Brokers and mutual fund companies are now required to keep records of cost basis, so securities acquired in the recent past are not a problem. But that won't help if your shares were originally on paper certificates, or were moved from one brokerage to another. Get the calculation wrong and the IRS could accuse you of underpaying your tax.
What is cost basis when selling stocks?
When you sell stocks and pay taxes on your capital gains, you'll have to figure out your cost basis. This is the amount you paid for the stock when you first purchased it -- modified for stock splits, dividends and capital distributions.
Do brokerage firms need to report cost basis?
In its Cost Basis Reporting FAQs, the IRS lays out what cost-basis reporting must be provided by brokerage firms and other financial institutions. Currently, brokerage firms must report cost basis and the type of capital gain (short-term or long-term) on Form 1099-B (or a substitute statement) for the sale of the following types of securities:
What happens to cost basis when a stock splits?
In a two-for-one split, for example, each share becomes two, and the cost basis is cut in half. Reinvested dividends, on the other hand, are added to the cost basis. So you can't just go into a newspaper archive to see what the stock traded at in 1930.
What determines the cost basis of an investment?
How much you paid for your investment determines your cost basis. When shares of stock are sold, it may affect your tax liability. If the shares are sold at a loss, you may be able to use that loss to save money on your taxes. If the shares are sold at a profit,...

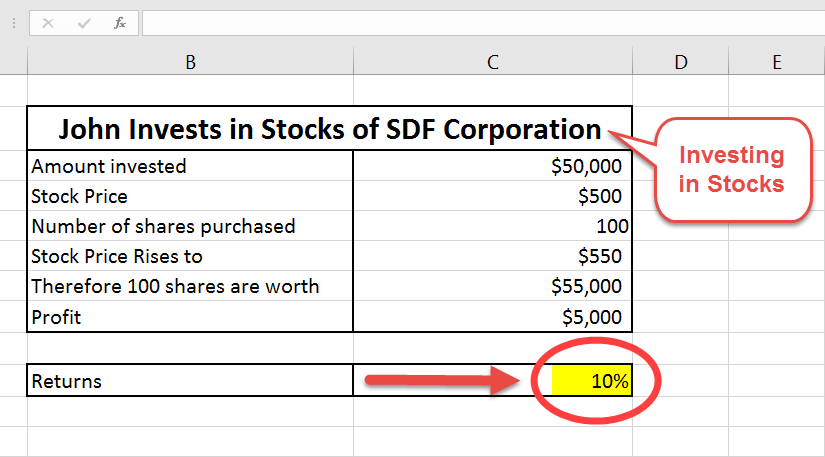
How do you calculate cost basis when selling stock?
You can calculate your cost basis per share in two ways: Take the original investment amount ($10,000) and divide it by the new number of shares you hold (2,000 shares) to arrive at the new per-share cost basis ($10,000/2,000 = $5).
Do brokers track cost basis?
Most brokerages offer cost basis tracking and report any necessary gains and losses to the IRS via Form 1099-B. The general default method for determining cost basis by brokerages is first-in, first-out (FIFO).
Does cost basis change when you sell shares?
If you reinvest a dividend that is paid out to you, the cost basis is the price you paid for the new shares. If you receive additional shares as part of stock split, your original cost basis does not change.
Do brokers report cost basis to IRS?
Specifically, brokers like Fidelity are now required to report adjusted basis (often referred to as “cost basis”) for “covered securities” on the IRS Form 1099-B part of the Fidelity consolidated tax reporting statement, if applicable, and to indicate whether the holding periods of disposed securities were short or ...
When did brokerage firms have to start tracking cost basis?
2008In 2008, Congress enacted mandatory cost basis reporting for brokers and mutual funds.
How does IRS verify cost basis?
Preferred Records for Tax Basis According to the IRS, taxpayers need to keep records that show the tax basis of an investment. For stocks, bonds and mutual funds, records that show the purchase price, sales price and amount of commissions help prove the tax basis.
