How are they different
| Stock | ETF | |
| Risk vs. potential return | An individual stock is a high risk inves ... | Because ETFs invest in dozens or even hu ... |
| We can see how this works in an example: ... | We can see how this works in an example: ... | |
| Cost to diversify | To get meaningful diversification with s ... | A single share of an ETF is inherently a ... |
| Market exposure | Stocks make it easy to focus some of you ... | The many different types of ETFs offer i ... |
Are ETF better than stocks?
While all investments carry risk, diversified ETFs can outperform in the long term. Are ETFs Safer Than Stocks? An individual investor who buys and holds affordable index ETFs for the long term will probably see better returns and a lower risk profile than if they hand-pick individual stocks. (Getty Images)
Are ETFs safer than stocks?
That said, if you're truly interested in diversified, " buy and hold " investing over the long term -- and most small, individual investors should be -- then ETFs could be safer than stocks in some important ways.
What are the advantages of owning individual stocks vs. ETFs?
What are the advantages of owning individual stocks vs. ETFs? And buying individual stocks allows you to make a focused investment in a company or business which you really believe in. In contrast, most ETFs may help reduce risk and give investors a way to diversify with less money as well as gain exposure to sectors, regions, and broader ...
What is ETF vs stock?
Whereas individual stock prices can fluctuate by huge margins, ETFs will generally move less dramatically. Returns from ETFs therefore tend to be less dramatic, but steadier over a long period of time. Stocks have the potential to bring investors better returns than ETFs — but they rarely do.

Are ETFs better than stocks?
Advantages of investing in ETFs ETFs tend to be less volatile than individual stocks, meaning your investment won't swing in value as much. The best ETFs have low expense ratios, the fund's cost as a percentage of your investment. The best may charge only a few dollars annually for every $10,000 invested.
What is the downside of ETFs?
However, there are disadvantages of ETFs. They come with fees, can stray from the value of their underlying asset, and (like any investment) come with risks. So it's important for any investor to understand the downside of ETFs.
Is buying an ETF the same as buying a stock?
ETFs are designed to match the performance of an index, meaning ETF investors never outperform the index. Individual stocks, on the other hand, have the potential to take off and earn outsized returns on your investment.
What are 3 advantages of ETFs?
Positive aspects of ETFs ETFs have several advantages over traditional open-end funds. The 4 most prominent advantages are trading flexibility, portfolio diversification and risk management, lower costs, and tax benefits.
Why you should not invest in ETFs?
There are many ways an ETF can stray from its intended index. That tracking error can be a cost to investors. Indexes do not hold cash but ETFs do, so a certain amount of tracking error in an ETF is expected. Fund managers generally hold some cash in a fund to pay administrative expenses and management fees.
Do ETF pay dividends?
ETFs are required to pay their investors any dividends they receive for shares that are held in the fund. They may pay in cash or in additional shares of the ETF. So, ETFs pay dividends, if any of the stocks held in the fund pay dividends.
Are ETFs good for beginners?
Are ETFs good for beginners? ETFs are great for stock market beginners and experts alike. They're relatively inexpensive, available through robo-advisors as well as traditional brokerages, and tend to be less risky than investing individual stocks.
What are the pros and cons of ETFs?
Pros vs. Cons of ETFsProsConsLower expense ratiosTrading costs to considerDiversification (similar to mutual funds)Investment mixes may be limitedTax efficiencyPartial shares may not be availableTrades execute similar to stocksMay 19, 2022
Should ETFs be held long term?
ETFs can make great, tax-efficient, long-term investments, but not every ETF is a good long-term investment. For example, inverse and leveraged ETFs are designed to be held only for short periods. In general, the more passive and diversified an ETF is, the better candidate it will make for a long-term investment.
How ETFs are taxed?
The IRS taxes dividends and interest payments from ETFs just like income from the underlying stocks or bonds, with the income being reported on your 1099 statement. Profits on ETFs sold at a gain are taxed like the underlying stocks or bonds as well.
How do you make money with ETFs?
Making money from ETFs is essentially the same as making money by investing in mutual funds because they are operated almost identically. However, the main difference between the two is that ETFs are actively traded at intervals throughout a trading day, where mutual funds are traded at the end of the trading day.
Why are ETFs becoming more popular?
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are growing in popularity because of their simplicity, cost-effective approach to investing, and the diversity they provide. As of June 2021, the U.S. ETF industry has grown to $3.9 trillion from $2.6 trillion pre-pandemic, aided by the 2019 rule passed by the SEC.
What is an ETF?
