Differences Between Stocks and Bonds
- Stocks Are Ownership Stakes. Stocks and bonds are two different ways for an entity to raise money to fund or expand its operations.
- Bonds Represent Debt. Bonds, on the other hand, are debt. ...
- The Difference for Investors. Each share of stock represents an ownership stake in a corporation. ...
How does a bond differ from stock?
Jul 17, 2020 · While bonds are issued by all types of entities – including governments, corporations, nonprofit organizations, etc. – stocks, on the other hand, are issued by sole proprietors , partnerships, and corporations. The basic idea behind a stock is that an entity needs to raise money and can sell stocks or shares in return for the required funds.
Are bonds safer than stocks?
Dec 03, 2021 · The difference between stocks and bonds is that stocks are shares in the ownership of a business, while bonds are a form of debt that the issuing entity promises to repay at some point in the future. A balance between the two types of funding must be achieved to ensure a proper capital structure for a business.
Which is better stocks or bonds?
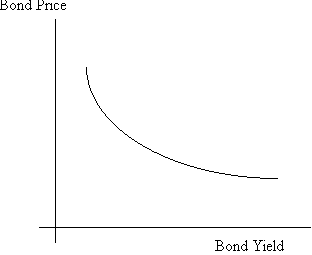
Jan 11, 2021 · This is an important distinction when it comes to the question “how do bonds differ from stocks” The bond therefore has a market price that depends on outside circumstances, particularly the market interest rates. Once it’s issued, a bond is a fixed instrument with defined terms—it will pay certain amounts at certain dates.
How are bonds different from stocks?
The value of the bond’s coupon payments is fixed at $100 per year, while the stock's dividend payment can differ each year. The upfront investment of $2,000 in the bond will be repaid at maturity, while the investment in the stock could be worth more or it could be less depending on the stock price. The Risk-Return Profiles of Bonds Versus Shares
What is the difference between a stock and a bond?
Stocks give you partial ownership in a corporation, while bonds are a loan from you to a company or government. The biggest difference between them is how they generate profit: stocks must appreciate in value and be sold later on the stock market, while most bonds pay fixed interest over time.
How do bonds and stocks make money?
To make money from stocks, you’ll need to sell the company’s shares at a higher price than you paid for them to generate a profit or capital gain.
Why are bonds sold on the market?
Bonds can also be sold on the market for capital gains if their value increases higher than what you paid for them. This could happen due to changes in interest rates, an improved rating from the credit agencies or a combination of these.
What happens if you sell stock?
In this instance, if you sold them, you’d lose money. Stocks are also known as corporate stock, common stock, corporate shares, equity shares and equity securities. Companies may issue shares to the public for several reasons, but the most common is to raise cash that can be used to fuel future growth.
What is a bond?
Bonds are a loan from you to a company or government. There’s no equity involved, nor any shares to buy. Put simply, a company or government is in debt to you when you buy a bond, and it will pay you interest on the loan for a set period, after which it will pay back the full amount you bought the bond for.
What does it mean to own stock?
Stocks represent partial ownership, or equity, in a company. When you buy stock, you’re actually purchasing a tiny slice of the company — one or more "shares." And the more shares you buy, the more of the company you own. Let’s say a company has a stock price of $50 per share, and you invest $2,500 (that's 50 shares for $50 each).
What is corporate bond?
A company’s ability to pay back debt is reflected in its credit rating, which is assigned by credit rating agencies like Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s. Corporate bonds can be grouped into two categories: investment-grade bonds and high-yield bonds. Investment grade. Higher credit rating, lower risk, lower returns.
What is the idea behind bond?
The basic idea behind a bond is that an entity needs to raise money, and therefore, can sell a bond in return for the required funds. In return, they promise to pay back the initial amount that they borrowed, in addition to interest.
Why are stocks beneficial?
Stocks are beneficial for investors who have a higher risk appetite. Stocks are much more volatile, and there is a higher chance of losing your investment since equity holders are subordinated to debt holders if a company is forced to liquidate. However, in return for the risk, stockholders have a greater potential return.
What is the IPO of stocks?
Stocks are issued initially through an Initial Public Offering (IPO), and can subsequently be traded among investors in the secondary market. Stock markets are tightly regulated by the Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) in the U.S. and are subject to tight regulation in other countries as well.
What is the most popular stock exchange in the US?
Stocks are well known for being sold on various financial exchanges – in the United States, the most popular exchanges are the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) is the largest securities exchange in the world, hosting 82% of the S&P 500, as well as 70 of the biggest.
What is interest in finance?
