
Why were the stock markets closed during the Great Depression?
As long as there were no significant swings in stock or bond prices, brokers had sufficient capital to settle their accounts. However, since traders relied on credit, large swings in prices could and would bankrupt many of the brokers, worsening the financial panic. To avoid this problem, stock markets were closed until a solution could be found.
What happened to the stock market in 1929?
The New York Stock Exchange was founded in 1817, although its origins date back to 1792 when a group of stockbrokers and merchants signed an agreement under a buttonwood tree on Wall Street. Stock prices began to decline in September and early October 1929, and on October 18 the fall began.
What year did the stock market crash in the US?
1929 Stock Market Crash. During the 1920s, the U.S. stock market underwent rapid expansion, reaching its peak in August 1929, after a period of wild speculation.
How did the Great Depression start and end?
The Great Depression was the worst economic downturn in the history of the industrialized world, lasting from 1929 to 1939. It began after the stock market crash of October 1929, which sent Wall Street into a panic and wiped out millions of investors. Securities and Exchange Commission.

How long did it take for stocks to recover from the Great Depression?
Wall Street lore and historical charts indicate that it took 25 years to recover from the stock market crash of 1929.
How long did the stock market crash in 1929 last?
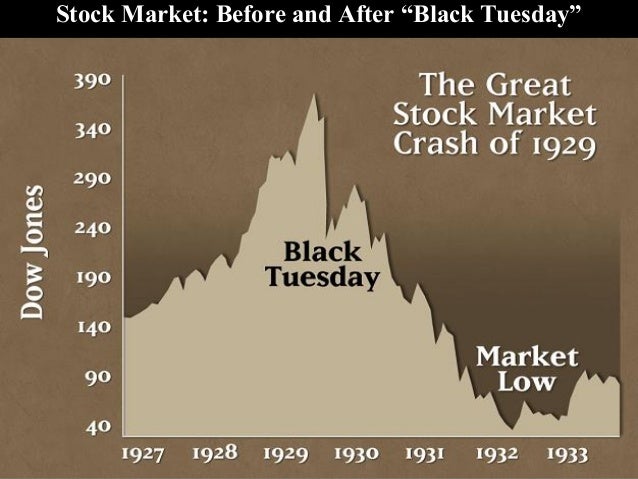
four business daysOver the course of four business days—Black Thursday (October 24) through Black Tuesday (October 29)—the Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped from 305.85 points to 230.07 points, representing a decrease in stock prices of 25 percent.
Did the stock market close during the Great Depression?
The decade, known as the "Roaring Twenties," was a period of exuberant economic and social growth within the United States. However, the era came to a dramatic and abrupt end in October 1929 when the stock market crashed, paving the way into America's Great Depression of the 1930s.
How long did the Great Depression affect the stock market?
In the aftermath of Black Tuesday, America and the rest of the industrialized world spiraled downward into the Great Depression (1929-39), the deepest and longest-lasting economic downturn in the history of the Western industrialized world up to that time.
How long did it take the stock market to recover after the 2008 crash?
The S&P 500 dropped nearly 50% and took seven years to recover. 2008: In response to the housing bubble and subprime mortgage crisis, the S&P 500 lost nearly half its value and took two years to recover. 2020: As COVID-19 spread globally in February 2020, the market fell by over 30% in a little over a month.
Who made money during the Great Depression?
Not everyone, however, lost money during the worst economic downturn in American history. Business titans such as William Boeing and Walter Chrysler actually grew their fortunes during the Great Depression.
How much did the average stock price drop between 1929 and 1932?
This is equivalent to an 18% annual growth rate in value for the seven years. From 1929 to 1932 stocks lost 73% of their value (different indices measured at different time would give different measures of the increase and decrease). The price increases were large, but not beyond comprehension.
Will the stock market crash 2022?
Stocks in 2022 are off to a terrible start, with the S&P 500 down close to 20% since the start of the year as of May 23. Investors in Big Tech are growing more concerned about the economic growth outlook and are pulling back from risky parts of the market that are sensitive to inflation and rising interest rates.
What were the best investments during the Great Depression?
Even though stocks cratered in the 1929 crash, government bonds were safe havens for investors. A position in bonds probably wouldn't have shielded you completely from stock-market losses, but it certainly would have softened the blow. 2. Keep cash in reserve.
