With a stock award, you receive the company's stocks as compensation. Depending on the type of stock, you may have to wait for a certain period before you can fully own it. A stock option, on the other hand, only gives you the right to buy the company's stocks in the future at a certain price.
Are stock awards taxable?
When no Section 83 (b) election is made, the stock’s value less any amount paid for it is recognized as taxable compensation for income and employment tax purposes when the stock becomes fully vested. Any stock appreciation between the date of the award and the date of the vesting is treated as high-taxed ordinary income from compensation.
How are stock awards taxed?
Requirements for the grant to qualify as an ISO include (but are not limited to):
- The option price must be at least the FMV of the stock at the grant date;
- The option must be granted pursuant to a written plan that generally must be approved by the shareholders within 12 months before or after the date the plan is adopted;
- Grants are only to employees and are generally nontransferable;
When are stock awards taxed?
NEW YORK, June 21, 2021 /PRNewswire/ -- Anchin, Block & Anchin LLP ("Anchin"), a leading accounting and advisory firm, announced that the firm's Private Client group has been named Best Tax Advisor by the annual Family Wealth Report Awards program.
What are stock awards and stock options?
- Stock Options. Exercise: The purchase of stock pursuant to an option. ...
- Restricted Stock. ...
- Phantom Stock and Stock Appreciation Rights. ...
- Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESPPs) Employee stock purchase plans (ESPPs) are formal plans to allow employees to set aside money over a period of time (called an offering period), usually ...
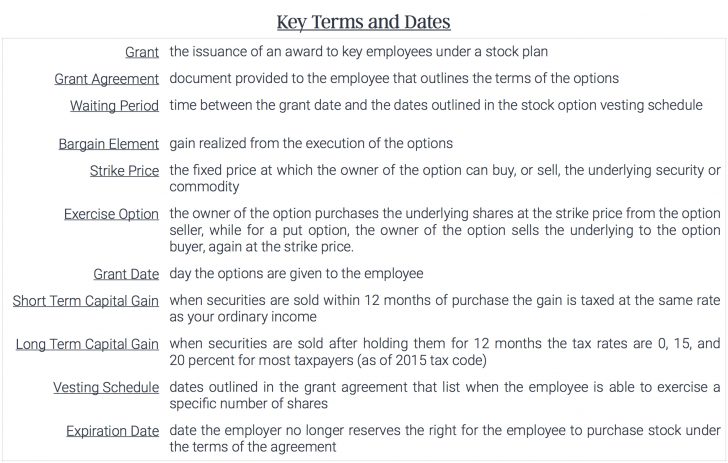
What does it mean to be awarded stock?
Related Definitions Stock Awards means any rights granted by the Company to Executive with respect to the common stock of the Company, including, without limitation, stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock, stock bonuses and restricted stock units.
Do stock awards count as income?
If you're granted a restricted stock award, you have two choices: you can pay ordinary income tax on the award when it's granted and pay long-term capital gains taxes on the gain when you sell, or you can pay ordinary income tax on the whole amount when it vests.
How are RSU awards calculated?
Like stock options, RSUs usually vest over several years. It's common to receive 1/4 of the RSUs you were granted after your first year of employment, and every month after that, receive another 1/36 of the remaining grant.
What are stock option awards?
Companies award stock options to recruit and retain key employees, executives and directors. These options give holders the right to buy the underlying shares at predetermined prices, known as strike prices, before specified expiration dates.
Do I pay taxes on stocks I don't sell?
And if you earned dividends or interest, you will have to report those on your tax return as well. However, if you bought securities but did not actually sell anything in 2020, you will not have to pay any "stock taxes."
Can I use stock income to buy a house?
The stock market can help you grow your savings to reach your investment goals, including saving up to buy a home. However, the IRS doesn't allow you to exclude any stock income just because you used the proceeds to buy a home, even if it's your first one.
Do you get more RSU after 4 years?
Restricted Stock Units (RSUs): Stock vests will begin on your first anniversary. You will receive additional stock vests at the end of year 2 and then every 6 months until you've been with the company for 4 years. Many Amazon employees receive additional refresher RSUs as an Amazon employee over time.
Should I sell RSUs immediately?
RSU is the most controlled and direct type of compensation given to the employees. Usually, it is recommended to sell the RSU immediately after the vesting period is complete to avoid any additional taxes. Insiders and employees that hold the RSU, need a RSU selling strategy.
