The impact of the Depression on Germany In October 1929 the Wall Street Crash on the US stock exchange brought about a global economic depression. In Europe, Germany was worst affected because American banks called in all of their foreign loans at very short notice.
What were the effects of the stock market crash of 1929?
Effects of the 1929 Stock Market Crash: The Great Depression On October 29, 1929, Black Tuesday hit Wall Street as investors traded some 16 million shares on the New York Stock Exchange in a single day. Billions of dollars were lost, wiping out thousands of investors.
How did the stock market crash affect Germany?
Germany: The end of the republic. …October 29, 1929, with the stock market crash on Wall Street, an event that signaled the onset of what quickly became a worldwide depression. The crash had an immediate effect in Germany as American investors, anxious about their financial position, began withdrawing their loans to Germany.
What caused the Great Depression of 1929?
The Great Depression was a period of economic turmoil between 1929 and the mid '30s. It was triggered by a stock market crash in New York, however, the impacts quickly spread globally. German companies had enjoyed an economic boom in the years prior to the crash, but it wasn't legitimate.
What was the impact of the Great Depression on Germany?
The impact of the Depression on Germany In October 1929 the Wall Street Crash on the US stock exchange brought about a global economic depression. In Europe, Germany was worst affected because American banks called in all of their foreign loans at very short notice.

How did the economic crisis of 1929 affect Germany?
Over the winter of 1929-30 the number of unemployed rose from 1.4 million to over 2 million. By the time Hitler became Chancellor in January 1933 one in three Germans were unemployed, with the figure hitting 6.1 million. Industrial production had also more than halved over the same period.
How did Germany react to the Great Depression?
The Great Depression was severely felt in Germany, where it caused widespread unemployment, starvation and misery. These conditions were instrumental in the rise to power of Adolf Hitler and the National Socialists (NSDAP).
How did Germany suffer from the Wall Street crash?
In 1929 as the Wall Street Crash led to a worldwide depression. Germany suffered more than any other nation as a result of the recall of US loans, which caused its economy to collapse. Unemployment rocketed, poverty soared and Germans became desperate.
Why did Germany suffer most from the Great Depression?
Why did Germany suffer so badly from the Great Depression? Germany was, indeed, especially hard-hit by the Great Depression. A major factor was the Treaty of Versailles, which was supposed to settle outstanding disputes following the cessation of hostilities in World War I.
How did Germany survive the Great Depression?
And crucial to Germany's recovery was government spending, much of it on public works, the most visible of which was a new highway system – the autobahn – which the army wanted for more efficient movements within Germany. There was also an electrification program, and government investment in industry.
How did the Great Depression affect Germany and France?
How did the Great Depression affect Germany and France? The Weimar Republic of Germany experienced severe inflation and unemployment rose to more than 4 million people; France experienced political unrest, with six different cabinets formed in a 19-month period.
How many people were unemployed in Germany in 1929?
Over the winter of 1929-30 the number of unemployed rose from 1.4 million to over 2 million. By the time Hitler became Chancellor in January 1933 one in three Germans were unemployed, with the figure hitting 6.1 million. Industrial production had also more than halved over the same period.
Why was Germany the worst affected by the Dawes Plan?
In Europe, Germany was worst affected because American banks called in all of their foreign loans at very short notice. These loans, agreed under the Dawes Plan in 1924, had been the basis for Weimar’s economic recovery from the disaster of hyperinflation. The loans funded German industry and helped to pay reparations.
How did unemployment affect Germany?
The impact of unemployment 1 The rise in unemployment significantly raised government expenditure on unemployment insurance and other benefits. 2 Germans began to lose faith in democracy and looked to extreme parties on the both the Left (the communists) and the Right (the Nazis) for quick and simple solutions.
What were the reasons for Hitler's rise to power?
Hitler was appointed Chancellor in January 1933. His rise to power was the result of many factors: the impact of the Depression, the weaknesses of Weimar democracy and the strengths of the Nazi party.
When people were unemployed, hungry and desperate, as millions were in Germany between 1930 and 1933, they often turn to
When people are unemployed, hungry and desperate, as millions were in Germany between 1930 and 1933, they often turn to extreme political parties offering simple solutions to their problems. Between 1930 and 1933 support for the extreme right-wing Nazis and the extreme left-wing communists soared.
