
Accrued interest is calculated as of the last day of the accounting period. For example, assume interest is payable on the 20th of each month, and the accounting period is the end of each calendar month. The month of April will require an accrual of 10 days of interest, from the 21st to the 30th.
What is the amount of accrued interest?
The amount of accrued interest to be recorded is the accumulated interest that has yet to be paid as of the end date of an accounting period. Accrued interest is calculated as of the last day of the accounting period. For example, assume interest is payable on the 20th of each month, and the accounting period is the end of each calendar month.
How are stocks affected by interest rates?
There are two main ways in which stocks are affected by interest rates: directly and indirectly. Here is a summary of how businesses, and therefore stocks, are affected by changes to interest rates: 1. Businesses are directly affected by bank rates because they affect the amount a company can afford to borrow.
What is the net effect of accruing interest on a bond?
Because the adjusting journal entry reverses in the second month, the net effect is that $82.19 ($123.29 - $41.10) of the payment is recognized in the second month. That is equivalent to the 20 days worth of interest in the second month. Accrued interest is an important consideration when purchasing or selling a bond.
What do rising interest rates mean for tech stocks?
If you are in the business of lending money, higher rates mean higher margins. On the other hand, rising rates tend to hurt growth stocks, like tech startups. In uncertain markets, investors tend to look for stable companies, like commodities, Dow Jones stalwarts or even older, established tech firms.
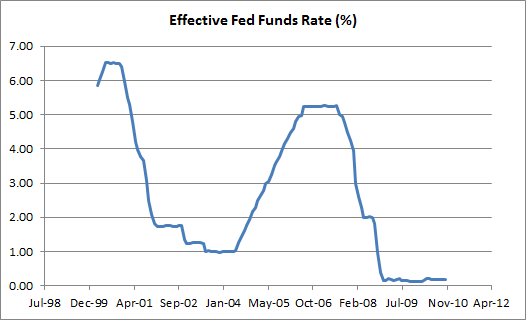
What is accrued interest in stock market?
What Is Accrued Interest? In accounting, accrued interest refers to the amount of interest that has been incurred, as of a specific date, on a loan or other financial obligation but has not yet been paid out.
How does interest rate accrue?
The amount of interest that accrues is based on your interest rate and your principal balance. Accounts that earn interest, such as high-yield savings accounts and certificates of deposit, also typically accrue interest daily, but the yield is based on your average daily balance.
How is accrued interest calculated on securities?
How is Accrued Interest Calculated?Step 1: Factor = 90 days / 180 days = 0.5.Step 2: Interest Rate = 5.0%, Interest Rate per Payment = 0.05 / 2 payments per year = 0.025.Step 3: Accrued Interest = $10,000 × 0.025 × 0.5 = $125.
How do you record accrued interest on investments?
To record the accrued interest over an accounting period, debit your Interest Expense account and credit your Accrued Interest Payable account. This increases your expense and payable accounts.
What is the difference between interest and accrued interest?
Accrued interest is the accumulated interest that has been recognized and recorded but has not been paid as of a specific date. Regular interest is the payment made in exchange for borrowing money from a lender.
Is accrued interest good or bad?
Accrued interest is used when an investment pays a steady amount of interest, which can be easily prorated over short periods of time. Bonds are good examples of investments where accrued interest calculations are useful.
How do you calculate monthly accrued interest?
Calculating monthly accrued interest To calculate the monthly accrued interest on a loan or investment, you first need to determine the monthly interest rate by dividing the annual interest rate by 12. Next, divide this amount by 100 to convert from a percentage to a decimal.
How do you calculate accrued and unpaid interest?
First, take your interest rate and convert it into a decimal. For example, 7% would become 0.07. Next, figure out your daily interest rate (also known as the periodic rate) by dividing this by 365 days in a year. Next, multiply this rate by the number of days for which you want to calculate the accrued interest.
What is interest accrued but not due?
Interest Accrued But Not Due means that portion of interest income on loans and advances which has accrued for the accounting period but has not become due for payment by borrower.
Where does accrued interest go on the balance sheet?
Borrowers list accrued interest as an expense on the income statement and a current liability on the balance sheet. Lenders list accrued interest as revenue and current asset, respectively.
Are interest paid and interest accrual both counted as being taxable?
Tax on interest income from fixed deposits Interest earned from fixed deposits is liable to be taxed on an accrual basis at the applicable slab rates. Interest is fully taxable at the slab rates applicable to the person. The deduction of Rs 10,000 is not applicable as it is allowed in the savings account interest.
What is accrued interest?
In accounting, accrued interest refers to the amount of interest that has been incurred, as of a specific date, on a loan or other financial obligation but has not yet been paid out. Accrued interest can either be in the form of accrued interest revenue, for the lender, or accrued interest expense, for the borrower.
