How do you calculate a stock price?
Stock price = price-to-earnings ratio / earnings per share. To calculate a stock's value right now, we must ensure that the earnings-per-share number we are using represents the most recent four ...
How to calculate the current price of a stock?
The Heromoto Corp’s financial data is listed below:
- Current Stock Price: INR 2,465
- Last 12-months earnings per share: 148.39
- Annual Sales: 30800.62
- Annual Dividends per share: 105
- Historical P/E ratio: 18.53
- Book Value per Share: 1840.79
How do you calculate share price?
- Where SP is the share price ($)
- D is the dividends per share ($)
- rr is the return rate (%)
- g is the growth rate (%)
What is the formula to calculate price per share?
- List the various prices at which you bought the stock, along with the number of shares you acquired in each transaction.
- Multiply each transaction price by the corresponding number of shares.
- Add the results from step 2 together.
- Divide by the total number of shares purchased.

How is the stock price calculated?
After a company goes public, and its shares start trading on a stock exchange, its share price is determined by supply and demand for its shares in the market. If there is a high demand for its shares due to favorable factors, the price will increase.
Who decides the rate of stock?
Stock prices are largely determined by the forces of demand and supply. Demand is the amount of shares that people want to purchase while supply is the amount of shares that people want to sell.
What makes a stock price go up?
If more people want to buy a stock (demand) than sell it (supply), then the price moves up. Conversely, if more people wanted to sell a stock than buy it, there would be greater supply than demand, and the price would fall. Understanding supply and demand is easy.
Why do stock prices change every second?
Stock prices change every second according to market activity. Buyers and sellers cause prices to change and therefore prices change as a result of supply and demand. And these fluctuations, supply, and demand decide between its buyers and sellers how much each share is worth.
How is share price calculated with example?
Let's suppose Heromoto's P/E ratio has been 18.53 in the past. 2465 divided by 148.39 = 16.6 times the current P/E ratio. The present stock price s...
How do you calculate share price issued?
In an initial public offering, the stock price is set based on the company's performance and net present value. The stock price will begin to fluct...
How do you calculate a company's share price?
To calculate a stock's market cap, you must first calculate the stock's market price. Take the most recent updated value of the firm stock and mult...
What is price per share?
The price per share, or PPS, refers to the monetary value paid or received for a single share of stock. The price per share can assist investors in...
How are stock prices determined?
Once a company goes public on the stock market and its shares start trading on an exchange, the share price is determined by supply and demand . But, over the long term, share prices are determined by the economics of the business . It's impossible to predict exactly what a stock will do and when, but we can study how share price movement works. Let's unpack Graham's statement a little more and go over how stock prices work.
How do stock prices work?
It starts with the initial public offering (IPO). Companies work with investment bankers to set a primary market price when a company goes public. That price is set based on valuation and demand from institutional investors.
How to calculate P/E?
The price-earnings ratio (P/E) shows the price of the stock relative to earnings. It's calculated by dividing the stock price by earnings per share. Earnings per share is a readily available number on most financial websites and the company's quarterly reporting documents.
What is market cap?
The market cap of a stock is equal to the total shares times the share price. It's the price it would take to buy all of a company's outstanding shares. Many stocks issue more shares to fund the business, so it is important to base valuation on the market cap and not just the stock price. The more shares that are issued, the less of a fraction of the business you own.
What happens when a company buys back shares?
On the other side, if a business buys back shares, the price of each one of your shares will need to go up to maintain the same market cap. Share buybacks are generally cheered by shareholders as long as the stock price isn't overvalued.
Where do stocks trade?
After that initial offering, the stock starts to trade on secondary markets -- that is, stock exchanges such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or the Nasdaq. This is where we get into the market being a voting machine.
Is the stock price vulnerable to the crowd?
In the short term, the price of a stock is vulnerable to the emotional whims of the crowd. But, in the long term, smart investors can pinpoint where the emotions of the crowd set up opportunity. Focus on the long term in your investing, and don't let other people's emotions affect your investment decisions.
