Earnings per share (EPS) is the portion of a company's profit allocated to each outstanding share of common stock. EPS (for a company with preferred and common stock) = (net income - preferred dividends) ÷ average outstanding common shares
- Earnings per share (EPS) is the portion of a company's profit allocated to each outstanding share of common stock.
- EPS (for a company with preferred and common stock) = (net income - preferred dividends) ÷ average outstanding common shares.
How to calculate earnings per share for the company?
The total average outstanding common shares of the company were 5 million. Calculate Earnings per share for the company. Earnings Per Share is calculated using the formula given below Earnings Per Share (EPS) = (Net Income of the Company – Dividend to Preferred Shareholders) / Average Outstanding Shares of the Company
Why do companies use average of outstanding shares for earnings?
Since the number of shares can frequently change, using an average of outstanding shares gives a more accurate picture of the earnings for the company. Earnings per share (EPS) is the portion of a company's profit allocated to each outstanding share of common stock.
How do you calculate the total number of shares outstanding?
Therefore, the total number of outstanding stocks is equal to: Outstanding stocks = 50000 – 3500 = 46500 stocks. Sometimes, companies don’t issue all the authorized stocks. Consider another example. ABC Corporation has 10000 authorized shares.
How do you calculate common stock on a balance sheet?
When you add up the liabilities and stockholder equity, their sum will always be equal to the total value of the company’s assets. To summarize, common stocks are listed under the equity section of the company balance sheet. From here, you can find the total number of outstanding common stocks.

What is the EPS ratio and how is it calculated?
Earnings per share ratio (EPS) is a financial ratio calculated by dividing net income by the total number of issued common shares. Investors use EPS to assess a company's performance and profitability before investing.
How do you calculate EPS on a balance sheet?
Basic earnings per share should be calculated by dividing the net profit or loss for the period attributable to equity shareholders by the weighted average number of equity shares outstanding during the period.
How do you calculate EPS without preferred dividends?
To calculate the EPS for common shares, subtract the preferred dividends from the corporation's net income and then divide the result by the number of common stock outstanding. You cannot calculate the EPS unless you know the number of preferred shares and the annual dividend payable to each preferred share.
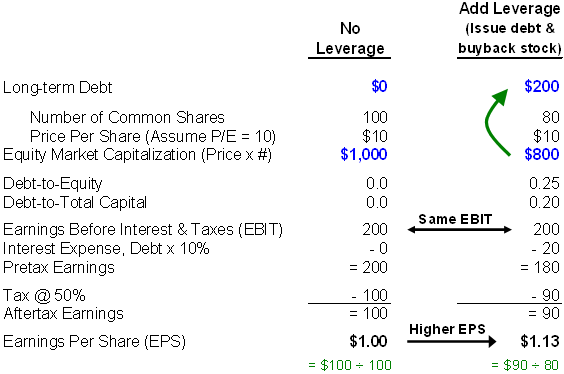
How do you calculate EPS from EBIT?
To calculate the level of EBIT where EPS remains stable, simply input the debt interest, current EPS and updated shares outstanding values and solve for EBIT: ($10.50 x 20,000) + 0 ÷ (1 - 0.3) + $500 = $300,500. Under this financing plan, the company must more than double its earnings to maintain a stable EPS.
How is EPS calculated example?
To determine the basic earnings per share you simply divide the total annual net income of the last year, by the total number of outstanding shares. Here is an example calculation for basic EPS: A company's net income from 2019 is 5 billion dollars and they have 1 billion shares outstanding.
How do I calculate EPS in Excel?
After collecting the necessary data, input the net income, preferred dividends and number of common shares outstanding into three adjacent cells, say B3 through B5. In cell B6, input the formula "=B3-B4" to subtract preferred dividends from net income. In cell B7, input the formula "=B6/B5" to render the EPS ratio.
Is earnings per share the same as dividends per share?
Earnings per share is a ratio that gauges how profitable a company is per share of its stock. On the other hand, dividends per share calculates the portion of a company's earnings that is paid out to shareholders.
How do you calculate EPS in capital structure?
Basic EPS = (Net Income – Preferred dividends)/ Weighted average number of common shares outstanding.If the company doesn't have preferred stock, then preferred dividends would be zero.The weighted average number of shares outstanding is a time weighting of common shares outstanding.
How is EBT calculated?
The calculation is revenue minus expenses, excluding taxes. EBT is a line item on a company's income statement. It shows a company's earnings with the cost of goods sold (COGS), interest, depreciation, general and administrative expenses, and other operating expenses deducted from gross sales.
What is EPS ratio?
EPS is a financial ratio. Financial Ratios Financial ratios are created with the use of numerical values taken from financial statements to gain meaningful information about a company. , which divides net earnings. Net Income Net Income is a key line item, not only in the income statement, but in all three core financial statements.
What does higher EPS mean?
Between two companies in the same industry with the same number of shares outstanding, higher EPS indicates better profitability . EPS is typically used in conjunction with a company’s share price to determine whether it is relatively “cheap” (low P/E ratio) or “expensive” (high P/E ratio).
