prediction came true like clockwork:
Systemic Risk Taking Worse Than 2008
While macro indicators of systemic risk were already topping pre-2008 levels about two years ago, they’re even worse today.
Dow to 13,600 in 2008 Crash Scenario
If markets end up with a crash as severe as 2008, the Dow won’t bottom out until it reaches the 13,600 handle. From its intra-day peak of 14,198 on Oct. 11, 2007, to the market low of 6,469 on Mar. 6, 2009, the Dow Jones Industrial average lost 54% of its value. If it loses 54% of its 29,551.42 all time high on Feb.

2007
- The Dow opened the year at 12,474.52.2 It rose despite growing concerns about the subprime mortgage crisis. On December 19, 2006, the U.S. Department of Commerce warned that October's new home permits were 28% fewer than the year before.4 But economists didn't think the housin…
2008
- At the end of January, the BEA revised its fourth-quarter 2007 GDP growth estimate down.9 It said growth was only 0.6%. The economy lost 17,000 jobs, the first time since 2004.10 The Dow shrugged off the news and hovered between 12,000 and 13,000 until March.2 On March 17, the Federal Reserve intervened to save the failing investment bank, Bear Stearns. The Dow dropped …
September 2008
- The month started with chilling news. On Monday, September 15, 2008, Lehman Brothers declared bankruptcy. The Dow dropped more than 200 points.2 On Tuesday, September 16, 2008, the Fed announced it was bailing out insurance giant American International Group Inc. It made an $85 billion loan in return for 79.9% equity, effectively taking ownership. AIG had run out of cash. It wa…
October 2008
- Congress finally passed the bailout bill in early October, but the damage had already been done.24 The Labor Department reported that the economy had lost a whopping 159,000 jobs in the prior month.25 On Monday, October 6, 2008, the Dow dropped by 800 points, closing below 10,000 for the first time since 2004.26 The Fed tried to prop up banks by lending $540 billion to money mar…
November 2008
- The month began with more bad news. The Labor Department reported that the economy had lost a staggering 240,000 jobs in October.34 The AIG bailout grew to $150 billion.35 The Bush administration announced it was using part of the $700 billion bailouts to buy preferred stocks in the nations' banks.36 The Big Three automakers asked for a federal bailout. By November 20, 20…
2009
- On January 2, 2009, the Dow climbed to 9,034.69.2 Investors believed the new Obama administration could tackle the recession with its team of economic advisers. But the bad economic news continued. On March 5, 2009, the Dow plummeted to its bottom of 6,594.44.37 Soon afterward, President Barack Obama's economic stimulus plan instilled the confidence nee…
Aftermath
- Investors bore the emotional scars from the crash for the next four years. On June 1, 2012, they panicked over a poor May jobs report and the eurozone debt crisis. The Dow dropped 275 points.39 The 10-year benchmark Treasury yield dropped to 1.47.40 This yield was the lowest rate in more than 200 years.41It signaled that the confidence that evaporated during 2008 had not q…
The Bottom Line
- The stock market crash of 2008 was a result of defaults on consolidated mortgage-backed securities. Subprime housing loans comprised most MBS. Banks offered these loans to almost everyone, even those who weren’t creditworthy. When the housing market fell, many homeowners defaulted on their loans. These defaults resounded all over the financial industry, which heavily i…