Will the European Central Bank’s latest monetary policy decision send stocks lower?
LONDON-European stocks are expected to open lower on Thursday with the region’s investors geared up for the European Central Bank ’s latest monetary policy decision, in which it’s widely expected to announce its first interest rate hike in years.
Why did the European Central Bank raise interest rates?
FRANKFURT, July 21 (Reuters) - The European Central Bank raised interest rates by more than expected on Thursday as concerns about runaway inflation trumped worries about growth, even while the euro zone economy is suffering from the impact of Russia's war in Ukraine.
What does the ECB’s Frankfurt policy meeting mean for investors?
The European Central Bank’s policy meeting in Frankfurt on Thursday is at the forefront of investors’ minds, with policymakers having given advance notice of a first hike in 11 years. Still, this comes against a backdrop of slowing growth, the war in Ukraine and threats to energy supplies.
Will the ECB slow asset purchases under Pepp due to inflation?
Rising inflation has led to speculation about when and how the ECB will begin to slow asset purchases under PEPP, which was set up last year to keep finance flowing easily and cheaply to the real economy as the COVID-19 pandemic struck.

What is the ECB interest rate 2022?
Key ECB interest rates Accordingly, the interest rate on the main refinancing operations and the interest rates on the marginal lending facility and the deposit facility will be increased to 0.50%, 0.75% and 0.00% respectively, with effect from 27 July 2022.
Why ECB increase interest rate?
We are the central bank for the euro, and it is our mandate to keep prices stable. When prices in our economy are rising too fast – that is, when inflation is too high – increasing interest rates helps us bring inflation back down to our 2% target over the medium term.
Did ECB raise rates?
The ECB raised its benchmark deposit rate by 50 basis points to 0 percent on Thursday, despite for weeks guiding markets to expect a 25 basis point increase.
When was the last time ECB raised rates?
July 2011The last time the bank raised rates, in July 2011, policymakers reversed the move just four months later as a crisis in the region's bond markets intensified. These days, policymakers are walking a fine line between easing price pressures and drawing the European economy into a recession.
What does raising the interest rate do?
Higher interest rates help to fight inflation by raising the cost of borrowing, encouraging people and businesses to borrow less and spend less. In theory that is meant to lead to lower demand and slow price rises - but it also means less economic activity.
What do Increased interest rates mean?
Banks. An increase in the Fed benchmark rate often means banks will pay more interest on deposits. Larger banks are less likely to pay consumers more, and online banks have already started raising some of their rates.
What is ECB rate now?
Fixed Rate Tender: 0.50%
How does raising interest rates affect inflation?
The higher cost of money reduces your purchasing power — what you can afford to buy — and the Fed is effectively making you buy less. And that should bring down inflation.”
Will interest rates go down?
We Expect the Fed to Pivot to Cutting Interest Rates in 2023 We project the federal-funds rate to fall from a peak 3% at the start of 2023 to 1.5% by 2024. Accordingly, longer-term yields—including mortgage rates— should fall as well. Falling inflation should clear the way for the Fed to cut interest rates.
Why does Europe have negative interest rates?
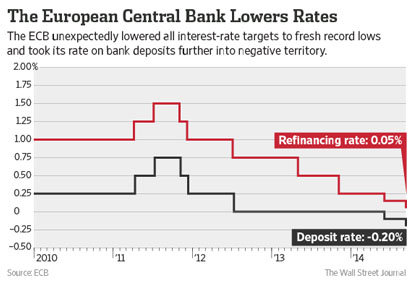
Since the global financial crisis, several central banks have deployed negative policy rates, after exhausting conventional easing measures. The European Central Bank introduced its negative interest rate policy (NIRP) in June 2014 when it cut its deposit facility rate below 0% for the first time, to -0.1%.
How often does the ECB set interest rates?
Every six weeksEvery six weeks, it takes its monetary policy decision, i.e. setting the key interest rates for the euro area.
What is Japan's interest rate?
The 10-year Japanese government bond (JGB) yield hit a six-year high of 0.268% in early trade on Friday, exceeding the BOJ's 0.25% cap, before retreating to 0.22% after the central bank's policy decision.
Has Europe raised interest rates?
The European Central Bank (ECB) has said it intends to raise interest rates for the first time in more than 11 years next month as it tries to control soaring inflation in the eurozone.
Are interest rates going up in Europe?
The European Central Bank (ECB) has raised interest rates for the first time since 2011 to tackle eurozone inflation that increased to 8.6% last month. In a surprise move, the ECB pushed its base rate up by 0.5 percentage points, after economists had expected a smaller 0.25 point rise.
Does raising interest rates actually help inflation?
The higher cost of money reduces your purchasing power — what you can afford to buy — and the Fed is effectively making you buy less. And that should bring down inflation.”
Is the ECB holding interest rates unchanged?
The European Central Bank's (ECB) governing council said on Thursday it would hold the eurozone's interest rates unchanged and keep its roster of unconventional monetary policy tools at the current calibrations, despite rising inflation across the bloc and an improving economic outlook.
Is the ECB slowing down PEPP?
Silvia Ardagna and Francois Cabau, economists at Barclays, said in a note last week that the ECB was unlikely to slow PEPP now "given still highly uncertain economic outlook and no meaningful change to a subdued medium-term inflation outlook".