
A call option is a contract that allows you to buy some assets at a fixed price called the strike price. In the case of a stock option, the call controls 100 shares of stock until it expires. To execute a call, you first must own one.
How do you calculate call option price?
- When the strike and stock prices are the same, the option is at-the-money.
- When the strike of a call is below the stock price, it is in-the-money (reverse for a put).
- When the strike of a call is above the stock price (reverse for a put), it is out-of-the-money.
What are call options and how do they work?
What are Options: Calls and Puts?
- Payoffs for Options: Calls and Puts. The buyer of a call option pays the option premium in full at the time of entering the contract. ...
- Applications of Options: Calls and Puts. Options: calls and puts are primarily used by investors to hedge against risks in existing investments.
- Additional Resources. ...
What does buy a call option mean?
Buying a call option entitles the buyer of the option the right to purchase the underlying futures contract at the strike price any time before the contract expires. This rarely happens, and there is not much benefit to doing this, so don’t get caught up in the formal definition of buying a call option.
How do you write a call option?
- Support quality journalism
- Get unlimited access to tucson.com and apps
- No more surveys blocking articles
Can a company buy call options on its own stock?
Much corporate options trading is in fact linked to buybacks. Companies either sell puts or buy calls in their own stocks, generally at a stock price close to the market at the time of the option sale.
Why do companies issue call options?
Why Would You Buy a Call Option? Investors will consider buying call options if they are optimistic—or "bullish"—about the prospects of its underlying shares. For these investors, call options might provide a more attractive way to speculate on the prospects of a company because of the leverage that they provide.
How does a call option WORK example?
Call option example Suppose XYZ stock currently sells for $100. You believe it will go up to $110 within the next 90 days. With traditional investing, you buy 100 shares of XYZ for $10,000, wait for it to go up to $110, sell your 100 shares for $11,000 and pocket $1,000 in profit.
Why would you buy a call option instead of the stock?
The primary reason you might choose to buy a call option, as opposed to simply buying a stock, is that options enable you to control the same amount of stock with less money.
Do I have to buy 100 shares on a call?
Each contract represents 100 shares of the underlying stock. Investors don't have to own the underlying stock to buy or sell a call. If you think the market price of the underlying stock will rise, you can consider buying a call option compared to buying the stock outright.
How do you place a call option?
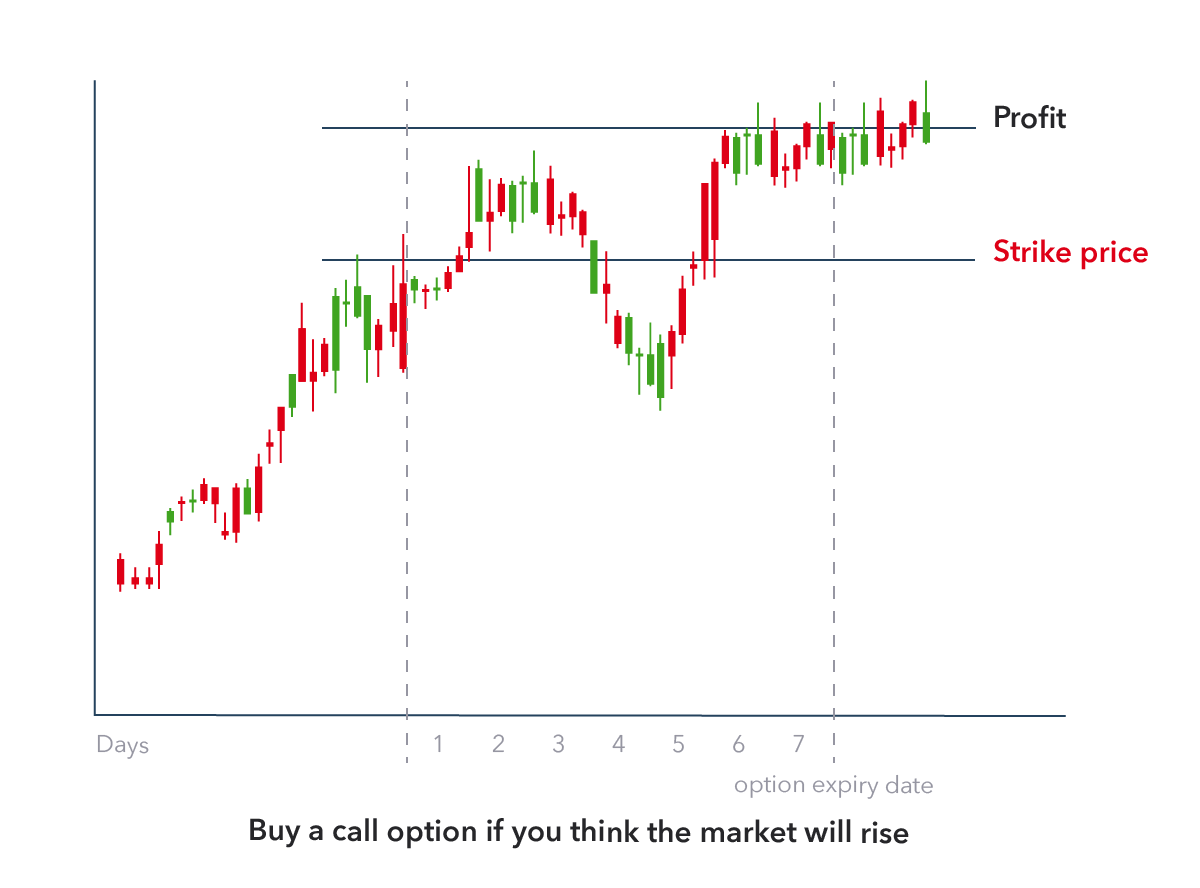
How a call option works. Call options are “in the money” when the stock price is above the strike price at expiration. The call owner can exercise the option, putting up cash to buy the stock at the strike price. Or the owner can simply sell the option at its fair market value to another buyer before it expires.