How Is Share Price Determined?
When a stock is sold, a buyer and seller exchange money for share ownership. The price for which the stock is purchased becomes the new market price. When a second share is sold, this price becomes the newest market price, etc.
What is stock price?
The stock price is a relative and proportional value of a company's worth. Therefore, it only represents a percentage change in a company's market cap at any given point in time.
How to find a company's market cap?
A company's worth—or its total market value —is called its market capitalization, or "market cap." A company's market cap can be determined by multiplying the company's stock price by the number of shares outstanding.
How is the market cap determined?
A company's market cap can be determined by multiplying the company's stock price by the number of shares outstanding. The stock price is a relative and proportional value of a company's worth.
How to calculate market capitalization?
In simple terms, a company's market capitalization is calculated by multiplying its share price by the number of shares outstanding :
What is market cap?
While market cap is often used synonymously with a company's market value, it is important to keep in mind that market cap refers only to the market value of a company's equity , not its market value overall (which can include the value of its debt or assets).
How are stock prices driven?
Generally speaking, the prices in the stock market are driven by supply and demand. This makes the stock market similar to other economic markets. When a stock is sold, a buyer and seller exchange money for share ownership. The price for which the stock is purchased becomes the new market price.
How to Calculate Share Price?
To calculate a stock’s market cap, you must first calculate the stock’s market price. Take the most recent updated value of the firm stock and multiply it by the number of outstanding shares to determine the value of the stocks for traders.
Share Price Formula in IPO
Via the primary market, firm stocks are first issued to the general public in an Initial Public Offering (IPO) to collect money to meet financial needs.
Conclusion
Stock prices are also depending on market sentiments. A stock at higher value looks cheaper in a bull market and a stock with lower value looks expensive in a bear market.
Frequently Asked Questions
Let's suppose Heromoto's P/E ratio has been 18.53 in the past. 2465 divided by 148.39 = 16.6 times the current P/E ratio. The present stock price should be 18 times its historical P/E ratio if it were trading at its historical P/E ratio of 18. 2754 is equal to 148.39. On this criteria, Heromoto's present stock price is undervalued.
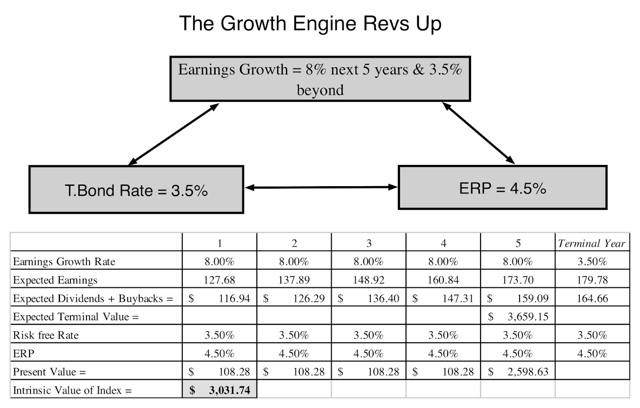
What is the stock market index?
A stock market index is, at its essence, just a number that represents a collection of stock prices manipulated arithmetically. The index is a quantity, but not really “of” anything you can taste or touch. Yet we can add another level of abstraction and create a futures contract for a stock index, the result of which is speculators taking positions on what direction the market at large will move in. In other words, buying and/or selling a number. A number of great cultural and perceived significance, but still, ultimately a number.
What is the difference between index futures and index funds?
But one huge difference between stock index futures and such index funds is that the former don’t take dividends into account. An index fund, by virtue of actually holding positions in the various stocks that comprise the index, is eligible for whatever dividends those stocks’ companies’ managers decide to pay out to shareholders.
Why are futures prices trending downward?
More fundamentally, why indeed are the upcoming futures prices trending downward rather than trending upward? Or even just staying neutral? The usual suspects are to blame – economic uncertainty, unimpressive growth, a base level of political agitation. Throw in other negatives, no matter how incidental they are to the stock market (e.g. ISIS, Ebola) and here we are.