How much is Amazon RSU worth?
It is gifted by Amazon at the start of your employment. For reference, one RSU equals one share of stock once you become vested. You receive your shares upon being hired, but they aren't worth anything just yet. You'll receive a vesting schedule based on your compensation.
What does 4 years vesting with 1 year cliff mean?
4 Years with a One Year Cliff Defined It means the stock grant, typically options, will be fully vested after 4 years. The one-year cliff is the anniversary of the stock's issuance. Each founder vests a quarter of their shares, with vested transfers coming monthly after that.
What is an employee stock option?
An employee stock option is a contract that grants an employee the right to buy shares in his or her employer at a specific, fixed price, known as the exercise price, after a designated date.
Do executive stock options have to be exercised?
It's common for executives to receive performance-based equity awards, meaning that their stock options may only be exercised, or they only receive full ownership of their RSUs, once certain performance goals are met. For rank-and-file employees, however, performance-based equity awards are more unusual.
Can an employee buy stock with an RSU?
Some employees may prefer RSUs to stock options because, in the case of options, an employee must spend his or her own money to buy the stock (even if they ultimately sell it), while an RSU is granted to an employee without any investment on his or her part.
What happens if stock prices fall during vesting?
If the stock price declined during the vesting period, there is a risk that more taxes would be paid based on the fair market value on the grant date than would have been paid at vesting. Timing of tax payment.
What happens if an employee accepts restricted stock?
Once an employee is granted a Restricted Stock Award, the employee must decide whether to accept or decline the grant. If the employee accepts the grant, he may be required to pay the employer a purchase price for the grant.
What is restricted stock?
A Restricted Stock Award Share is a grant of company stock in which the recipient’s rights in the stock are restricted until the shares vest (or lapse in restrictions). The restricted period is called a vesting period. Once the vesting requirements are met, an employee owns the shares outright and may treat them as she would any other share ...
Can restricted stock be forfeited?
Risk of forfeiture. If the restricted stock award is forfeited (e.g., by leaving the company before the stock vests), a loss cannot be claimed for tax purposes with respect to the restricted stock award. Additionally, there is no refund on the tax paid on the restricted stock award.
Is restricted stock award taxed?
Under normal federal income tax rules, an employee receiving a Restricted Stock Award is not taxed at the time of the grant (assuming no election under Section 83 (b) has been made, as discussed below). Instead, the employee is taxed at vesting, when the restrictions lapse. The amount of income subject to tax is the difference between ...
Is a stock held as a capital asset subject to capital gains tax?
Capital gains treatment. Assuming the stock is held as a capital asset, future gains (or losses) would be taxed only as capital gains, and, therefore, would be subject to favorable capital gains tax rates. There are also several potential disadvantages of making a Special Tax 83 (b) election: Falling share prices.
What is stock award?
With a stock award, you receive the company's stocks as compensation. Depending on the type of stock, you may have to wait for a certain period before you can fully own it. A stock option, on the other hand, only gives you the right to buy the company's stocks in the future at a certain price.
Why do you give stock awards instead of cash?
Granting stock awards and stock options instead of cash also minimizes the company's expenses and generates tax benefits.
Why do companies give stock options to employees?
Offering these incentives aligns the interests of the stockholders and the employees of the company. Because you benefit if the stock value increases, you might try harder to maximize the company's wealth.
How long do you have to work to get stock awards?
A common requirement of stock awards and stock options is for you to work for the company for a minimum number of years. After this vesting period, you can then claim the monetary value of the stock awards and stock options. This encourages employees to stay with the company.
Do you have to spend money to get a stock award?
With a stock award, you don't have to spend any money to obtain the stocks. Even it the stock price decreases, the stock award would still be worth something. However, stock awards provide less opportunity to earn profits, because most companies grant fewer stock awards than they do stock options, according to "USA Today.". References.
Do you have to spend money to buy stock options?
Also, you have to spend money to use the option to buy stocks. With a stock award, you don't have to spend any money to obtain the stocks.
What happens if you sell stock before the FMV?
If you sell before that, you’ll pay short-term capital gains tax , which is the same as your income tax rate. So imagine you take Section 83(b) on an award of 100 shares and pay $5 a share, which is much lower than the fair market value (FMV) of $20.
What happens if a company's stock tanked?