When you buy an ETF (which stands for Exchange-Traded Fund) you’re buying a whole collection of different stocks (or bonds, etc.). But more than that, an ETF is like investing in the market as a whole, rather than trying to pick individual “winners” and “losers.”.
Is it safe to invest in ETFs?
It's even safer when you invest in a portfolio of several different types of ETFs, so that if one part of the market goes down, you'll still be invested in other parts. ETFs also have much smaller fees than actively traded investments like mutual funds. Get started with Wealthsimple Trade.
Where does Andrew Goldman live?
Andrew's past work has been published in The New York Times Magazine, Bloomberg Businessweek, New York Magazine and Wired. Television appearances include NBC's Today show as well as Fox News. Andrew holds a Bachelor of Arts (English) from the University of Texas. He and his wife Robin live in Westport, Connecticut with their two boys and a Bedlington terrier. In his spare time, he hosts “The Originals" podcast.
Is it safer to buy stocks or sell them?
One is that you can buy and sell them like a stock. Another is that they're safer than buying individual stocks. One company's fortunes may go down, but it's less likely that the value of lots of companies will be quite as volatile.
How are ETFs and stocks similar?
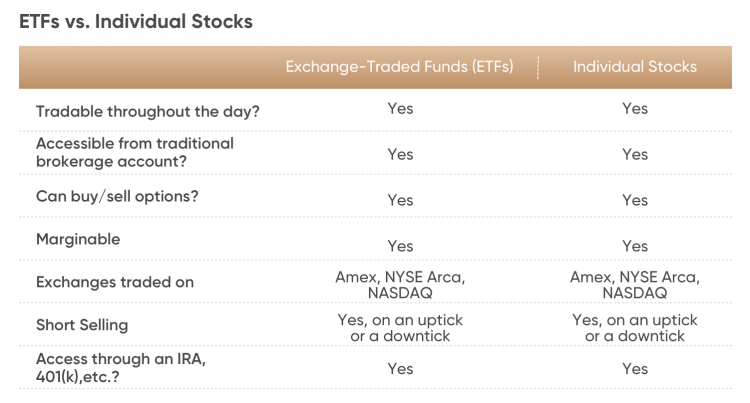
Trading ETFs vs stocks is very similar as both can typically be sold short, bought on margin, and offer options. ETFs share some common features with mutual funds – they both are made up of a diversified basket of securities – but do not typically require a minimum investment like most mutual funds.
What is exchange traded fund?
An exchange-traded fund is a marketable security with an associated price that can be easily bought or sold. ETFs usually offer lower expense ratios and broker fees, than investing in individual stocks. Comparing investor shares vs ETFs, you should note that ETFs will almost always carry much higher transaction fees.
What is the most commonly traded investment instrument?
Stocks are the most commonly traded instrument on major financial exchanges, hence the name “stock” exchange. However, there is another commonly traded investment instrument called Exchange Traded Fund (ETF), which has grown greatly in popularity among traders and investors.
What is the price of a stock based on?
When trading in stocks there is a buyer and seller. The price is based on what these two parties agree the stock is worth. At any given time, the price of a particular stock is based on supply and demand. The greater the supply of sellers on the market the less the stock will be worth and the more buyers there are the higher the price will go.
What does greater supply mean in stock market?
The greater the supply of sellers on the market the less the stock will be worth and the more buyers there are the higher the price will go. This is a simplistic explanation of stock price but it is the underlying principle behind all stock market valuation as the total value of all the shares in a company does not necessarily represent ...
Do ETFs have higher transaction fees?
Comparing investor shares vs ETFs, you should note that ETFs will almost always carry much higher transaction fees. On the other side if the investor is looking for a long-term investment and does not have the time or desire to be actively trading, they may find exchange traded funds to be a lower cost option.
Do preferred stock owners have voting rights?
Owners of preferred stock do not have voting rights but do have the right to be paid dividends before the owners of common stock.
What is the difference between ETFs and mutual funds?
They can be traded on an exchange just like a stock. So compared to mutual funds, ETFs can offer more flexibility. They can also be less expensive in terms of the expense ratio you pay to own them.
What is an ETF?
An ETF represents a basket or collection of different securities. This basket can include stocks as well as bonds, cash and other investments. A fund manager is responsible for deciding what to hold inside the ETF and how to manage fund assets, according to a specific investment goal.
What are the benefits of ETFs?
Exchange-traded funds mirror stocks in a lot of ways, though the biggest difference obviously is that you’re owning multiple securities vs. just one. Some of the other benefits of ETFs include: 1 Diversification across sectors with a single investment 2 Index tracking if you prefer index ETFs to other types of funds 3 Low minimum investments
What are the drawbacks of the stock market?