Who profited from the stock market crash of 1929?
The classic way to profit in a declining market is via a short sale — selling stock you've borrowed (e.g., from a broker) in hopes the price will drop, enabling you to buy cheaper shares to pay off the loan. One famous character who made money this way in the 1929 crash was speculator Jesse Lauriston Livermore.
What happens to your money in the bank during a depression?
The good news is your money is protected as long as your bank is federally insured (FDIC). The FDIC is an independent agency created by Congress in 1933 in response to the many bank failures during the Great Depression.
Can the Great Depression happen again?
Could a Great Depression happen again? Possibly, but it would take a repeat of the bipartisan and devastatingly foolish policies of the 1920s and ' 30s to bring it about. For the most part, economists now know that the stock market did not cause the 1929 crash.
When did the stock market crash?
The 1929 stock market crash was the first in modern history, but it wasn't the last. The U.S. stock market also crashed in 1987, 2000, 2008, and 2020. There have also been several flash crashes since the 2008 crash.
How did the stock market crash affect people?
The crash wiped people out. They were forced to sell businesses and cash in their life savings. Brokers called in their loans when the stock market started falling. People scrambled to find enough money to pay for their margins. They lost faith in Wall Street.
What were the three key trading dates of the Dow crash?
The three key trading dates of the crash were Black Thursday, Black Monday, and Black Tuesday. The latter two days were among the four worst days the Dow has ever seen, by percentage decline.
What happened on September 26th 1929?
September 26: The Bank of England also raised its rate to protect the gold standard. September 29, 1929: The Hatry Case threw British markets into panic. 6. October 3: Great Britain's Chancellor of the Exchequer Phillip Snowden called the U.S. stock market a "speculative orgy.".
How much did the Dow rise in 1933?
On March 15, 1933, the Dow rose 15.34%, a gain of 8.26 points, to close at 62.1. 8. The timeline of the Great Depression tracks critical events leading up to the greatest economic crisis the United States ever had. The Depression devastated the U.S. economy.
What happened in 1929?
Updated September 02, 2020. The stock market crash of 1929 was a collapse of stock prices that began on Oct. 24, 1929. By Oct. 29, 1929, the Dow Jones Industrial Average had dropped 24.8%, marking one of the worst declines in U.S. history. 1 It destroyed confidence in Wall Street markets and led to the Great Depression .
Why did banks honor 10 cents for every dollar?
That's because they had used their depositors' savings, without their knowledge, to buy stocks. November 23, 1954: The Dow finally regained its September 3, 1929, high, closing at 382.74. 8.
How many times did stock prices go up in 1929?
Until the peak in 1929, stock prices went up by nearly 10 times. In the 1920s, investing in the stock market became somewhat of a national pastime for those who could afford it and even those who could not—the latter borrowed from stockbrokers to finance their investments. The economic growth created an environment in which speculating in stocks ...
What was the stock market like in the 1920s?
In the first half of the 1920s, companies experienced a great deal of success in exporting to Europe, which was rebuilding from World War I. Unemployment was low, and automobiles spread across the country, creating jobs and efficiencies for the economy. Until the peak in 1929, stock prices went up by nearly 10 times. In the 1920s, investing in the stock market became somewhat of a national pastime for those who could afford it and even those who could not—the latter borrowed from stockbrokers to finance their investments.
Why did companies acquire money cheaply?
Essentially, companies could acquire money cheaply due to high share prices and invest in their own production with the requisite optimism. This overproduction eventually led to oversupply in many areas of the market, such as farm crops, steel, and iron.
What was the result of the Great War?
The result was a series of legislative measures by the U.S. Congress to increase tariffs on imports from Europe.
What happens when the stock market falls?
However, when markets are falling, the losses in the stock positions are also magnified. If a portfolio loses value too rapidly, the broker will issue a margin call, which is a notice to deposit more money to cover the decline in the portfolio's value.
Why did people buy stocks in 1929?
In mid-1929, the economy stumbled due to excess production in many industries, creating an oversupply. Essentially, companies could acquire money cheaply due to high share prices and invest in their own production with the requisite optimism.
Why did the economy stumbled in 1929?
In mid-1929, the economy stumbled due to excess production in many industries, creating an oversupply.
