What is the Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac bailout?
The Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac bailout occurred September 6, 2008. The bailout came as the U.S. Treasury Department was authorized to purchase up to $100 billion in preferred stock of the organizations and buy mortgage-backed securities. As a result, Fannie and Freddie were put into conservatorship by the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA). 1.
What happened to Fannie Mae in 2007?
In August 2007, Fannie Mae announced it would skip a benchmark debt offering for the first time since May 2006. 11 Investors rejected even the highly-rated mortgage-backed securities offered by the GSEs. Most investors thought Fannie had enough cash to allow it to wait until the market improved.
What is Fannie Mae's role in the secondary market?
Fannie Mae has a federal charter and operates in America's secondary mortgage market to ensure that mortgage bankers and other lenders have enough funds to lend to home buyers at low rates. In 2008, we mark our 70th year of service to America's housing market.
When did Fannie and Freddie take on $100 billion in securities?
March 24, 2008, the Federal Housing Finance Board agreed to let the regional Federal Home Loan Banks take on an extra $100 billion in mortgage-backed securities for the next two years. Fannie and Freddie guaranteed those loans as well. 18.
See more
Is Fannie Mae stock a good buy?
FNMA scores best on the Stability dimension, with a Stability rank ahead of 80.88% of US stocks. The strongest trend for FNMA is in Growth, which has been heading up over the past 179 days. FNMA's current lowest rank is in the Sentiment metric (where it is better than 12.91% of US stocks).
Is FNMA a Pink Sheet stock?
At the market open Thursday, Fannie and Freddie will start trading on the over-the-counter bulletin board -- also known as pink sheets -- under the symbols "FNMA" and "FMCC."
What is the future of FNMA stock?
Stock Price Forecast The 2 analysts offering 12-month price forecasts for Federal National Mortgage Association have a median target of 1.00, with a high estimate of 1.00 and a low estimate of 1.00. The median estimate represents a +70.65% increase from the last price of 0.59.
Why did FNMA stock drop?
Shares of the mortgage giants Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac lost a third of their value after a Supreme Court decision threw cold water on the companies' path out of government control and a White House official said the administration was replacing the head of the agency that oversees them.
Where can I find Pink Sheet stocks?
Where can you buy pink sheet stocks? Unlike the stock for most major companies, you can't buy and sell shares of pink sheet stocks on a major stock exchange. Instead, pink sheets are traded over-the-counter by a company called OTC Markets Group Inc.
What does pink sheets mean in stocks?
Key Takeaways. Pink sheets are listings for stocks that trade over-the-counter (OTC). Pink sheet listings are not listed on a major U.S. stock exchange. Most pink sheet stocks are considered penny stocks that trade for less than $5 per share. Pink sheet stocks are considered risky due to a lack of regulatory oversight.
Can Pink Sheet stocks be delisted?
When a stock's price falls below $1 on the NYSE of NASDAQ, the stock is automatically delisted. Delisted stocks can still be traded through pink sheets or over-the-counter services.
How do you know if a stock is OTC?
Over-the-Counter stocks are traded on the OTCBB Markets yet are not listed on any national exchange. The only way to determine whether a stock is trading on OTC is by checking the OTC Markets Group website for more information. A new set of stocks is added to the Over-The-Counter market every year.
When did Fannie Mae hit a 52 week low?
What happened to Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac?
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac hit at a new 52-week-low - Jul. 7, 2008.
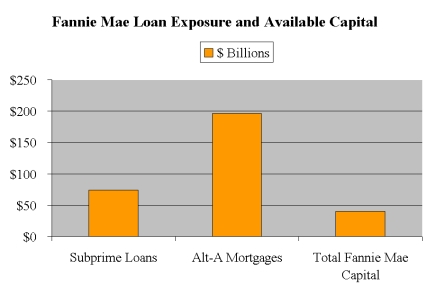
How much capital does Fannie Mae need?
Shares of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac plummeted Monday after a Lehman Brothers report raised fears the two would need to raise more capital.
Is there a bailout for Fannie and Freddie?
The potential accounting change would require Fannie Mae to add $46 billion of capital and Freddie Mac to add $29 billion of capital, Harting noted. Fannie Mae was not immediately available for comment about the Lehman report. Sharon McHale, spokesperson for Freddie Mac, said that Freddie Mac will "not comment on changes in the stock price.".
Do Fannie and Freddie need to raise capital?
As such, concerns have grown about their need for more capital. Some analysts have even suggested that a government bailout of the two may be necessary. But one analyst said the accounting changes discussed in the Lehman report were so drastic, that it's hard to imagine Fannie and Freddie being forced to adopt them.
When did Fannie Mae stop offering benchmark debt?
Nonetheless, the thought that Fannie and Freddie may need to raise more capital further spooked Wall Street, which prior to the Lehman report already had plenty of reasons to be worried about Fannie and Freddie as well as other financial stocks.