What was the effect of the rise in unemployment?
The rise in unemployment significantly raised government expenditure on unemployment insurance and other benefits. Germans began to lose faith in democracy and looked to extreme parties on the both the Left (the communists) and the Right (the Nazis) for quick and simple solutions.
What were the causes of the 1929 stock market crash?
Among the other causes of the stock market crash of 1929 were low wages, the proliferation of debt, a struggling agricultural sector and an excess of large bank loans that could not be liquidated.
What was the stock market crash of 1929?
The stock market crash of 1929 was not the sole cause of the Great Depression, but it did act to accelerate the global economic collapse ...
What happened to stock market in 1929?
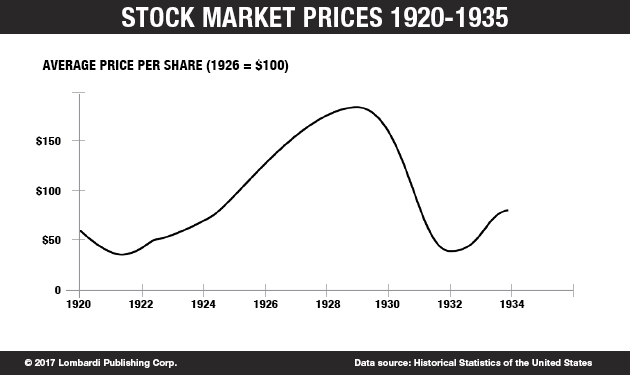
Stock prices began to decline in September and early October 1929, and on October 18 the fall began. Panic set in, and on October 24, Black Thursday, a record 12,894,650 shares were traded. Investment companies and leading bankers attempted to stabilize the market by buying up great blocks of stock, producing a moderate rally on Friday. On Monday, however, the storm broke anew, and the market went into free fall. Black Monday was followed by Black Tuesday (October 29, 1929), in which stock prices collapsed completely and 16,410,030 shares were traded on the New York Stock Exchange in a single day. Billions of dollars were lost, wiping out thousands of investors, and stock tickers ran hours behind because the machinery could not handle the tremendous volume of trading.
What happened on October 29, 1929?
On October 29, 1929, Black Tuesday hit Wall Street as investors traded some 16 million shares on the New York Stock Exchange in a single day. Billions of dollars were lost, wiping out thousands of investors. In the aftermath of Black Tuesday, America and the rest of the industrialized world spiraled downward into the Great Depression (1929-39), ...
What happened after Black Tuesday?
In the aftermath of Black Tuesday, America and the rest of the industrialized world spiraled downward into the Great Depression (1929-39), the deepest and longest-lasting economic downturn in the history of the Western industrialized world up to that time .
When did stock prices drop in 1929?
Stock prices began to decline in September and early October 1929 , and on October 18 the fall began. Panic set in, and on October 24, Black Thursday, a record 12,894,650 shares were traded.
When did the stock market peak?
During the 1920s, the U.S. stock market underwent rapid expansion, reaching its peak in August 1929 after a period of wild speculation during the roaring twenties. By then, production had already declined and unemployment had risen, leaving stocks in great excess of their real value.
What was the 1929 stock market crash?
The Wall Street crash of 1929, also called the Great Crash, was a sudden and steep decline in stock prices in the United States in late October of that year.
What caused the stock market to go down in 1929?
Other causes included an increase in interest rates by the Federal Reserve in August 1929 and a mild recession earlier that summer, both of which contributed to gradual declines in stock prices in September and October, eventually leading investors to panic. During the mid- to late 1920s, the stock market in the United States underwent rapid ...
What was the Great Depression?
Stock market crash of 1929, also called the Great Crash, a sharp decline in U.S. stock market values in 1929 that contributed to the Great Depression of the 1930s. The Great Depression lasted approximately 10 years and affected both industrialized and nonindustrialized countries in many parts of the world. Crowds gathering outside the New York ...
How many points did the Dow close down?
Still, the Dow closed down only six points after a number of major banks and investment companies bought up great blocks of stock in a successful effort to stem the panic that day. Their attempts, however, ultimately failed to shore up the market. The panic began again on Black Monday (October 28), with the market closing down 12.8 percent.
