As stock prices rise, call options will increase in value, while put options decrease. The change in call and put option prices also works the other way around when stock prices decline. As for options trading affecting stock prices, pinning occurs if many options are outstanding and the expiration date is approaching.
What are call options and how do they work?
What are Options: Calls and Puts?
- Payoffs for Options: Calls and Puts. The buyer of a call option pays the option premium in full at the time of entering the contract. ...
- Applications of Options: Calls and Puts. Options: calls and puts are primarily used by investors to hedge against risks in existing investments.
- Additional Resources. ...
How does a call option trade work?
What Is a Call Option and How Does It Work?
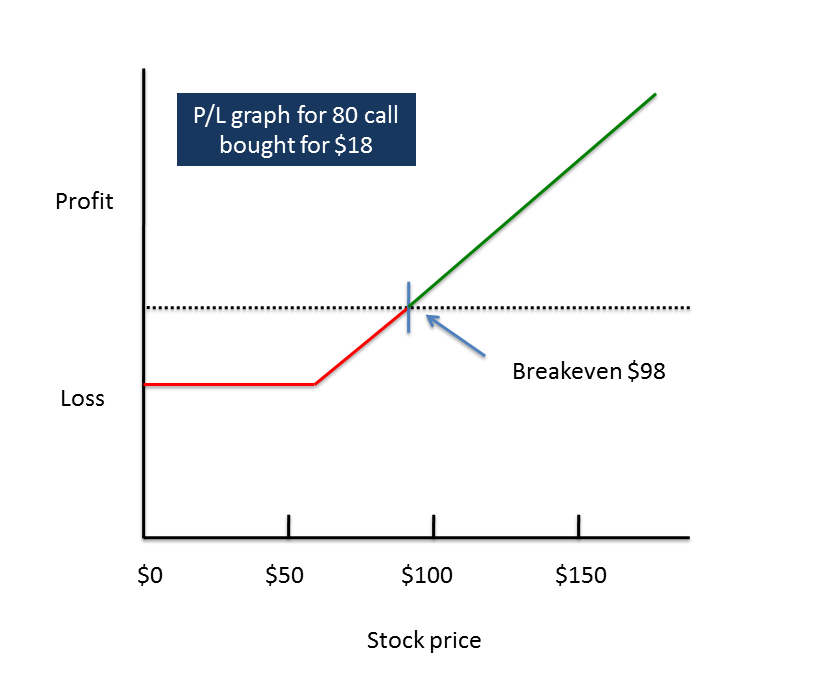
- Profit and Loss of a Call Option. Let’s talk about intrinsic value and how you can look at a call option’s potential profit before you enter a trade.
- Call Option Strategies. Covered calls involve selling call options on underlying stocks that someone already owns. ...
- Conclusion. That’s a wrap call options for now. ...
How do you buy a call?
Things to consider when buying call options include:
- Duration of time you plan on being in the trade
- The amount you can allocate to buying a call option
- The length of a move you expect from the market
What are call and put options?
One of the key inputs that goes into the price an option buyer is willing to pay, is the time value, so with 186 days until expiration the newly trading contracts represent a potential opportunity for sellers of puts or calls to achieve a higher premium ...

Does buying call options raise stock price?
The biggest advantage of buying a call option is that it magnifies the gains in a stock's price. For a relatively small upfront cost, you can enjoy a stock's gains above the strike price until the option expires. So if you're buying a call, you usually expect the stock to rise before expiration.
Do call options change stock price?
The value of calls and puts are affected by changes in the underlying stock price in a relatively straightforward manner. When the stock price goes up, calls should gain in value because you are able to buy the underlying asset at a lower price than where the market is, and puts should decrease.
Do call options lower stock prices?
Selling a call option Call sellers generally expect the price of the underlying stock to remain flat or move lower. If the stock trades above the strike price, the option is considered to be in the money and will be exercised.
Can call options predict stock price?
Option prices significantly predict stock returns: stocks earn low returns when put options are expensive relative to call options. We attribute most of this predictability to the association between option prices and the conditions in the securities lending market.
Do Stocks Go Up When options expire?
The results of the options expiration week effect If we enter at the close of the last trading day before the options expiration week, normally a Friday, the average gain increases to 0.35% per trade for the S&P 500.
What happens when call option reaches strike price?
When the strike price is reached, your contract is essentially worthless on the expiration date (since you can purchase the shares on the open market for that price). Prior to expiration, the long call will generally have value as the share price rises towards the strike price.
Why is my call option going down when the stock is going up?
Decreased Market Volatility The higher the overall implied volatility, or Vega, the more value an option has. Generally speaking, if implied volatility decreases then your call option could lose value even if the stock rallies.
How do call options work for dummies?