What happens if you don't have cost basis for stock?
If options 1 and 2 are not feasible and you are not willing to report a cost basis of zero, then you will pay a long-term capital gains tax of 10% to 20% (depending on your tax bracket) on the entire sale amount. Alternatively, you can estimate the initial price of the share.
What is the best cost basis method?
Choosing the best cost basis method depends on your specific financial situation and needs. If you have modest holdings and don't want to keep close track of when you bought and sold shares, using the average cost method with mutual fund sales and the FIFO method for your other investments is probably fine.
Why is basis not reported to the IRS?
Short Term sales with cost basis not reported to the IRS means that they and probably you did not have the cost information listed on your Form 1099-B.
How do I know if basis was reported to IRS?
Sample of Form 1099-B 1545-0715) SHORT-TERM TRANSACTIONS FOR WHICH BASIS IS REPORTED TO THE IRS–Report on Form 8949, Part I, with Box A checked. Section A indicates whether the cost basis for the transaction was reported to the IRS and if the transaction is a short-term or long-term transaction.
Is brokerage included in capital gains?
Expenditure in connection with transfer/sale: It includes brokerage charges, registry charges or other expenses made on the asset sale. In equity shares and units of equity oriented mutual funds where STT is charged on sale transaction, the STT charges can't be deducted while computing capital gains.
When did cost basis start getting reported to IRS?
Back in 2008, Congress passed a law requiring brokers to report the cost basis of certain securities to the IRS when a sale occurred. The reporting requirements were rolled out in phases beginning in 2011.
What form do I need to report a covered securities transaction?
IRS regulations now require financial providers such as brokers and mutual fund companies to track basis, holding period, and sales proceeds for “covered securities” and to report this information to the investor and the IRS on Form 1099-B.
Do mutual fund distributions have to be included in basis calculations?
Investors often fail to include automatic reinvestments of mutual fund distributions in their basis calculations, which can be a costly mistake. Be sure to retain brokerage account and mutual fund statements and confirmations. If you are unable to adequately document your basis, the IRS will assume that it is zero.
What is cost basis?
Cost basis is the amount you paid to purchase an asset. When you invest in a stock, mutual fund or real estate, your cost basis is the price (or cost) of the asset on the day you bought it. Keeping track of your cost basis can help you determine your potential profit or loss should you decide to sell your asset.
Why is cost basis important?
Understanding the cost basis for your investments is important for tax purposes. Generally, selling an asset and realizing a profit or loss on that investment is considered a taxable event. In order to fully understand the tax consequences for the sale of an asset, you’ll need to know the original cost basis.
Ways to calculate cost basis
For equities such as stocks, mutual funds and exchange-traded funds, there are three primary methods investors use to calculate cost basis:
Examples of cost basis
Typically, when you purchase shares of stock, the cost basis is simply the price you paid for each share.
Why is cost basis important?
One reason calculating the cost basis correctly is important is it can affect your taxes. (Getty Images) Years and years ago, a beloved grandmother gave you a stock certificate for shares she'd cherished for decades, and now you're selling them for your child's fall semester. It happens all the time.
Do mutual funds keep cost basis?
Brokers and mutual fund companies are now required to keep records of cost basis, so securities acquired in the recent past are not a problem. But that won't help if your shares were originally on paper certificates, or were moved from one brokerage to another.
Can stock split over and over?
Over the years, the stock may have split over and over, dividends may have been reinvested, or the original company may have merged or been split apart. Each event can affect the cost basis. "For an investment that you purchase one time, it's easy to calculate – it's simply the price you pay for the investment the day you purchased it, ...
Should dividends be added to the price originally paid for the shares?
If she paid tax on dividends that were invested in more shares, then the dividends should be added to the price originally paid for the shares. Raising that cost reduces the profit after a sale, cutting the capital gains tax after you unload the shares.
What is the cost basis?