How long did it take the stock market to recover from the Great Depression?
You may have heard that it took 25 years for the stock market to recover during the Great Depression. I’ve heard it and simply accepted it as truth, until today. It’s true that the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA or just “Dow”) peaked at 381.17 on September 3rd, 1929. It is also true that the DJIA did not reach that level of 381.17 again until November 23rd, 1954. That is a span of over 25 years.
How long did it take for the Dow to recover?
The truth is that it took about 7 years for an investor to recover (1929-1936), even if they invested all their money at the very peak. This came 4.5 years after the Dow hit its period low of 41.22 in the middle of 1932. Why?
What was the dividend yield in 1932?
The absolute dividend payout did not drop nearly as severely as the prices. When the Dow hit a low of 41.22 on July 8, 1932 (that 90% drop you’ve read about), the dividend yield was close to 14% .
How many stocks are in the DJIA?
Human misjudgment. The DJIA is composed of 30 stocks, which are picked by humans to represent the broad market. According to this article, a total of 18 companies were swapped in and out of the DJIA between 1929 to 1932. That was the highest number of changes to the Dow ever in such a short amount of time. This was a stressful time, and the Dow committee often “sold low” and “bought high” when picking companies to remove and add.
Was the Great Depression painful?
The Great Depression was still an extraordinarily painful time with minimal social safety nets, followed closely by World War II. I recommend reading The Great Depression: A Diary by Benjamin Roth for a vivid picture of what it felt like to live through the Great Depression.
Was the Great Depression a deflationary period?
Deflation. “The Great Depression was a deflationary period. And because the Consumer Price Index in late 1936 was more than 18 percent lower than it was in the fall of 1929, stating market returns without accounting for deflation exaggerates the decline.” Every dollar actually bought significantly more in 1936 than in 1929.
When did the stock market reopen?
Although global stock markets reopened between 1914 and 1917, it wasn’t until the 1980s that the restrictions on financial markets that prevented the free flow of capital that had existed before 1914 were removed. Only after the fall of Communism did stock markets become as globally integrated as they had been before 1914.
When did the NYSE close?
Although the NYSE was closed between July 30 and December 12 of 1914, stocks were quoted by brokers and traded off the exchange.
Why did the stock market close in 1914?
Ironically, it was because of the openness of global financial markets before the war that the global closure of stock markets occurred. At the beginning of 1914, capital was free to flow from one country to another without hindrance. All the major countries of the world were on the Gold Standard, and differences in exchange rates were arbitraged ...
How did Europe solve the problem of preventing catastrophic declines in stock prices?
In Europe, the problem of preventing catastrophic declines in stock prices was solved by putting a floor on share prices. Initially, stocks and bonds were not allowed to trade below the price they had been trading at on July 31, 1914.
Why did the European exchanges shut down?
Traders throughout the world could sell bonds and shares instantly, and it was the fear of massive selling, and the impact this would have on global markets that led to the shutdown of European exchanges. There was a concern that investors would try to repatriate their money leading to massive selling, a sharp fall in prices, and large amounts of capital flowing out of one country and into another.
Why did the stock market decline during World War I?
This was due not only to the decline in earnings that occurred and general selling of shares to raise capital, but just as importantly, because of the lack of new buying and the shift of capital to government war debt.
What were the financial effects of World War I?
After the war was over, financial markets had to deal with the dislocations created by the war: inflation, increased government debt, reparation payments, the Russian Revolution, the creation of new countries, England’s failed attempt to return to the Gold Standard, the stock market crash of 1929, the Great Depression, debt defaults, competitive devaluations, the concentration of gold in France and the United States and a hundred other financial repercussions that resulted from World War I.
Why did the stock market crash in 1929?
Richardson says that Americans displayed a uniquely bad tendency for creating boom/bust markets long before the stock market crash of 1929. It stemmed from a commercial banking system in which money tended to pool in a handful of economic centers like New York City and Chicago. When a market got hot, whether it was railroad bonds or equity stocks, these banks would loan money to brokers so that investors could buy shares at steep margins. Investors would put down 10 percent of the share price and borrow the rest, using the stock or bond itself as collateral.
What was the message of the stock market in 1929?
