
When and how is a grant of restricted stock or RSUs taxed?
- Your taxable income is the market value of the stock at that time, minus any amount paid for the stock.
- You have compensation income subject to federal and employment tax ( Social Security and Medicare) and any state and local tax.
- It is then subject to mandatory supplemental wage withholding. ...
What are the tax implications of restricted stock?
Jan 31, 2017 · When the restricted stock is received, the recipient recognizes income for federal tax purposes in one of two ways: 1. Without Section 83(b) Election: The restricted stock award results in the recognition of ordinary compensation income in the year the restriction causing the substantial risk of forfeiture lapses. The amount included in compensation income is the …
What is restricted stock and how is it taxed?
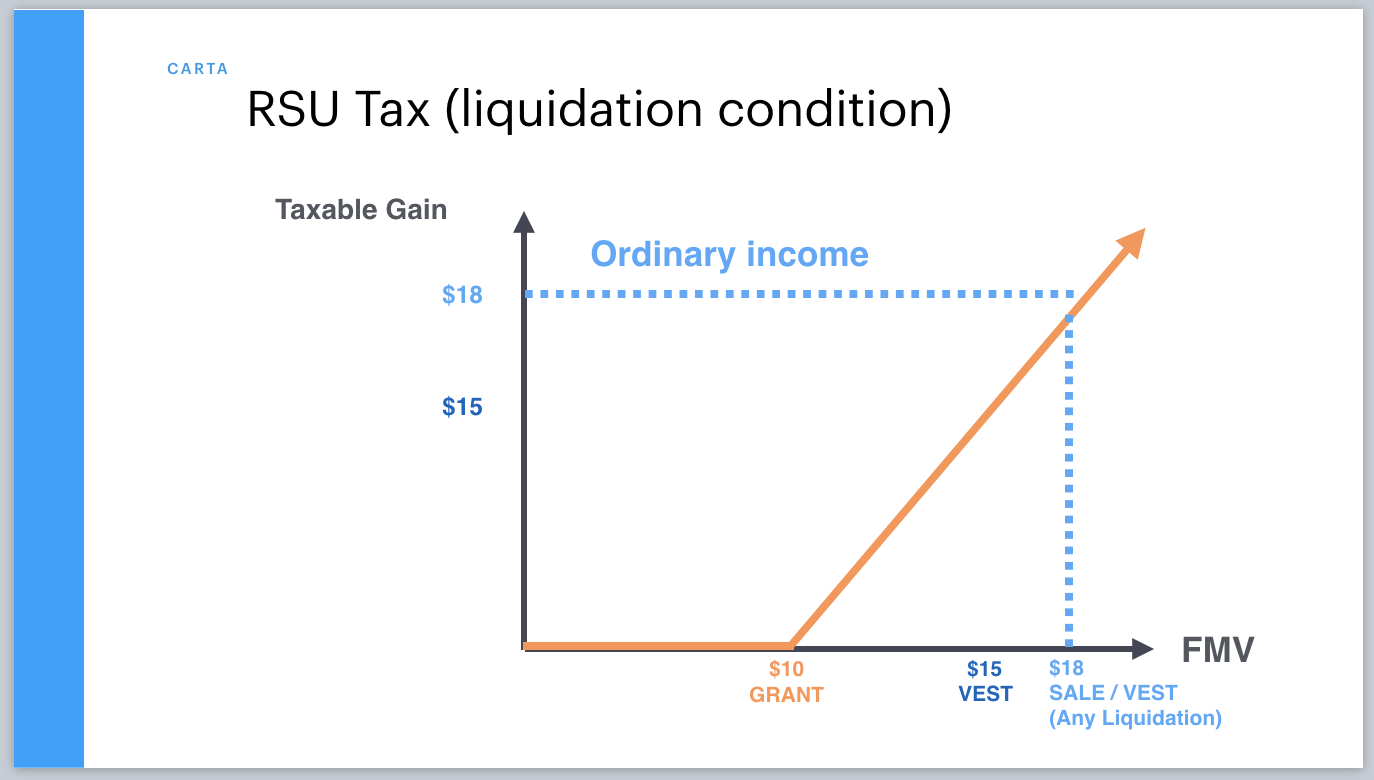
Oct 07, 2021 · How Are Stock Units Taxed? Since a stock unit award doesn’t pay out unless a certain contingency is met – whether this is the passage of time or achievement of a performance goal – the award is not taxable upon receipt. Instead, the employee is taxed when the award vests and the shares (or cash equivalent) is received.