What was the cause of the 1929 Wall Street crash?
The main cause of the Wall Street crash of 1929 was the long period of speculation that preceded it , during which millions of people invested their savings or borrowed money to buy stocks, pushing prices to unsustainable levels. Other causes included an increase in interest rates by the Federal Reserve in August 1929 and a mild recession earlier ...
Why did people sell their Liberty bonds?
People sold their Liberty Bonds and mortgaged their homes to pour their cash into the stock market. In the midsummer of 1929 some 300 million shares of stock were being carried on margin, pushing the Dow Jones Industrial Average to a peak of 381 points in September.
How did the 1929 stock market crash affect Germany?
The crash had an immediate effect in Germany as American investors, anxious about their financial position, began withdrawing their loans to Germany. German indebtedness to these investors had by 1929 reached nearly 15 billion marks. Prices on the German stock exchanges fell drastically during the last month of the year.
What happened to the German stock market in 1930?
Business failures multiplied. Early in 1930 Germany’s second largest insurance firm collapsed. Unemployment rose to three million during the course of the year. By the winter of 1932 it reached six million.
What percentage of the vote did the Nazis get?
The result was a disaster for Papen and another triumph for the Nazis, who took 37 percent of the vote, the largest total they were ever to acquire in a free election. The Communists won 15 percent of the vote. Thus the two parties dedicated to destroying German democracy held a majority in the Reichstag.
What was Hitler's appeal?
Hitler ’s charismatic appeal and the youthful energies of his movement were attractive to large segments of a populace fearful of being ruined by economic and social disaster. Hitler’s record as a war veteran lent authority to the hypernationalism he expressed in racist terms.
How many members did Hitler have in 1929?
The power of Hitler’s appeal was reflected in the party’s growing membership lists—from 170,000 members in 1929 to 1,378,000 in 1932—and in the swelling ranks of the Nazi Party’s paramilitary SA (Sturmabteilung), the infamous storm troopers.
What was the effect of the Weimar Republic?
An unintended effect of the anti-Young Plan campaign was to give widespread public exposure to Hitler, who used his access to the Hugenberg-owned press empire and to its weekly movie newsreels to give himself and his Nazi movement national publicity. An additional assist to Hitler’s career came on October ...
How old was Hindenburg when Hitler won the presidency?
Hitler’s opponents recognized that the 84-year-old Hindenburg, now fading into senility, was their only hope to prevent Hitler from winning the presidency, and, with great difficulty, they convinced Hindenburg, who wanted to retire, to seek a second term. The year 1932 was to be one of continuous election campaigning.
How many times did stock prices go up in 1929?
Until the peak in 1929, stock prices went up by nearly 10 times. In the 1920s, investing in the stock market became somewhat of a national pastime for those who could afford it and even those who could not—the latter borrowed from stockbrokers to finance their investments. The economic growth created an environment in which speculating in stocks ...
What happened in 1929?
In October of 1929, the stock market crashed, wiping out billions of dollars of wealth and heralding the Great Depression. Known as Black Thursday, the crash was preceded by a period of phenomenal growth and speculative expansion. A glut of supply and dissipating demand helped lead to the economic downturn as producers could no longer readily sell ...
Why did companies acquire money cheaply?
Essentially, companies could acquire money cheaply due to high share prices and invest in their own production with the requisite optimism. This overproduction eventually led to oversupply in many areas of the market, such as farm crops, steel, and iron.
What was the result of the Great War?
The result was a series of legislative measures by the U.S. Congress to increase tariffs on imports from Europe.
What happens when the stock market falls?
However, when markets are falling, the losses in the stock positions are also magnified. If a portfolio loses value too rapidly, the broker will issue a margin call, which is a notice to deposit more money to cover the decline in the portfolio's value.
Why did the economy stumbled in 1929?
In mid-1929, the economy stumbled due to excess production in many industries, creating an oversupply.
What happens if a broker doesn't deposit funds?
If the funds are not deposited, the broker is forced to liquidate the portfolio. When the market crashed in 1929, banks issued margin calls. Due to the massive number of shares bought on margin by the general public and the lack of cash on the sidelines, entire portfolios were liquidated.