On the con side, there are two key drawbacks to consider. The first is risk. Stocks and the stock market are susceptible to volatility. The market environment during the first part of 2020 was a great example of how quickly stock prices can dip because of things that are completely outside an investor’s control.
Why are stocks better than bonds?
Compared to bonds, for example, stocks can produce higher returns over time. The more time you have to invest, the more your stock portfolio can grow through the power of compounding. That’s arguably the biggest pro in favor of stock investing. But other advantages include: Diversification and the ability to manage risk.
What are the drawbacks of diversification?
Diversification and the ability to manage risk . Potential to earn dividends for income or to reinvest in additional shares of stock. Liquidity and the ease with which stock shares can be converted to cash. On the con side, there are two key drawbacks to consider. The first is risk.
What happens when you buy shares of a company?
When you buy one or more shares of stock, what you’re getting is an equity stake in the underlying company. The value of that equity can increase or decrease over time as the stock’s share price rises or falls. Publicly traded companies can issue shares of preferred stock or common stock.
What is an ETF basket?
The ETF managers will buy stocks, commodities, bonds, and other securities, creating what is generally referred to as a basket of funds. The funds within the basket are called holdings. Fund managers then sell shares of the holdings to investors.
What is an asset in ETFs?
While these terms might seem confusing, they really are not. An asset is anything of value you might own, and a security is an asset that you can trade, either in whole or in part.
What is inverse fund?
There are even inverse funds available, which means the funds are designed to move in the opposite direction of the market with the intent of hedging the risk of their portfolio. Hedging is the term used for purchasing investments that will reduce the risk of market shifts that might cause losses. 1.
Why are investments volatile?
Investments can be volatile. Many factors affect investments; company executive turnover, supply problems, and changes in demand are only a few. Investments also come with inflation risk, which is a loss of value due to the decrease of value in the dollar. For instance, you might receive a $1.50 distribution from a stock issuer one year, ...
How long does it take to trade penny stocks?
On the other hand, penny stocks may take weeks or days to trade (if you can at all). 3.
What are the risks of investing $1.50?
The $1.50 you receive next year is able to purchase less than the previous year, making it less valuable. Other risks are interest rate risk, which affects bonds (the risk of rates rising, which decreases the bond's price), and liquidity risk, which is the risk of not being able to sell an investment if prices drop.
What is stock ownership?
Stocks, also known as equities, are shares of ownership issued by companies to raise funding. A share of stock gives you a portion of voting ownership in a company unless you purchase preferred shares (relinquishing voting rights brings higher priority in payment and often higher payments than common shares).
What is Robinhood trading?
Robinhood is the broker for traders who want a simple, easy-to-understand layout without all the bells and whistles other brokers offer. Though its trading options and account types are limited, even an absolute beginner can quickly master Robinhood’s intuitive and streamlined platform.
How do stocks and ETFs work?
2. Stocks and ETFs settle at the same price. Both stocks and ETFs settle at the price at the time of the purchase or sale. Experienced investors know the price of an equity can change by the second, the minute, or the hour — especially if there is news moving the price.
How do ETFs work?
ETFs hold the underlying assets, usually stocks, and investors buy shares of the fund, much like mutual funds — but ETFs are easier to trade because they can be traded through an online broker and don’t require a full-service broker or buying directly from the mutual fund company.
What is the difference between ETFs and stocks?
The differences between stocks and ETFs go beyond the obvious, which is that ETFs are made up of more than one holding. The differences that affect your portfolio performance revolve around diversification and focus of the investment.
What is an ETF?
An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is an investment fund that trades on a stock exchange along with stocks for individual companies. ETFs are flexible investment vehicles which purchase various types of assets to meet their investment goals. They can track an index like the S&P 500, track a sector, represent a commodity (like gold, oil, ...
What is a publicly held company?
With a publicly-held company, shares are traded on exchanges, allowing investors to easily enter or exit positions or to build a long-term position with a single stock or a portfolio of stocks. Check out the SEC’s guide on stock trading basics if you’d like to know more.
Why are mutual funds up or down?
Owners of mutual fund shares are along for the ride, whether up or down, because the price of the trade settles at the end of the trading day after the fund rebalances. Stock and ETF trades settle at the executed trade price, which may be higher or lower than the end of day price, but which won’t be a surprise.
How are ETFs created?
Most ETFs are created by financial firms, such as brokerages. First, a brokerage purchases all the stocks that are going to be included in the fund. All the stocks in the fund will produce dividends, and possibly even interest payments. The brokerage then sell shares of the ETF to investors.