0:002:433 Minutes! Call Option Explained with Call Options Tutorial ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipCall options explain in three minutes imagine a stock price is $100. You do not want to buy it yetMoreCall options explain in three minutes imagine a stock price is $100. You do not want to buy it yet right now. But you're thinking that you might want to buy it in the future. However you're worried
How do call options make money?
A call option writer stands to make a profit if the underlying stock stays below the strike price. After writing a put option, the trader profits if the price stays above the strike price. An option writer's profitability is limited to the premium they receive for writing the option (which is the option buyer's cost).
How do you know if a stock will go up the next day?
The closing price on a stock can tell you much about the near future. If a stock closes near the top of its range, this indicates that momentum could be upward for the next day.
How do you read options to predict stock movements?
11:5915:23How to Use Options to Predict Stocks - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou're going to get a signal. For that when these lines cross. So when you see the green lineMoreYou're going to get a signal. For that when these lines cross. So when you see the green line crossing above the yellow line that's your in to start paying attention.
Why do options prices predict stock returns?
We argue that option-implied prices provide an anchor for fundamental stock values that helps to distinguish stock price movements resulting from pressure versus news. Overall, our results are consistent with stock price pressure being the primary driver of the option price-based stock return predictability.
Why is my call option going down when the stock is going up?
Decreased Market Volatility The higher the overall implied volatility, or Vega, the more value an option has. Generally speaking, if implied volatility decreases then your call option could lose value even if the stock rallies.
Do option prices change pre market?
That is patently false. The opening price for a security is set by an auction in which buyers and sellers submit limit orders prior to the market open. The opening price will be a price at which the greatest volume will be executed according to those submitted orders.
Can you lose more money on a call option?
The maximum loss on a covered call strategy is limited to the price paid for the asset, minus the option premium received. The maximum profit on a covered call strategy is limited to the strike price of the short call option, less the purchase price of the underlying stock, plus the premium received.
How do calls work in the stock market?
When you buy a call, you pay the option premium in exchange for the right to buy shares at a fixed price (strike price) on or before a certain date (expiration date). Investors most often buy calls when they are bullish on a stock or other security because it offers leverage.
How do options affect stock price?
Options prices are affected by stock prices, and this is measured by delta. As stock prices rise, call options will increase in value, while put options decrease. The change in call and put option prices also works the other way around when stock prices decline.
Why is there an increase in demand for stock?
The increased demand for stock can be due to options trading or not. For instance, if a company is making significant changes or has a big announcement coming, their stock price can increase or decrease depending on the changes and speculation people make regarding the event.
What happens when you exercise your options?
All of this activity from people exercising their options can cause the stock prices to pin but not necessarily change based on the options.
What is a pinned stock?
However, they can affect how stock prices move in a process known as pinning. Pinning is when the stock price nears the strike price of popular options as the expiration date of the options approaches. The term comes from the idea that the stock price stays “pinned” to the strike price until expiration.
What is Delta in options?
The following definition is from Investopedia regarding the Options Delta, which will help us to explain how options trading and stock prices are correlated: “Delta is the ratio that compares the change in the price of an asset, usually marketable securities, to the corresponding change in the price of its derivative.”.
Do put options decrease or increase?
For put options, the value will decrease as stock prices increase. The change in options prices relative to the stock price is not a direct correlation. However, options do show an increase or decrease in the price depending on the sign of the delta, meaning that a positive delta means a price increase, and a negative delta means a price decrease.
Can you see a change in stock price when you buy options?
Sometimes, you will notice a change in stock prices as you buy or sell your options. The difference could be from exercising your options, especially if many people are exercising their options simultaneously. However, this does not always happen, and there are an infinite amount of other factors that could affect stock prices.
Does shorting stock affect stock price?
No. Just as shorting stock does not affect whether or not share price declines, trading in options doesn't affect stock prices directly simply because the options are traded. It really doesn't matter how many different option strategies you employ.
Does trading options affect demand?
Trading in options is truly a side play and has no affect on supply and demand for shares, among either buyers or sellers. One exception to this: There is a tendency for stock prices to gravitate to the closest strike near expiration, known as "pinning to the strike.".
Do expired options affect stock prices?
Once expired, the options do not affect stock prices any more. Even the volatility aspect of options is far removed from stock price behavior. Implied volatility (IV) is an estimate of future value and not a reflection (directly at least) of how options affect stock prices. It works in the opposite direction.
Does historical volatility reflect market forces?
Historical volatility reflects market forces, of course. But it also reflects fundamental volatility itself. In this respect, the fundamental trends (including earnings, dividends, and debt management, among other trends) directly affect the technical side and historical volatility. That, in turn, affects option premium and volatility.