Why is it more accurate to use a weighted average number of common shares over the reporting term?
It is more accurate to use a weighted average number of common shares over the reporting term because the number of shares can change over time. Any stock dividends or splits that occur must be reflected in the calculation of the weighted average number of shares outstanding.
How to calculate EPS?
To calculate a company's EPS, the balance sheet and income statement are used to find the period-end number of common shares, dividends paid on preferred stock (if any), and the net income or earnings.
Why is EPS higher?
A higher EPS indicates greater value because investors will pay more for a company's shares if they think the company has higher profits relative to its share price. EPS can be arrived at in several forms, such as excluding extraordinary items or discontinued operations, or on a diluted basis. 1:10.
How can a company game its EPS?
For instance, a company can game its EPS by buying back stock, reducing the number of shares outstanding, and inflating the EPS number given the same level of earnings. Changes to accounting policy for reporting earnings can also change EPS.
What is diluted EPS?
Analysts will sometimes distinguish between “basic” and “diluted” EPS. Basic EPS consists of the company’s net income divided by its outstanding shares. It is the figure most commonly reported in the financial media, and it is also the simplest definition of EPS.
What is EPS adjusted for?
It is common for a company to report EPS that is adjusted for extraordinary items and potential share dilution. The higher a company's EPS, the more profitable it is considered to be.
Does basic EPS factor in dilutive effect?
The formula in the table above calculates the basic EPS of each of these select companies. Basic EPS does not factor in the dilutive effect of shares that could be issued by the company. When the capital structure of a company includes items such as stock options, warrants, or restricted stock units (RSU), these investments—if exercised—could increase the total number of shares outstanding in the market.
How to calculate dividends on preferred stock?
Here's how to calculate it: Determine the company's dividends on preferred stocks. Subtract the company's dividends from its annual net income. Divide the difference by the average amount of outstanding shares. 1. Determine the company's dividends on preferred stocks.
What is the most useful measure to evaluate a company's financial strength and stock value?
One of the most useful measures to evaluate a company's financial strength and stock value is its earnings per share. In this article, define earnings per share , how to calculate earnings per share and how knowing what it means can help you make better investment decisions.
Why is weighted earnings per share more accurate?
Weighted earnings per share is a more accurate calculation of EPS because it considers the dividends, also known as preferred stocks, that a company issues to its shareholders. A dividend is the amount of money a company pays out to its shareholders from its profit, usually on a quarterly basis.
Why do stocks use trailing EPS?
Most stock market values use trailing EPS because it uses actual figures. However, investors may not look much at trailing EPS since it does not project future EPS figures.
What is EPS in accounting?
Earnings per share (EPS) is the portion of a company's net income, that would be earned per share if all profits were paid out to shareholders. EPS tells you a lot about a company, including a company's current and future profitability. EPS is easily calculated from basic financial information you can find online.
How to calculate EPS?
1. Determine the company's net income from the previous year. Using a company's net income or earnings for the primary number is the most basic way to determine EPS. This information is normally found on their website or a financial webpage. Be careful not to mistake quarterly net income for annual. 2.
What does higher EPS mean?
A higher EPS means a higher payout. A bigger EPS number means a company is more profitable and able to pay out more money to you as a shareholder. It's important to note, however, that no specific fixed number indicates you should buy shares or sell your shares.
How much was ABC's net income in FY18?
Assume ABC Corporation reported a net income of $10 million for the fiscal FY18. The common outstanding shares of the company at the start of fiscal FY18 were 5 million. During the fiscal FY18, the company had made a buyback of 1 million common shares from the open market.
Why do investors use multiple valuation metrics?
Investors in the financial world use multiple valuation metrics to value a company’s share prices and also to compare the valuation of companies in a specific industry. When earnings per share (EPS) is used on a standalone basis, it does not really tell much about a company and it is not very useful.
Why are common stocks listed in the equity section?
Common stocks are listed in the equity section because stocks are considered as an asset. From the total number of stocks, we can calculate the number of outstanding stocks. Outstanding stocks are stocks that are issued to the public and owned by stockholders, investors, and company members. If we deduct the number of treasury stocks ...
What is a claim on a company's assets?
The claims on a company’s assets are comprised of liability and equity. Liability includes the claims on the company’s assets by external firms or individuals. Mortgage and loans are examples of liabilities of a company.
What is equity in a company?
Equity is the claim of shareholders claims on the company assets. By purchasing stocks of the company, they have the right to claim ownership in the company. Their ownership percentage is determined by the ratio of shares owned to the total number of outstanding shares.
What is Treasury stock?
Treasury stocks are stocks that have been repurchased by the company that issued the stocks in the first place. These shares have no voting rights or dividend payments. Neither does this stock receive any assets after the company liquidates. To summarize the formula, Outstanding stocks = Issued stocks – Treasury stocks.
What happens when a company goes public?
When a company goes public from private, it offers an opportunity for investors to claim partial ownership in the company by buying its stocks. This initial offering is known as IPO and this is when the company becomes a publicly owned company.
Is equity a common stock?