How is accrued interest calculated?
Accrued interest is calculated as of the last day of the accounting period. For example, assume interest is payable on the 20th of each month, and the accounting period is the end of each calendar month. The month of April will require an accrual of 10 days of interest, from the 21st to the 30th. It is posted as part of ...
How many days of interest is accrued in April?
The month of April will require an accrual of 10 days of interest, from the 21st to the 30th. It is posted as part of the adjusting journal entries at month end. Accrued interest is reported on the income statement as a revenue or expense, depending on whether the company is lending or borrowing.
What is the ultimate goal of accruing interest?
The ultimate goal when accruing interest is to ensure that the transaction is accurately recorded in the right period. Accrual accounting differs from cash accounting, which recognizes an event when cash or other forms of consideration trade hands.
Is receivable a short term asset?
The receivable is consequently rolled onto the balance sheet and classified as a short-term asset. The same amount is also classified as revenue on the income statement. The accrued interest for the party who owes the payment is a credit to the accrued liabilities account and a debit to the interest expense account.
Is accrued interest a current asset?
In addition, the portion of revenue or expense yet to be paid or collected is reported on the balance sheet, as an asset or liability. Because accrued interest is expected to be received or paid within one year, it is often classified as a current asset or current liability .
Interest rates are going up
Super-easy pandemic monetary policy gave strong support to asset prices. The prices of bonds in the secondary markets increased as new bonds could be issued at lower rates (and thus lower current yields - see example on how interest rates affect bonds).
How do stocks perform when interest rates rise?
Historically, when rates increase it's actually good for stocks overall. Again, the implications are that rates are going up to slow (not stop) the rate of economic growth. A strong economy can be very good for companies.
Diversification, my old friend
The purpose of diversification is because like broad-based market moves, there’s no way to know when certain sectors, styles, or factors are going to outperform or underperform, for how long, and to what extent.
What is accrued interest?
Accrued interest is interest that has been earned on an annuity, bond, or other investment but has not yet been paid out. Accrued interest on an annuity is tax-deferred until it is withdrawn. Interest accrued since the last payment date on a bond sold on the secondary market is owed to the seller at the time of the sale.
Why is accrued interest paid to sellers?
Accrued interest maintains an equitable balance between buyers and sellers. It’s paid to sellers because they earned it during the time they owned the bond. When the new owner receives the next full semiannual interest payment, it will include interest earned prior to the time the new owner actually owned the bond.
How often do bonds pay interest?
The coupon rate of interest is what the bond will earn in an entire year. And most bonds pay interest semiannually, that is, two times a year. Since the accrual period is typically measured in days, we need to compute the bond’s daily earnings.
What is the face value of a bond?
There are just three components to it: the face value of the bond, which is also referred to as the “par” value; the “coupon rate” of the bond, which is the annual yield paid by the issuer; and the length of the accrual period. Face value of a bond is its nominal, or par, value. This is the amount printed on the face of the certificate.
Do bonds have accrued interest?
Other Instruments that Accrue Interest. Bonds are not the only financial instruments that accrue interest. Anyone who has ever sold a home or paid off an auto loan has encountered accrued interest. The principal is the same. Interest accrues and is due to the lender before a regular payment date.
Do zero coupon bonds pay interest?
Like regular bonds, zero-coupon bonds pay a stated rate of interest. They just don’t pay it out in regular semiannual distributions. Instead, zero-coupon bonds are sold to investors at a deep discount to their face value and pay all of the interest at maturity.
Is accrued interest taxable?
Accrued interest isn’t taxable, per se. For a cash basis taxpayer interest income is taxable when it is received, not when it is earned, or accrued. Bonds accrue interest every day, but they pay interest only twice a year. When those payments are received, they become taxable — assuming the bond is a taxable bond.
What is accrued interest?
Accrued interest is the amount of extra money owed on a loan or credit that has accumulated over an accounting period and has yet to be paid. If you take out a mortgage or make purchases on a credit card, you will typically wind up being charged interest in exchange for having access to these funds. On the other hand, if you purchase bonds, you are ...
What is regular interest?
If you have a regular interest loan, the payment due will be the same so long as it is made within the contracted period. A regular interest agreement establishes a set interest rate that spans the entirety of the credit or loan agreement. This means that calculating the interest payment for the whole contract is as simple as multiplying ...
How to find average daily balance?
To determine the account's average daily balance, add up the principal balance on each day of the month and then divide by the number of days in the month. This is important to use with accounts that have fluctuating balances. For example, if you had a $1,000 balance on an account for the first 10 days of a 30-day month ...
How does interest rate affect stock market?
Interest rate impacts on stocks. In contrast to bonds, interest rate changes do not directly affect the stock market. However, Fed actions can have trickle-down effects that, in some cases, impact stock prices. When the Fed raises interest rates, banks increase their rates for consumer loans.