How to value a stock?
The most common way to value a stock is to compute the company's price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio . The P/E ratio equals the company's stock price divided by its most recently reported earnings per share (EPS). A low P/E ratio implies that an investor buying the stock is receiving an attractive amount of value.
What is a stock?
A single share of a company represents a small ownership stake in the business. As a stockholder, your percentage of ownership of the company is determined by dividing the number of shares you own by the total number of shares outstanding and then multiplying that amount by 100. Owning stock in a company generally confers to the stock owner both corporate voting rights and income from any dividends paid.
What is GAAP earnings?
GAAP is shorthand for Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, and a company's GAAP earnings are those reported in compliance with them. A company's GAAP earnings are the amount of profit it generates on an unadjusted basis, meaning without regard for one-off or unusual events such as business unit purchases or tax incentives received. Most financial websites report P/E ratios that use GAAP-compliant earnings numbers.
Why do investors use adjusted earnings to calculate P/E?
Non-repeating events can cause significant increases or decreases in the amount of profits generated, which is why some investors prefer to calculate a company's P/E ratio using a per-share earnings number adjusted for the financial effects of one-time events. Adjusted earnings numbers tend to produce more accurate P/E ratios.
How to calculate forward P/E ratio?
The forward P/E ratio is simple to compute. Using the P/E ratio formula -- stock price divided by earnings per share -- the forward P/E ratio substitutes EPS from the trailing 12 months with the EPS projected for the company over the next fiscal year . Projected EPS numbers are provided by financial analysts and sometimes by the companies themselves.
Why should investors consider companies' strengths and weaknesses when gauging a stock's value?
Aside from metrics like the P/E ratio that are quantitatively computed, investors should consider companies' qualitative strengths and weaknesses when gauging a stock's value. A company with a defensible economic moat is better able to compete with new market participants, while companies with large user bases benefit from network effects. A company with a relative cost advantage is likely to be more profitable, and companies in industries with high switching costs can more easily retain customers. High-quality companies often have intangible assets (e.g., patents, regulations, and brand recognition) with considerable value.
Why do P/S ratios vary?
Across industries, P/S ratios can vary greatly because sales volumes can vary greatly. Companies in industries with low profit margins typically need to generate high volumes of sales.
When to count in stock?
Generally, we recommend counting an item as in-stock if it has at least one day of expected demand or the median customer order quantity (whichever is greater) in stock at the start of the day. However, we find that unless you run an extremely tight inventory, the result you get using this method will be extremely close to the result achieved if you count any item that has any units available as in-stock.
What is the fill rate?
Fill rate and backorder rate both refer to the percentage of actual demand from customers that you were able to fill immediately from inventory on the shelf. In companies that do not allow backordering, order lines that cannot be filled from stock are generally cancelled, and the customer is notified.
What is the difference between 100% and 90% line fill rate?
Many companies will instead measure their line fill rate. The difference is that 100% of the units on a line must be in-stock for that line to count as in-stock. So if a customer placed a 10 line order and all lines were fully in stock except the one above, that order would have a 90% line fill rate - we don't get any credit for the 50 unit partial fill.
How does order fill rate work?
An order fill rate works the same way - all units on all lines of the order must be 100% in-stock in order for the order to count as in-stock. If we received 10 customer orders and all but the order above were 100% in-stock, we'd end up with a 90% order fill rate. We don't get any credit for the 9 perfect lines on that last order, because the 10th line only had a 50% unit fill rate. Another term for order fill rate is "perfect order rate" since from the customer's perspective, a successfully filled order, where all units on all lines are in-stock, is the best possible outcome.
Why are sales depressed when an item is out of stock?
What this means is that fill rate (which measures only actual demand from customers) is going to be a falsely optimistic measure of performance , since you can't have a backorder if the customer never bought the item! This is the main reason to utilize in-stock rates as well as fill rates in your metrics. (We'll do a future article on "spill rate" which will allow you to quantify the financial impact of lost sales when out of stock.)