Interest represents the compensation rate that the investor, who is the lender in this situation, requires. They are also called fixed-income instruments because they provide a fixed amount of return, which comes in the form of interest.
Is fixed income more volatile than stocks?
Fixed-income investments are much less volatile than stocks, and also much less risky. Again, as mentioned earlier, stocks are subordinated to bonds in the event of a liquidation. However, bonds have a lower potential for excess returns than stocks do.
Is a bond sold on the central exchange?
Bonds are not sold in central exchanges. Instead, they are sold over-the-counter (OTC), which essentially means that they are traded among individual brokers from buyers and sellers, instead of on a centralized platform. It makes bonds much more illiquid, and more difficult to buy and sell relative to stocks.
What is the difference between a stock and a bond?
Key Differences. A stock is a financial instrument issued by a company depicting the right of ownership in return for funds provided as equity. A bond is a financial instrument issued for raising an additional amount of capital.
Why are bonds issued by the government?
Bonds issued by the government are extensively used and also depicts the financial stability of the country. If the yields offered are less it means the nation is in a good position to pay off its debt and does not need everyone to lend to them and vice-versa.
What is bond loan?
Bonds are actually loans that are secured by a specific physical asset. It highlights the amount of debt taken with a promise to pay the principal amount in the future and periodically offering them the yields at a pre-decided percentage. In this article, we shall understand the importance of Stocks vs Bonds and the differences between them.
Is a stock an equity or debt?
Stocks are treated as equity instruments whereas bonds are debt instruments. Debt Instruments Debt instruments provide finance for the company's growth, investments, and future planning and agree to repay the same within the stipulated time. Long-term instruments include debentures, bonds, GDRs from foreign investors.
Do stockholders have to pay DDT?
The stock market has a secondary market in place ensuring centralized trading as opposed to bonds in which trading is done Over the Counter (OTC). Stockholders may have to pay DDT (Dividend distribution tax) in case of the returns received which can further curtail the returns received but bonds are not exposed to such tax burdens.
Do bondholders get voting rights?
Bondholders are creditors to the company and do not get voting rights. The risk factor is high in stocks since the returns are not fixed or proportional ...
Do bonds have fixed returns?
On the other hand, bonds have fixed returns that have to be paid irrespective of the performance of the borrower since it is a debt amount.
What is the difference between bonds and stocks?
The difference between stocks and bonds. The difference between stocks and bonds is that stocks are shares in the ownership of a business, while bonds are a form of debt that the issuing entity promises to repay at some point in the future.
Why do you convert to stock?
Converting to stock also gives a former bond holder the right to vote on certain company issues. Both stocks and bonds may be traded on a public exchange.
Is it riskier to invest in stocks or bonds?
This means that stocks are a riskier investment than bonds. Periodic payments. A company has the option to reward its shareholders with dividends, whereas it is usually obligated to make periodic interest payments to its bond holders for very specific amounts.
Can bonds be traded on a public exchange?
Both stocks and bonds may be traded on a public exchange. This is a common occurrence for larger publicly-held companies, and much more rare for smaller entities that do not want to go through the inordinate expense of going public.
Is a stock a riskier investment than a bond?
This means that stocks are a riskier investment than bonds. Periodic payments. A company has the option to reward its ...
What happens when investors buy bonds?
If investors buy the company’s bonds, then they become lenders to the company. There are several key differences between an investment in bonds and an investment in stocks, as highlighted in the table below. The investor owns part of the company. The investor lends money to the company.
What are the risks of investing in the bond market?
Investing in the bond market is subject to risks, including market, interest rate, issuer, credit, inflation risk, and liquidity risk. The value of most bonds and bond strategies are impacted by changes in interest rates.
What happens to dividends when a company goes bankrupt?
Dividend payments may decrease and the investor may lose capital through a decreased stock price. Coupon payments will remain the same and the investor will receive back the agreed principal. If a company declares bankruptcy. Stocks will become worthless and investors may lose 100% of their capital.
What is covered bond?
Covered bonds. Debt securities issued by banks that are secured against a pool of assets (generally mortgages), which are held on the bank’s balance sheet. Credit market. The market whereby companies and governments can raise funds by allowing investors to purchase their debt securities.
What is duration in bond?
Expressed as a number of years, duration is a measure of how sensitive a bond is to changes in interest rate risk. The approximate percentage change in a bond’s value in response to a percentage point change in yield.
What is capital structure?
Both are a way for the company to raise money needed to fund its activities. The overall mix of debt and equity that the company uses is referred to as its capital structure.