Are restricted stock awards included on the W-2?
Feb 03, 2021 · How Are Restricted Stock Units (RSUs) Taxed? RSUs are taxed at the ordinary income rate and tax liability is triggered once they vest. This is different from incentive stock options , which are taxed at the capital gains rate and tax liability is …
How are RSUs taxed when sold?
Feb 01, 2012 · Consequently, a restricted stock award will result in taxable income to the employee under Sec. 83 in an amount equal to the excess of the stock’s FMV on the date the restriction lapses, over the stock’s sale price to the employee. The employee adjusts his or her original basis in the stock by the income amount.
Are restricted stock awards taxable?
Under normal federal income tax rules, an employee receiving a Restricted Stock Award is not taxed at the time of the grant (assuming no election under Section 83(b) has been made, as discussed below). Instead, the employee is taxed at vesting, when the restrictions lapse.
How do you report restricted stock awards on taxes?
When your award is vested or distributed, your employer will withhold ordinary income and FICA† taxes. The tax amounts, along with the value of your shares, are reported on your W-2. Form 1099-NEC. The information on your W-2 (or 1099-NEC) is used to fill out tax form 1040.
Do my RSUs get taxed twice?
Are RSUs taxed twice? No. The value of your shares at vesting is taxed as income, and anything above this amount, if you continue to hold the shares, is taxed at capital gains.Mar 4, 2021
Are restricted stock awards included in W-2?
Since stock you receive through stock grants and RSUs is essentially compensation, you'll usually see it reported automatically on your W-2. Typically, taxes are withheld to go against what you might owe when you do your taxes.Jan 21, 2022
Why are RSU taxed so high?
Since RSUs amount to a form of compensation, they become part of your taxable income, and because RSU income is considered supplemental income, the withholding rate can vary from 22% to 37%.
How much tax is withheld from RSU?
22%Most employers withhold RSU income based on predetermined supplemental schedules at a flat rate of 22%. The problem is that as a result of your RSU windfall, combined with your regular salary, your actual marginal tax rate, when paying taxes next year may be much higher than the supplemental withholding rate.
Are RSUs taxed differently?
Taxation. With RSUs, you are taxed when the shares are delivered, which is almost always at vesting. Your taxable income is the market value of the shares at vesting. You have compensation income subject to federal and employment tax (Social Security and Medicare) and any state and local tax.
What happens to RSU when stock splits?
RSUs are real shares, they're just not available to you until the vesting date. But since they actually exist and aren't IOUs, they will split just like common stock would.
How are RSU taxed in Canada?
Generally, tax at vesting for RSU. Taxable amount is fair market value of the shares on the tax event; no deduction available. If RSUs are settled in cash or can be settled in cash or shares, depending on other terms of the RSUs, salary deferral arrangement rules may apply, resulting in tax at grant. Tax on sale.
How do you calculate cost basis on restricted stock awards?
Your cost basis is the amount your employer included on your W-2, which is the closing price on the vesting date times the number of shares vested.Feb 25, 2008
How do I report an RSU on my taxes in Canada?
Restricted Stock Units (RSUs) RSU's are effectively deferred employee bonuses. When the RSU's vest (when you're able to sell them), you'll receive a taxable benefit equal to the value of the shares received or cash received. This amount should be reported on your T4 from your employer.
Do you report restricted stock awards on W-2?
Unless you made an 83 (b) election, don't report a restricted stock award. In fact, you won't report anything until the stock vests. However, if you have an arrangement where you receive dividends on the award prior to vesting, the dividends should be included in box 1 (wages) of your W-2. If you did make a Section 83 (b) election, your employer ...
Can restricted stock be transferred?
Also called letter stock or Section 1244 stock, a restricted stock award comes with strings attached. For example, it cannot be transferred and it may be forfeited if the recipient fails to meet expectations. Unless you made an 83 (b) election, don't report a restricted stock award. In fact, you won't report anything until the stock vests.
What is restricted stock?
Restricted Stock Basics. In a typical restricted stock arrangement, an executive receives company stock subject to one or more restrictions. The most common restriction is a requirement for continued employment through a designated date. Often, the stock is transferred at no or minimal cost. The right to keep the shares is forfeited if ...
What happens when restricted stock is received?
When the restricted stock is received, the recipient recognizes income for federal tax purposes in one of two ways: 1. Without Section 83 (b) Election: The restricted stock award results in the recognition of ordinary compensation income in the year the restriction causing the substantial risk of forfeiture lapses.
What happens to the right to keep shares?