Cost basis refers to the amount paid to buy an asset and extra fees such as commission and transaction cost. When you liquidate your holding, your tax due depends on the original price of buying the asset (i.e., cost basis) and the selling price. If the selling price is higher than the purchase price, the transaction is profitable.
What is the importance of cost basis?
Monitoring the cost basis is essential for a number of reasons. You should keep this figure every time you make transactions for the following purposes:
How to compute the cost basis?
There are two common ways to calculate cost basis. These are the average cost technique and FIFO technique. The image below shows three techniques, but the last technique is not fairly common.
Which calculation technique is better?
We cannot say one cost basis calculation technique is better than the other because each one has its own upsides and downsides. You have the freedom to choose which method to use when computing the cost basis. When you do this, think about your financial condition and goal.
Factors affecting cost basis
There are several factors that can impact the cost basis of your holdings. We list down three factors below.
Final thoughts
Tracking the cost basis allows you to stay on top of your tax obligations related to capital gain. This will help you save money on taxes when you liquidate investments. Therefore, keeping a record of the cost of investments, the number of shares, and the date of purchase is important.
How to figure out capital gains tax?
To figure out your capital gains tax, you subtract your cost basis -- the fair market value when the stock vested in Year Five -- from the price you sold the stock for, or $75 a share in Year 10. You pay the long-term capital gain tax on the $25,000 increase in value from Year Five to Year 10.
What is fair market value?
Typically, the fair market value of the stock is based on an internal formula the company uses to value its stock. The company bases this valuation formula on some element of profitability, asset value or book value.
Do you have to report company purchased stock?
Company-Purchased Stock Taxes. Since the Internal Revenue Services considers company-purchased stock as compensation, you'll have to report it and pay taxes on it in the year you receive it. You can put this off if there's a considerable risk of you losing the stock -- meaning the stock is not vested, or owned by you.
Do you pay taxes on stock?
You pay taxes on the stock as ordinary income the year it vests. If you sell the stock later at a higher price, you'll also have to pay a long-term capital gains tax on the appreciation of the stock.
What is cost basis?
Cost basis is the price you paid to purchase a security plus any additional costs such as broker's fees or commissions. When you sell a security, your tax liability is determined by how much you spent to buy the security (cost basis) and your sales price.
How are capital gains taxed?
Capital gains are taxed at different rates depending on your tax bracket and how long you've held a security. If you sell a security that you've held for more than a year, any resulting capital gains are considered long-term and are taxed at lower rates than ordinary income. Conversely, short-term capital gains are taxed as ordinary income.
How long after a sale can you claim a wash sale?
However, if you purchase additional shares of the same or substantially identical security within 30 days before or 30 days after the sale date, you will have made a "wash sale," and you cannot claim the loss on your income tax return. Instead, you can add the disallowed loss to the basis of the security in your account.
Do you report capital gains on a mutual fund?
Capital gains and cost basis. If you sell an investment such as a stock or mutual fund, the IRS requires that you report any capital gains or losses along with cost basis information.
Who has to report sales on 1099-B?
Taxpayers have a long-standing responsibility to report gains and losses, and related cost basis information when they file their income tax returns. Brokers, such as Fidelity, also have a requirement to report sales information to the IRS on Form 1099-B.
Is a sale of a security taxable?
If you sell a security for more than the original purchase price, the difference is taxable as a capital gain. Gains from the sale of securities are generally taxable in the year of the sale, unless your investment is in a tax-advantaged account, such as an IRA, 401 (k), or 529 plan.
What happens when you sell shares of stock?
When shares of stock are sold, it may affect your tax liability. If the shares are sold at a loss, you may be able to use that loss to save money on your taxes. If the shares are sold at a profit, the money made on the sale is taxable income.
What is the fourth method of selling stocks?
The fourth method allowed by the IRS — and the second method approved for the sale of individual stocks and bonds — is the specific share method. When you give your broker instructions to sell, you also provide, in writing, a notation of which specific shares you want to sell. You must also receive from your broker confirmation in writing ...