How does the Federal Reserve affect stocks?
When the Federal Reserve changes interest rates, it can affect your portfolio. Interest rate fluctuations can send ripple effects throughout the economy. While the recent interest rate cuts are meant to support and stimulate current economic activity, it’s possible these effects could have an impact on stocks, bonds and other investments.
What happens when the Fed raises interest rates?
When the Fed raises interest rates, banks increase their rates for consumer loans. In theory, this means there’s less money available for consumer spending. Also, increased rates for business loans can sometimes cause companies to halt expansions and hires.
Why does the Fed lower interest rates?
If economic growth is lagging and unemployment is rising, the Fed can lower interest rates to make it cheaper to borrow, which should spur hiring, investing and consumer spending. On the other hand, when the economy is growing quickly, the Fed may become concerned about inflation.
Does a rate hike affect stocks?
Reduced consumer and business spending can both lower the value of a company’s stock. Still, there’s no guarantee that a rate hike will negatively impact stocks. Typically, rising interest rates occur during periods of economic strength. In this scenario, increased rates often coincide with a bull market.
Can interest rate hikes hurt real estate?
Commodity prices may fall when interest rates rise, suggesting that an interest rate hike sometimes creates an unfavorable climate for these investments and vice versa. If you have holdings in real estate, an interest rate hike can be detrimental, while a cut can be beneficial.
Do bonds have higher coupons?
Newly issued bond s will have higher coupons after rates rise, making bonds with low coupons issued in the lower-rate environment worth less. It’s helpful to understand the following three concepts regarding the bond and interest rate relationship.
How are stocks affected by interest rates?
There are two main ways in which stocks are affected by interest rates: directly and indirectly. Here is a summary of how businesses, and therefore stocks, are affected by changes to interest rates: 1. Businesses are directly affected by bank rates because they affect the amount a company can afford to borrow. ...
Why are stocks attractive when interest rates fall?
It may seem easier to find attractive stocks when interest rates fall because lower rates can lead to higher disposable income in an economy, along with potentially lower borrowing costs for companies. Some stocks that may embark on an bullish theme around these scenarios include:
What happens to stock prices when interest rates decrease?
When interest rates decrease, it’s cheaper for companies to borrow capital with the aim of achieving growth, and this may encourage stock prices to rise. 2.
Why do central banks have volatility?
When central banks are due to announce changes in interest rates, this in and of itself can cause volatility around the markets. As mentioned previously, the stock market is quick to react to changes in interest rates, so traders will often be making their projections ahead of major central bank announcements.
Why is borrowing more expensive?
Borrowing becomes more expensive and there is more incentive to save money, so people may be encouraged to spend less. Lower interest rates may boost economic growth. Borrowing becomes cheaper and there is less incentive to save money, so people may be encouraged to spend or invest.
How long does it take for the stock market to catch up to interest rate changes?
The stock market often reacts quickly to interest rate changes – certainly more quickly than many other areas of the economy, which may take up to 12 months to catch up. This can mean many opportunities for traders who analyze stock markets, both when buying and holding or employing a shorter-term speculative approach.
What are the different types of interest rates?
There are different types of interest rates that will affect the stock market – the main distinction is: Bank rates: This is the rate at which banks lend to each other. It’s also the rate that directly influences the stock market. In the US, this is called the Fed Funds rate. Consumer interest rates: These are the rates charged on loans ...

What Is Accrued Interest?
- In accounting, accrued interest refers to the amount of interestthat has been incurred, as of a specific date, on a loan or other financial obligation but has not yet been paid out. Accrued interest can either be in the form of accrued interest revenue, for the lender, or accrued interest expense, for the borrower. The term accrued interest also re...
Understanding Accrued Interest
- Accrued interest is calculated as of the last day of the accounting period. For example, assume interest is payable on the 20th of each month, and the accounting period is the end of each calendar month. The month of April will require an accrual of 10 days of interest, from the 21st to the 30th. It is posted as part of the adjusting journal entriesat month-end. Accrued interest is rep…
Accrued Interest Example - Accounting
- Consider the following example. Let us assume there is a $20,000 loan receivable with an interest rate of 7.5%, on which payment has been received for the period through the 20th day of the month. In this scenario, to record the extra amount of interest revenue that was earned from the 21st to the 30th of the month, the calculation would be as follows: 1. (7.5% x (10 / 365)) x $20,00…
Accrued Interest Example - Bonds
- Accrued interest is an important consideration when purchasing or selling a bond. Bonds offer the owner compensation for the money they have lent, in the form of regular interest payments. These interest payments, also referred to as coupons, are generally paid semiannually.1 If a bond is bought or sold at a time other than those two dates each year, the purchaser will have to tack on…