The right to keep the shares is forfeited if the executive fails to fulfill the terms. Tax-wise, the executive’s recognition of taxable income and the employer’s right to claim the related compensation deduction are both generally deferred until vesting, or when ownership of the shares is no longer restricted.
How long do you have to forfeit shares of a company?
Under the terms of the deal, you must forfeit the shares back to your employer if you leave the company for any reason before three years after the date of the transfer. If you sell the shares, whoever buys them must also forfeit them if you leave the company before the magic date.
When is a stock taxable for income and employment?
When no Section 83 (b) election is made, the stock’s value less any amount paid for it is recognized as taxable compensation for income and employment tax purposes when the stock becomes fully vested.
What is the major tax planning consideration for the executive?
The major tax planning consideration for the executive is deciding whether or not to make a Section 83 (b) election. In many cases, the risks of making the election will be perceived as greater than the potential tax-saving benefit, but you should consult your tax advisor before making that call.
Is a restricted stock subject to income tax?
As a result, the shares are considered restricted stock and are subject to the income and withholding tax considerations.
How Does Vesting Work?
Restricted Stock Units (RSUs) typically become payable to the employee (vest) over a period of time with the total award divided into increments that vest according to a schedule. Frequently, RSU awards are paid out in equal increments over 3-5 years.
What is Vesting?
There is no standard vesting schedule, so be sure to check the official grant document provided by your employer for details on how your award will vest.
How Are Stock Units Taxed?
Since a stock unit award doesn’t pay out unless a certain contingency is met – whether this is the passage of time or achievement of a performance goal – the award is not taxable upon receipt. Instead, the employee is taxed when the award vests and the shares (or cash equivalent) is received.
Vesting and Taxation for Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESOPs)
An ESOP is a form of qualified retirement plan in which your employer places company stock in a trust for your benefit. Vesting can occur gradually over a period of years (graded vesting) or all at once after a minimum number of years of service are met (cliff vesting).
What is the FMV of restricted stock?
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) allows for restricted stock shareholders to report the fair market value (FMV) of the stock when it is granted, as opposed to when the employee earns it through vesting. This is called the Section 83 (b) Election.
When are RSUs taxed?
Ordinary Income Tax : RSUs are taxed at the ordinary income rate when issued, typically after a vesting schedule. Capital Gains Tax : RSUs are only exposed to capital gains tax if the stockholder holds onto the stock and it appreciates in value before selling it.
What is the most important thing to understand about RSUs, vesting, and taxes?
The most important thing to understand about RSUs, vesting, and taxes is when the RSUs vest, their ownership is transferred to the employee or executive and they immediately have tax liability on the value of the RSUs.
Why do corporations grant RSUs?
Many corporations grant RSUs to executive with the purpose of incentivizing them to add as much value to the company as possible so they can benefit in the increasing stock price. RSUs are a form of restricted stock, which means they are ‘restricted’ in some form.
Is restricted stock a legal form?
RSUs and other forms of employee compensation are typically put in place using a legal agreement. If you need help with this type of employee compensation agreement, feel free to post a job in the ContractsCounsel marketplace for free to get bids from qualified lawyers.
Does restricted stock go on W-2?
Given restricted stock is routinely granted as a form of employee compensation, you will usually see it reported on your W-2. Typically, employees withhold taxes on behalf of their employees, which will go against what you owe when doing your taxes.
Do you have to pay taxes on RSUs?
No, RSUs are not taxed twice. However, it can seem like RSUs are taxed twice if you hold onto the stock and it increases in value before you sell it. RSUs are taxed at the ordinary income tax rate when they are issued to an employee, after they vest and you own them.
Why are restricted stock awards used?
One of the reasons for the shift to restricted stock is the reduced charge against income provided by restricted stock awards as compared to stock option grants. Restricted stock is also less dilutive to the company’s stock than options, because value to the employee can be achieved with fewer shares.
Why do employers issue restricted stock units?
Some employers choose to issue restricted stock units (RSUs) to employees rather than restricted stock, because employees cannot make a Sec. 83 (b) election in connection with restricted stock units. RSUs are unfunded promises to pay cash or stock to the employee based on a vesting schedule. One RSU is typically equal in value to one share ...
Why is the Sec 83 B election invalid?
83 (b) election was invalid because the company held the shares in escrow and they were not legally transferred to him.
Why is restricted stock less dilutive than options?
Restricted stock is also less dilutive to the company’s stock than options, because value to the employee can be achieved with fewer shares. Executive compensation practices came under increased congressional scrutiny when abuses at corporations such as Enron became public.