How are call options sold?
A call option is covered if the seller of the call option actually owns the underlying stock. Selling the call options on these underlying stocks results in additional income, and will offset any expected declines in the stock price.
What happens if the strike price of a call option rises?
Alternatively, if the price of the underlying security rises above the option strike price, the buyer can profitably exercise the option. For example, assume you bought an option on 100 shares of a stock, with an option strike price of $30.
What is the difference between a call and a put option?
On the contrary, a put option is the right to sell the underlying stock at a predetermined price until a fixed expiry date. While a call option buyer has the right (but not obligation) to buy shares at the strike price before or on the expiry date, a put option buyer has the right to sell shares at the strike price.
What is naked call option?
A naked call option is when an option seller sells a call option without owning the underlying stock. Naked short selling of options is considered very risky since there is no limit to how high a stock’s price can go and the option seller is not “covered” against potential losses by owning the underlying stock.
How do call options make money?
They make money by pocketing the premiums (price) paid to them. Their profit will be reduced, or may even result in a net loss if the option buyer exercises their option profitably when the underlying security price rises above the option strike price. Call options are sold in the following two ways: 1.
What happens if the strike price of a security does not increase?
If the price of the underlying security does not increase beyond the strike price prior to expiration, then it will not be profitable for the option buyer to exercise the option, and the option will expire worthless or “out-of-the-money”. The buyer will suffer a loss equal to the price paid for the call option.
How many shares are in a call option?
Usually, options are sold in lots of 100 shares. The buyer of a call option seeks to make a profit if and when the price of the underlying asset increases to a price higher than the option strike price. On the other hand, the seller of the call option hopes that the price of the asset will decline, or at least never rise as high as ...
Why do investors use call options?
Some investors use call options to achieve better selling prices on their stocks. They can sell calls on a stock they’d like to divest that is too cheap at the current price. If the price rises above the call’s strike, they can sell the stock and take the premium as a bonus on their sale.
What happens when you buy a call option?
Call buyers generally expect the underlying stock to rise significantly, and buying a call option can provide greater potential profit than owning the stock outright. If the stock's market price rises above the strike price, the option is considered to be “in the money.”.
What happens to the call buyer if the stock doesn't rise above the strike price?
The entire investment is lost for the option holder if the stock doesn’t rise above the strike price. However, a call buyer’s loss is capped at the initial investment. In this example, the call buyer never loses more than $500 no matter how low the stock falls.
Why is an in the money call option intrinsic value?
An in the money call option has “intrinsic value” because the market price of the stock is greater than the strike price. The buyer has two choices: First, the buyer could call the stock from the call seller, exercising the option and paying the strike price.
What is call option?
A call option is a contract that gives the owner the option, but not the requirement, to buy a specific underlying stock at a predetermined price (known as the “strike price”) within a certain time period (or “expiration”). For this option to buy the stock, the call buyer pays a “premium” per share to the call seller.
What is a short call position?
Call sellers (writers) have an obligation to sell the underlying stock at the strike price and have a “short call position.” The call seller must have one of these three things: the stock, enough cash to buy the stock, or the margin capacity to deliver the stock to the call buyer. Call sellers generally expect the price of the underlying stock to remain flat or move lower.
What does it mean to buy long call positions?
Buying calls, or having a long call position, feels a lot like wagering. It allows traders to pay a relatively small amount of money upfront to enjoy, for a limited time, the upside on a larger number of shares than they’d be able to buy with the same cash.
What is an option strike in equities?
In individual equities, when monthly expiration looms, investors can look for option strikes that have a level of open interest that 1) is much higher than other nearby strikes and 2) is worth a meaningful percentage of the value of the stock's average daily volume.
What happens if you close a put option at 615?
If GOOG closes above $615, the put options will expire worthless, allowing the trader to keep the premium received from the sale.
What is gamma in options?
Gamma is the risk variable that measures how much an option's stock price sensitivity (its delta) will change for each point move in the underlying. High gamma means that option hedgers will need to buy and sell more shares than they otherwise would if the options in question had many weeks or months to expiration.
Why do investors buy call options?
When looking for a smart investment strategy, some investors buy call options. Call options often enable investors to maximize profits while minimizing risk. Purchasing a call option may yield profit that is significantly higher than if you bought a security outright.
What are the downsides of buying a call option?
Disadvantages. The downside of buying a call option is if the stock price only increases a bit, you could actually lose money on the investment. For example, if the stock price from the example above only rose to $63, and you bought 100 shares outright, you would profit $300.
How much money can I make if my stock price skyrocketed?
However, if the stock price skyrocketed, to say $103 per share, an investor could make upward of $4,000, minus the premium for the call option transaction. If the investor didn’t purchase the stock when it was at a lower price, they may have missed their opportunity to profit.