If the company’s stock tanks, it will be worth little or nothing if you sell. In either case, you’ve paid income tax on the strike price, but you won’t see a profit. In effect you’ll have paid taxes on income you never received. Every RSA is different, as are the conditions in which they’re granted.
Why do companies use RSUs?
That’s because the share price may be too high for employees to afford to pay for options.
Why do executives take restricted stock?
Many executives will take restricted stock along with a lower salary since there is potential for significant gain if the company succeeds and increases in value. Bottom Line. Restricted stock, whether RSAs or RSUs, can hold a lot of potential value and are often coveted forms of compensation.
Can a restricted stock grant be paid?
The recipient of a restricted stock grant may sometimes have to pay for the shares, in addition to fulfilling the vesting requirements.
What is stock option?
Stock Options Definition. Stock optionsare a form of compensation. Companies can grant them to employees, contractors, consultants and investors. These options, which are contracts, give an employee the right to buy or exercise a set number of shares of the company stock at a pre-set price, also known as the grant price.
How long do stock options last?
You can find this in your contract. It’s common for options to expire 10 years from the grant date, or 90 days after you leave the company. When You Should Exercise Stock Options. When and how you should exercise your stock options will depend on a number of factors.
How long does it take to exercise stock options?
A four-year vesting period means that it will take four years before you have the right to exercise all 20,000 options. The good news is that, because your options vest gradually over the course of this vesting period, you’ll be able to access some of your stock options before those four years are up.
How long after a stock exercise can you sell?
If you sell the shares as soon as you exercise them, the bargain element is treated as regular income. If you hold the stock for at least one year after exercise AND you don’t sell the shares until at least two years after the grant date, the tax rates you pay are the long-term capital gains rates. Bottom Line.
What are the two types of stock options?
For starters, it’s important to note that there are two types of stock options: Non-qualified stock options(NQSOs) are the most common. They do not receive special tax treatment from the federal government. Incentive stock options(ISOs), which are given to executives, do receive special tax treatment.
Why do employees come on board at a lower salary?
Employees come on board at perhaps a lower-than-normal salary in exchange for the possibility of a big payday later on. If you’ve been offered optionsas part of a compensation package, or if you’re considering exercising and selling those options, be sure you know how they work.
Why are stock grants important?
Stock grants are designed with the benefit of being equitable property. Due to this, these stock grants have some intrinsic value. When the stock market is classified as being volatile, stock options are known to become less valuable than a company's employee cost. This makes stock options seemingly worthless. With that being said, stock grants are equipped to constantly remain at some value, as the employees of a business haven't outright purchased these stocks.
What is incentive stock option?
Incentive stock options, or ISOs, are designed in a way that qualifies these stock options for special tax treatment when placed under the US Internal Revenue Code. In addition to this, these ISOs aren't subjected to Medicare, Social Security, or withholding taxes. Nonetheless, to qualify for these taxation treatments, these stock options are required to meet rigid criteria under the US tax code. In addition to this, the mechanisms making up incentive stock options detail that these can only be granted to employees. Such stock options can't be released to contractors or consultants, which is unlike NQSOs.
What is restricted stock?
As the use of 'restricted' entails, any restricted stock has certain restrictions on how the employee and future owner of this stock may use it. Generally speaking, an employee of a company is required to hold onto this restricted stock for a specific time.
What is non qualified stock option?
Non-qualified stock options are one type of stock option that doesn't feature any favorable tax treatment when dealt with under the US Internal Revenue Code. As a result of this, the use of the word, 'non-qualified' applies to the tax treatment of these stocks because it isn't eligible for special tax treatment or any other favorable considerations.
Why do investors want equity compensation?
Investors want equity compensation to be earned for reasons beyond just higher stock prices or your continued employment. Though stock options lead to profit only when the stock price rises, you still receive the gains if the stock price has failed to outperform the market index or the stock performance of competitors.
How do performance shares differ from restricted stock?
How Performance Shares Differ From Restricted Stock. In grants of restricted stock, shares are issued up front at grant, but you do not own them outright until the restrictions lapse at vesting, and thus you cannot sell or transfer the shares until then. Standard restricted stock units (RSUs) are similar, except that the shares are not issued ...
What is performance share grant?
While the structure (and even the definition) of performance share grants can vary, the common feature is a specified goal or metric that must be achieved before you can profit from the grant. For these grants, the goals can be highly customized. Performance shares are not issued up front and are usually part of a long-term performance ...