Back in 1929, the message was “Stop loaning money to investors, ” says Richardson. “This is creating a problem.”. Recommended for you.
What was the first warning sign of a looming market correction?
He says that the first warning sign of a looming market correction was a general consensus that the blistering pace at which stock prices were rising in the late 1920s was unsustainable. “People could see in 1928 and 1929 that if stock prices kept going up at the current rate, in a few decades they’d be astronomic,” says Richardson.
What was the rallying of the economy in 1929?
economy was riding high on the decade-long winning spree called the Roaring Twenties, but the Fed was raising interest rates to slow a booming market and an increasingly vocal minority of economists and bankers were beginning to wonder how long the party could possibly last.
When did the stock market throw signals back?
Hindsight is 20/20, but the stock market threw signals back in the summer of 1929 that trouble lay ahead. In the spring and summer of 1929, the U.S. economy was riding high on the decade-long winning spree called the Roaring Twenties, but the Fed was raising interest rates to slow a booming market and an increasingly vocal minority ...
When did the Fed raise interest rates?
General Photographic Agency/Getty Images. In a last ditch effort to undercut the spike in stock prices, the Fed decided to raise interest rates in August 1929.
When did the Dow Jones Industrial Average hit rock bottom?
When the market collapse finally hit rock bottom in 1932 , the Dow Jones Industrial Average had withered away by a staggering 90 percent. Hindsight is 20/20, but there were signals back in the summer of 1929 that trouble lay ahead.
When did the Great Depression end?
Is this a valid comparison? What might we expect from stocks going forward? The Great Depression “officially” began August 1, 1929 and ended February 28, 1933, three years and seven months later.
What was the impact of the 1930s on the stock market?
During this period, stock markets took investors on a wild ride as volatility (risk) was extremely high. The 1930s brought a great deal of pain and suffering to millions of people as U.S. unemployment approached 25%, economic growth declined precipitously , 9,000 U.S. banks failed (4,000 failed in 1933), food supply lines were disrupted, ...
How much did the Dow fall during the Depression?
During the depression, the Dow fell 48% from its September 1929 peak in a little over two months, reducing our initial $100,000 investment to $52,126 (Point A). From there it rose 48%, recouping some of what was lost, bringing the portfolio’s value up to $77,149 (Point B).
Why do stocks fluctuate during bear markets?
This occurs because investors are uncertain as to what to expect.
A Timeline of What Happened
Financial Climate Leading Up to The Crash
- Earlier in the week of the stock market crash, the New York Times and other media outlets may have fanned the panic with articles about violent trading periods, short-selling, and the exit of foreign investors; however many reports downplayed the severity of these changes, comparing the market instead to a similar "spring crash" earlier that year, after which the market bounced b…
Effects of The Crash
- The crash wiped many people out. They were forced to sell businesses and cash in their life savings. Brokers called in their loans when the stock market started falling. People scrambled to find enough money to pay for their margins. They lost faith in Wall Street. By July 8, 1932, the Dow was down to 41.22. That was an 89.2% loss from its record-high close of 381.17 on September …
Key Events
- March 1929:The Dow dropped, but bankers reassured investors.
- August 8: The Federal Reserve Bank of New York raised the discount rate to 6%.16
- September 3: The Dow peaked at 381.17. That was a 27% increase over the prior year's peak.1
- September 26: The Bank of England also raised its rate to protect the gold standard.17
Black Thursday
Before The Crash: A Period of Phenomenal Growth
Overproduction and Oversupply in Markets
Global Trade and Tariffs
Excess Debt
The Aftermath of The Crash
- The stock market crash and the ensuing Great Depression (1929-1939) directly impacted nearly every segment of society and altered an entire generation's perspective and relationship to the financial markets. In a sense, the time frame after the market crash was a total reversal of the attitude of the Roaring Twenties, which had been a time of great...
Stock Market Crash Basics
Early U.S. Stock Market Crashes
- The first U.S. stock market crash took place in March of 1792.2 Prior to the Financial Crisis of 1791 to 1792, the Bank of the United States over-expanded its credit creation, which led to a speculative rise in the securities market. When a number of speculators ultimately defaulted on their loans, it set off panic selling of securities. In respons...
Contemporary Us Crashes
Other Crashes That Affected The U.S.
The Bottom Line