How do call options make money?
A call option writer stands to make a profit if the underlying stock stays below the strike price. After writing a put option, the trader profits if the price stays above the strike price. An option writer's profitability is limited to the premium they receive for writing the option (which is the option buyer's cost).
What does a $5 call option mean?
In the example, the investor pays the $5 premium upfront and owns a call option, with which it can be exercised to buy the stock at the $45 strike price. The option isn't going to be exercised until it's profitable or in-the-money.
How does selling call options work?
When selling a call option, you're selling the right, but not the obligation, to someone else to purchase an underlying security at a set price before a certain date. The seller gets a premium for agreeing to deliver the underlying security for a pre-set price before a set date if the buyer demands it.
How does buying call options work?
A call option is a contract between a buyer and a seller to purchase a certain stock at a certain price up until a defined expiration date. The buyer of a call has the right, not the obligation, to exercise the call and purchase the stocks.
How do I buy call options example?
For example, if a stock price was sitting at $50 per share and you wanted to buy a call option on it for a $45 strike price at a $5.50 premium (which, for 100 shares, would cost you $550) you could also sell a call option at a $55 strike price for a $3.50 premium (or $350), thereby reducing the risk of your investment ...
How do you buy options before the market opens?
No, you cannot place options orders in pre-market trading. Only equity cash is allowed to be traded in the pre-market session. However, you use AMO (After Market Order) facility offered by brokers to place your orders after the market closes for the next day trading. Check with your broker on AMO facility.
What is call option?
What Is a Call Option? Call options are financial contracts that give the option buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy a stock, bond, commodity or other asset or instrument at a specified price within a specific time period. The stock, bond, or commodity is called the underlying asset. A call buyer profits when ...
How long can you hold an Apple stock option contract?
As the value of Apple stock goes up, the price of the option contract goes up, and vice versa. The call option buyer may hold the contract until the expiration date, at which point they can take delivery of the 100 shares of stock or sell the options contract at any point before the expiration date at the market price of the contract at that time.
What is call buyer?
A call buyer profits when the underlying asset increases in price. A call option may be contrasted with a put, which gives the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at a specified price on or before expiration.
How does covered call work?
Covered calls work because if the stock rises above the strike price, the option buyer will exercise their right to buy the stock at the lower strike price. This means the option writer doesn't profit on the stock's movement above the strike price. The options writer's maximum profit on the option is the premium received.
Is a call put option taxable?
While gains from call and put options are also taxable, their treatment by the IRS is more complex because of the multiple types and varieties of options. In the case above, the only cost to the shareholder for engaging in this strategy is the cost of the options contract itself.
Is selling options a bearish behavior?
Conversely, selling call options is a bearish behavior, because the seller profits if the shares do not rise. Whereas the profits of a call buyer are theoretically unlimited, the profits of a call seller are limited to the premium they receive when they sell the calls.
What is call option?
What are call options? A call option is a contract between a buyer and a seller to purchase a certain stock at a certain price up until a defined expiration date. The buyer of a call has the right, not the obligation, to exercise the call and purchase the stocks.
What happens when you exercise an option call?
Upon exercise of a call, shares are deposited into your account and cash to pay for the shares and commission is withdrawn (just like a normal stock purchase). It's important to note that exercising is not the only way to turn an options trade profitable.
What happens if you short a call?
A short call investor hopes the price of the underlying stock does not rise above the strike price. If it does, the long call investor might exercise the call and create an "assignment." An assignment can occur on any business day before the expiration date. If it does, the short call investor must sell shares at the exercise price.
Why do you use short calls?
A short call is used to create income: The investor earns the premium but has upside risk (if the underlying stock price rises above the strike price). Both new and seasoned investors will use short calls to boost their income but, more often than not, do so when the call is "covered.".
What is a long call?
A long call can be used for speculation. For example, take companies that have product launches occurring around the same time every year. You could speculate by purchasing a call if you think the stock price will appreciate after the launch. A long call can also help you plan ahead.