What is call option?
Call options give investors the opportunity, but not the obligation, to purchase a stock, bond, commodity or other security at a certain price, within a specific time frame. The sellers must let the buyers exercise this option.
How do I buy call options?
You can purchase a call option through an online brokerage account or on a variety of exchanges. However, you must first be approved, which is based on the level of experience and amount of knowledge with options trading.
What is a trade amount?
Trade amount. The trade amount is the maximum amount you want to spend on a call option transaction. Number of contracts. When you buy a call option, you will need to decide the number of shares you would like to purchase. Strike price. Regardless of what the current stock price is, an owner of a call option can decide at what strike price they ...
Why are call options less expensive?
Call options are less expensive leading up to the ex-dividend date because of the expected fall in the price of the underlying stock. At the same time, the price of put options increases due to the same expected drop. The mathematics of the pricing of options is important for investors to understand so they can make informed trading decisions.
Why are call options cheaper?
Call options become cheaper due to the anticipated drop in the price of the stock, although for options this could start to be priced in weeks leading up to the ex-dividend. To understand why puts will increase in value and calls will drop, we look at what happens when an investor buys a call or put.
How does dividend payment affect stock options?
The payment of dividends for a stock impacts how options for that stock are priced. Stocks generally fall by the amount of the dividend payment on the ex-dividend date (the first trading day where an upcoming dividend payment is not included in a stock's price). This movement impacts the pricing of options.
What is put option?
A put option on a stock is a financial contract where the holder has the right to sell 100 shares of stock at the specified strike price up until the expiration of the option. The writer or seller of the option has the obligation to buy the underlying stock at the strike price if the option is exercised.
What is implied volatility?
The implied volatility in the formula is the volatility of the underlying instrument. Some traders believe the implied volatility of an option is a more useful measure of an option’s relative value than the price. Traders should also consider the implied volatility of an option on a dividend-paying stock.
How do dividends affect options?
The Impact of Dividends on Options. Both call and put options are impacted by the ex-dividend date. Put options become more expensive since the price will drop by the amount of the dividend (all else being equal). Call options become cheaper due to the anticipated drop in the price of the stock, although for options this could start ...
Why do brokers move limit orders?
Some brokers move limit orders to accommodate dividend payments. Using the same example, if an investor had a limit order to buy stock in ABC Inc. at $46, and the company is paying a $1 dividend, the broker may move the limit order down to $45.
How are call options and put options affected?
Call option and put option premiums are impacted inversely as interest rates change. However, the impact on option prices is fractional; option pricing is more sensitive to changes in other input parameters, such as underlying price, volatility, time to expiry, and dividend yield. Take the Next Step to Invest.
What are the factors that affect the value of an option?
A change in interest rates also impacts option valuation, which is a complex task with multiple factors, including the price of the underlying asset, exercise or strike price, time to expiry, risk-free rate of return (interest rate), volatility, and dividend yield.
What is rho in options?
Rho is a standard Greek that measures the impact of a change in interest rates on an option price. It indicates the amount by which the option price will change for every 1% change in interest rates. Assume that a call option is currently priced at $5 and has a rho value of 0.25. If the interest rates increase by 1%, then the call option price will increase by $0.25 (to $5.25) or by the amount of its rho value. Similarly, the put option price will decrease by the amount of its rho value.
How much does it cost to buy a call option at $100?
Interest Advantage in Call Options. Purchasing 100 shares of a stock trading at $100 will require $10,000, which, assuming a trader borrows money for trading, will lead to interest payments on this capital. Purchasing the call option at $12 in a lot of 100 contracts will cost only $1,200.
Does shorting a stock bring in cash?
Theoretically, shorting a stock with an aim to benefit from a price decline will bring in cash to the short seller. Buying a put has a similar benefit from price declines, but comes at a cost as the put option premium is to be paid. This case has two different scenarios: cash received by shorting a stock can earn interest for the trader, while cash spent in buying puts is interest payable (assuming the trader is borrowing money to buy puts).
Does interest rate change affect stock price?
Also, a change in interest rates usually has an inverse impact on stock prices, which has a much larger impact on option prices. Overall, due to the small proportional change in option price due to interest rate changes, arbitrage benefits are difficult to capitalize upon.
Is it possible to benefit from arbitrage on expected rate changes?
Is it possible to benefit from arbitrage on expected rate changes? Usually, markets are considered to be efficient and the prices of options contracts are already assumed to be inclusive of any such expected changes. Also, a change in interest rates usually has an inverse impact on stock prices, which has a much larger impact on option prices. Overall, due to the small proportional change in option price due to interest rate changes, arbitrage benefits are difficult to capitalize upon.