What happens when you are an ETF shareholder?
When you’re an ETF shareholder, you’ll receive a portion of the ETF’s profits. That might sound like a massive sum of money, but remember that ETFs often have hundreds, if not thousands of other investors that you’ll be splitting profits with (just like with a corporation).
What is an ETF?
An exchange traded fund (commonly referred to as an “ETF”) is a basket of stocks. A single ETF may contain hundreds, if not thousands, of different stocks. But you can also find ETFs that only contain a small number of stocks. ETFs are not issued by a single company like stocks are.
How does a corporate stock work?
With corporate stocks, the dividends you earn may fluctuate in value, depending on how much the company is earning. When the company is doing very well, your shares will be more valuable and produce higher dividends.
How often do companies pay dividends?
The portion of the company’s profits that are paid to you is known as a “dividend.”. Companies may pay out dividends monthly, quarterly, or annually. The terms are stipulated when you purchase your first share. The more shares you own, the higher your dividends will be.
Why is a company's structure good?
First, it legally separates the company and the investors so that neither party can terminate the other’s assets. Second, it provides incentives for investors to keep putting money into the company (so they can increase their share of profits).
Why do companies issue stocks?
Stocks are primarily issued as a fundraising method for the company. Let’s say that a company wants to raise money for a new enterprise. For instance, an electronics company decides that it’s going to create a new line of state-of-the-art computers. The company is going to need lots of money to launch its new products.
ETF vs Stock
The difference between ETF and Stock is that ETFs can be made up of shares from a single industry, such as IT, technology, or healthcare, or they can be made up of shares from a variety of industries, such as technology healthcare, and many more. However, on the contrary, Stocks have a fixed number of shares.
What is ETF?
ETFs, or Exchange-Traded Funds, combine the shares of several companies into a single package. ETFs can be made up of shares from a single sector, such as IT, technology, or healthcare, or they can be made up of shares from numerous sectors, such as technology, healthcare, and many more.
What is Stock?
Stocks are limited-edition shares issued by a single company. Stocks are exclusively made up of shares in the parent corporation. In the case of stocks, the number of shares is usually steady and not fluctuating. Individual stocks are preferred by people who have enough time to watch the market or who work in the same area.
Main Differences Between ETF and Stock
ETF or Exchange-Traded Funds offer multiple company’s shares as a bundle. On the other hand, stocks refer to those shares which are from an individual firm only.
Conclusion
Stocks and ETFs provide easy access to the market and maybe traded on almost any financial platform. Many investors choose to mix the two in their portfolios because each has its own set of benefits.
What is the difference between ETFs and stocks?
ETFs vs. stocks: Differences. Stocks represent shares within individual companies, whereas ETFs offer shares of multiple companies within a packaged bundle. ETFs aren’t bound to a single company, so they can contain stocks in a particular sector or contain stocks that approximate a particular index, like the S&P 500, ...
Why are ETFs easy to trade?
ETFs are easy to trade because they can be traded using online brokerages, and you don’t need a full-service broker or to interact with a particular company to make your transaction. ETFs are made more accessible through the introduction of fractional investing.
What is an ETF fund?
An exchange-traded fund, or ETF, is an investment fund that can be bought and sold on the stock market just like an individual company’s stocks. ETFs are a way to build a diverse portfolio in a single transaction because they can contain commodities, stocks, bonds, or track an entire sector of the stock market, such as the S&P 500.
Can ETFs be steady streams of income?
Income stream differences. Both stocks and ETFs can be steady streams of income, although by different means . There are stocks you can invest in that pay out dividends regularly. And there are ETFs you can invest in that contain bonds, loans made to governments or corporations, that are paid back on a regular basis.
Is an ETF risky?
It depends. Stocks and ETFs are equally risky in that their relative risk depends on which stock and ETF you are investing in. An ETF that mimics a volatile sector like oil and gas can be just as risky as a high-volatility stock.
Do ETFs have liquidity?
Stocks and ETFs have nearly the same level of liquidity, meaning the ease with which they can be converted into cash. The ease of liquidity can vary based on the quality of ETF and stocks being traded. In general, high-quality stocks and ETFs have higher liquidity, whereas penny stocks and the ETF equivalent could take longer to convert.
Do you pay taxes on dividends?
Personal investors must pay taxes on any dividends and/or capital gains accrued from stocks and ETFs. Dividends are a portion of a company’s profits that are doled out to investors, whereas capital gains represent the income you make when an investment rises in value.
/GettyImages-1064145406-928f8bf183454149b7fd31e28c41b500.jpg)