How much does an ABC 110 call cost?
A call buyer must pay the seller a premium: for example, a price of $3 per share. Since the ABC 110 call option then costs $300 and paid out $1,000, the net return is $700. These examples do not include any commissions or fees that may be incurred, as well as tax implications.
Why do investors buy call options?
When looking for a smart investment strategy, some investors buy call options. Call options often enable investors to maximize profits while minimizing risk. Purchasing a call option may yield profit that is significantly higher than if you bought a security outright.
How do I buy call options?
You can purchase a call option through an online brokerage account or on a variety of exchanges. However, you must first be approved, which is based on the level of experience and amount of knowledge with options trading.
What are the downsides of buying a call option?
Disadvantages. The downside of buying a call option is if the stock price only increases a bit, you could actually lose money on the investment. For example, if the stock price from the example above only rose to $63, and you bought 100 shares outright, you would profit $300.
What is call option?
Call options give investors the opportunity, but not the obligation, to purchase a stock, bond, commodity or other security at a certain price, within a specific time frame. The sellers must let the buyers exercise this option.
How much money can I make if my stock price skyrocketed?
However, if the stock price skyrocketed, to say $103 per share, an investor could make upward of $4,000, minus the premium for the call option transaction. If the investor didn’t purchase the stock when it was at a lower price, they may have missed their opportunity to profit.
What is the purpose of stock options?
Stock options give key employees the opportunity to benefit from the increase in the company’s value by granting them the right to buy shares of common stock at a future point in time at a price (i.e., the “exercise” or “strike” price) generally equal to the fair market value of such shares at the time of the grant.
Why should entrepreneurs establish reasonable vesting schedules with respect to the stock options issued to employees?
Entrepreneurs should establish reasonable vesting schedules with respect to the stock options issued to employees in order to incentivize the employees to remain with the company and to help grow the business.
What is failure to register a securities transaction in which an exemption is not available?
Failure to register a securities transaction in which an exemption is not available is a violation of Section 5 of the Securities Act, which can lead to enforcement action by the SEC and/or private lawsuits by recipients of securities that do not comply with the law.
Why can a service provider use Rule 701?
If the service provider is open to this solution, then the company actually can use Rule 701 because the options are being issued to an individual. If the options need to be issued to the entity itself, and the entity is an accredited investor, then the company can rely on Rule 506 as an exemption to registration.
Can you use 506 for angel financing?
This is the same rule that is normally used in angel and VC financings. Technically, you could use Rule 50 6 even if the service provider entity is not accredited – but the disclosure requirements to comply with Rule 506 are almost as onerous as registering, so for practical purposes, you would not want to do that.
Can you split fees due under a service contract?
Negotiate with the service provider to split the fees due under the services contract into cash (if any) paid to the entity and equity comp directly to the owner (s) of the entity. This is often acceptable if the entity is owned by one or two individuals but it can be a problem if there is a larger ownership group.
What is call option?
A call option is a contract that allows you to buy some assets at a fixed price called the strike price. In the case of a stock option, the call controls 100 shares of stock until it expires. To execute a call, you first must own one. The purchase price of a call is called the premium.
What happens when you execute a stock call?
Upon execution, the option disappears from your account, your cash balance is reduced by an amount of money equal to 100 times the strike price and 100 shares of the underlying stock are deposited into your account. Step 1.

What Is A Call Option?
Understanding Call Options
- Let's assume the underlying asset is stock. Call options give the holder the right to buy 100 shares of a company at a specific price, known as the strike price, up until a specified date, known as the expiration date. For example, a single call option contract may give a holder the right to buy 100 shares of Apple stock at $100 up until the expiration date three months later. There are many ex…
Types of Call Options
- There are two types of call options as described below. 1. Long call option:A long call option is, simply, your standard call option in which the buyer has the right, but not the obligation, to buy a stock at a strike price in the future. The advantage of a long call is that it allows you to plan ahead to purchase a stock at a cheaper price. For example, you might purchase a long call option in an…
How to Calculate Call Option Payoffs
- Call option payoff refers to the profit or loss that an option buyer or seller makes from a trade. Remember that there are three key variables to consider when evaluating call options: strike price, expiration date, and premium. These variables calculate payoffs generated from call options. There are two cases of call option payoffs.
Purposes of Call Options
- Call options often serve three primary purposes: income generation, speculation, and tax management.
Example of A Call Option
- Suppose that Microsoft stock is trading at $108 per share. You own 100 shares of the stock and want to generate an income above and beyond the stock's dividend. You also believe that shares are unlikely to rise above $115.00 per share over the next month. You take a look at the call options for the following month and see that there's a $115.00 call trading at $0.37 per contract…
The Bottom Line
- Call options are financial contracts that give the option buyer the right but not the obligation to buy a stock, bond, commodity, or other asset or instrument at a specified price within a specific time period. The stock, bond, or commodity is called the underlying asset. Options are mainly speculative instruments that rely on leverage. A call buyer profits when the underlying asset incr…