What is a capital loss deduction?
1.83-2 (a) does permit a capital loss deduction for the excess paid for forfeited stock above any amount realized upon the forfeiture, including any amount of the purchase price restored by the employer to the employee. Regs. Sec. 1.83-2 (a) also warns that a sale or other disposition of the property ...
Do CPAs have to be familiar with restricted stock awards?
With the increased popularity of restricted stock, CPA tax practitioners must be familiar with the rules governing taxation of restricted stock awards when advising clients who have been or may be offered restricted stock awards, as well as when advising corporations that make the awards.
Is 83 B deductible?
83 (b) carries at least two risks to the employee. One is that the property may not in fact appreciate but, rather, depreciate during the restricted period. In such case, the amount included in income when the employee made the election is not now deductible.
What is restricted stock unit?
Restricted stock units (RSUs) and stock grants are often used by companies to reward their employees with an investment in the company rather than with cash. As the name implies, RSUs have rules as to when they can be sold. Stock grants often carry restrictions as well.
How long do you have to hold stock to get taxed?
Here are the different ways you can be taxed: If you hold the stock for less than one year, your gain will be short term, and you'll owe ordinary income tax on it. If you hold the stock for one year or more, your gain will be long term, meaning you'll pay tax at the more favorable capital gains rate.
Do you have to pay taxes on RSU?
When you receive an RSU, you don't have any immediate tax liability. You only have to pay taxes when your RSU vests and you receive an actual payout of stock shares. At that point, you have to report income based on the fair market value of the stock.
Do stock grants vest?
Many stock grants have a vesting period, during which you may still lose the rights to the stock. Only when you are fully vested in the stock do you have 100% ownership rights to do with the stock as you please. As with RSUs, stock grants typically vest after a period of time, or after certain performance measures are met.
Do you report stock grants on W-2?
Since stock you receive through stock grants and RSUs is essentially compensation, you'll usually see it reported automatically on your W-2. Typically, taxes are withheld to go against what you might owe when you do your taxes.
What is restricted stock awards?
Restricted stock awards are a form of employee compensation where you're paid in stock, though you're not immediately free to sell the stock until you've been employed for a certain amount of time – when the stock is said to vest.
Why is restricted stock advantageous?
If employees anticipate that their restricted stock will gain in value between when it's awarded and when it actually vests and is available to sell, this can be advantageous because they will pay the lower capital gains tax rate rather than the ordinary income rate on that price difference.
What happens when restricted stock vests?
When restricted stock vests, employees are taxed on the market value of the stock, minus anything that they paid for it. Often stock grants simply give the restricted stock to employees as compensation, so they will have paid nothing for it and will be taxed on the market value of the stock. Employers often are required to withhold tax ...
Do employers pay employees in stock?
Employers sometimes prefer to pay employees a portion of their payment in stock, rather than in ordinary cash. They often don't want to immediately transfer the stock without restrictions to employees, though, and instead set up a so-called vesting schedule where the stock gradually becomes available to sell.
Do employers have to withhold tax on restricted stock?
Employers often are required to withhold tax from employee paychecks to cover this restricted stock as it vests. Sometimes, employees can have employers withhold some of the stock itself to pay the tax.
When do restricted stock make sense?
The two times restricted stock make sense are at formation (or shortly thereafter) when the value of the granted stock is nominal and when the recipient has sufficient means to pay the taxes and is willing to accept the tradeoff of paying taxes right up front in return for capital gains treatment upon sale.
What are the downsides of restricted stock?
The one downside to restricted stock is you have to pay income taxes on the stock grant. The stock grant will be valued at fair market value (which is likely to be the 409a valuation we discussed last week) and you will be taxed on it.
What happens if you don't make an 83 B election?
If the employee does not make an 83 (b) election within 30 days of receiving the shares, then the employer will have a tax withholding obligation on vesting.
What happens when an employee withholds taxes?
Employee Withholding. If the recipient is an employee, then the employer has to withhold income and employment taxes from the employee. This means the employee will have to write a check to the employer upon the taxing of the award. The taxing of the award can happen either at the time of grant or upon vesting.
Can you make an 83b election?
You can make an 83b election which will accelerate the tax to the time of grant and thus lock in a possibly lower valuation and lower taxes. …. This taxation issue is the reason most companies issue options instead of restricted stock.
Is stock award taxed?
Here is a short summary: 1) If the stock award is an award of fully vested shares, then the recipient of the award is taxed when he or she receives the shares, based on the value of the shares at that time.