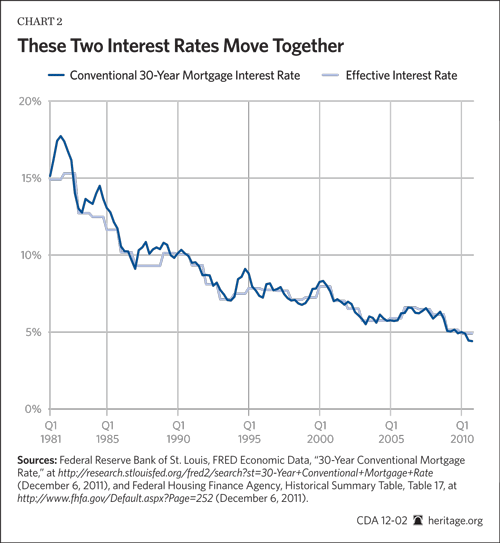
What was the mortgage rate in 2008?
In August 2007, Fannie Mae announced it would skip a benchmark debt offering for the first time since May 2006. Investors rejected even the highly-rated mortgage-backed securities offered by the GSEs. Most investors thought Fannie had enough cash to allow it to wait until the market improved.
How much money did Fannie and Freddie pay back in 2012?
Despite the bailout, mortgage rates continued to rise. By August 22, 2008, rates on a 30-year mortgage were 6.52%. That was a 30% increase since March and the same as a year ago. Rates rose despite a decline in U.S. Treasury bond yields. Those fell as investors fled to the safety of government-backed bonds. (Bond yields fall when demand for the underlying bond rises.)
What was the purpose of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac?
Fannie remitted $147 billion, and Freddie paid $98 billion. The Fannie and Freddie bailout was greater ...
What was the bailout of Fannie and Freddie?
Building a House for the Bailout. Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac were two government-sponsored enterprises (GSE) that bought mortgages from banks, a process known as buying on the secondary market. These purchased loans were then repackaged into mortgage-backed securities (MBS).
How much did Fannie and Freddie pay?
Treasury Department was authorized to purchase up to $100 billion in preferred stock of the organizations and buy mortgage-backed securities . As a result, Fannie and Freddie were put into conservatorship by the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA).
Why did Fannie and Freddie take risks?
Fannie remitted $147 billion, and Freddie paid $98 billion. The Fannie and Freddie bailout was greater than the 1989 saving and loan crisis, which cost the taxpayers $124 billion. It was on par with the subsequent 2008 bailout of AIG, which started at $85 billion but grew to $182 billion. Both were small potatoes compared to ...
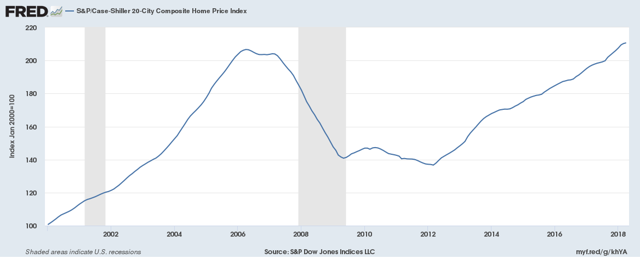
What happened in 2008 housing market?
However, that set-up was flawed and became a part of the problem. With a lack of self-control, Fannie and Freddie took excessive risks to boost their stock prices, knowing they would be bailed out if their risky practices turned south.
How much of Fannie and Freddie are owned by the government?
This of course created large losses on the insured mortgage portfolios and created a potential claim several hundred billions greater than the capitalization of the enterprises.
How long have Freddie and Fannie been cash cows?
So the government decided that the best course of action would be to take Fannie and Freddie into conservatorship. The government now owns warrants on 79.9% of the companies and, until very recently, received all of their profits. Close to $300 billion over 12 years. And the government STILL owns 79.9% of the companies.
What would happen if the mortgage industry failed?
In other words, Fannie and Freddie have been significant cash cows for the U.S. Treasury for more than six years.
What did the Department of Treasury do to the mortgages?
Additionally, because they own the majority of mortgages in the US, had they failed, the government (or the mortgage industry) would have had quite a mess on its hands, trying to figure out how to deal with the high number of foreclosures as well as dealing with the passthrough of funds from existing mortgages to the MBS investors.
Did Fannie Mae stock fall?
The Department of Treasury injected the required capital in exchange for a claim on all future profits that the enterprises may ever create. This in essence wiped out the existing equity investors but protected the holders of the insured mortgages.
What is net profit sweep?
Fannie Mae stock fell from the mid-60s in 2007 to under $1 in 2008. Freddie Mac was similarly afflicted. Both of the GSEs (Government Sponsored Enterprises) are directly involved in supporting the housing market. When the housing market crashed in 2008, there was concern that Fannie and Freddie would become insolvent. to say that that would have exacerbated the financial crisis in 2008 would be akin to saying the bomb over Hiroshima was a loud pop. Had they failed, the trillions (yes, that’s a T) of dollars in mortgage-backed securities that they guaranteed wou