Keep in mind that equity is not just comprised of common stocks. It also includes retained earnings, treasury stock, and preferred stocks. When you add up the liabilities and stockholder equity, their sum will always be equal to the total value of the company’s assets.
How to calculate earnings available for common stockholders?
To calculate earnings available for common stockholders, take the company's after-tax profit -- also called net income or earnings -- and subtract any amount of that profit that must be distributed to a senior class of shareholders. Dividends on preferred stock are the most common example of such a distribution.
What does "available" mean in stock?
"Available" mostly means that these earnings can be used to calculate earnings per share.
Is earnings available to stockholders?
Earnings vs. Cash. The fact that earnings are "available" to common stockholders doesn't mean common stockholders will be getting a check for their share of the profits. For one thing, profits do not necessarily equate to excess cash flow; all sorts of non-cash factors go into calculating a company's profit figure.
How to calculate common stock?
The formula for common stock can be derived by using the following steps: Step 1: Firstly , determine the value of the total equity of the company which can be either in the form of owner’s equity or stockholder’s equity. Step 2: Next, determine the number of outstanding preferred stocks and the value of each preferred stock.
What is the formula for common stock?
However, in some of the cases where there is no preferred stock, additional paid-in capital, and treasury stock, then the formula for common stock becomes simply total equity minus retained earnings. It is the case with most of the smaller companies that have only one class of stock.
What is common stock?
The term “common stock” refers to the type of security for ownership of a corporation such that the holder of such securities has voting rights that can be exercised for various corporate events. Examples of such events include a selection of the board of directors or other major corporate decision.
Why is common stock important?
The common stock is very important for an equity investor as it gives them voting rights which is one of the most prominent characteristics of common stock. The common stockholders are entitled to vote on various corporate subjects which may include acquisition of another company, who should constitute the board and other similar big decisions. Usually, each common stockholder gets one vote for every share. Another striking feature of common stock is that these stocks usually outperform another form of securities, like bonds and preferred stocks, in the long run. However, common stock comes with a strong downside, that in case a company goes into bankruptcy, then the common stockholders get nothing until the creditors are fully paid off. In other words, when the company has to sell off its assets, then the cash generated from the sale will first go to the lenders, creditors, and other stakeholders, then the common stockholders are paid if anything is left. As such, common stock is another appropriate example of the trade-off between risk and returns, such that these stocks offer a higher return as they are riskier than another form of securities.
What is the difference between a balance sheet and an income statement?
A balance sheet summarizes the financial assets and liabilities of a company, while the company's income statement shows the company's income and expenditures. To calculate the earnings per share, or EPS, you have to use the common shares outstanding from the balance sheet and the net income and preferred stock dividends from the income statement, ...
What is EPS in accounting?
EPS measures the amount of profit the company has for the year for each share. The higher the EPS for a company, the more profit it brings in for every outstanding common share. Find the company's net profit, dividends paid to the preferred shareholders and outstanding number of common shares on the income statement.
What is the Basic Earnings per Share Formula?
Basic earnings per share is the amount of a company’s earnings allocable to each share of its common stock. It is a useful measure of performance for companies with simplified capital structures.
Contingent Stock
If there is contingently issuable stock, treat it as though it were outstanding as of the date when there are no circumstances under which the shares would not be issued.
Weighted-Average Shares
Use the weighted-average number of shares during the period in the denominator. You do this by adjusting the number of shares outstanding at the beginning of the reporting period for common shares repurchased or issued in the period. This adjustment is based on the proportion of the days in the reporting period that the shares are outstanding.

The Significance of Earnings Per Share
Calculating Earnings Per Share
- EPS is calculated as follows: EPS=NI −PD AOCS where:PD=Preferred dividends \begin{aligned}&\text{EPS} = \frac { \text{ NI } - \text{ PD } }{ \text{ AOCS } } \\&\textbf{where:} \\&\text{PD} = \text{ Preferred dividends } \\\end{aligned}EPS=AOCS NI −PD where:PD=Preferred dividends As an example, suppose the …
The Bottom Line
- EPS becomes especially meaningful when investors look at both historical and future EPS figures for the same company, or when they compare EPS for companies within the same industry. Bank of America, for example, is in the financial services sector. As a result, investors should compare the EPS of Bank of America with other stocks in the financial services field, such as JP…
What Is Earnings Per Share (EPS)?
Formula and Calculation For EPS
- Earnings per share value is calculated as net income (also known as profits or earnings) divided by available shares. A more refined calculation adjusts the numerator and denominator for shares that could be created through options, convertible debt, or warrants. The numerator of the equation is also more relevant if it is adjusted for continuing operations.1 To calculate a compa…
How Is EPS used?
- Earnings per share is one of the most important metrics employed when determining a firm's profitability on an absolute basis. It is also a major component of calculating the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, where the E in P/E refers to EPS. By dividing a company's share price by its earnings per share, an investor can see the value of a stock in terms of how much the market is willing to …
Basic EPS vs. Diluted EPS
- The formula in the table above calculates the basic EPSof each of these select companies. Basic EPS does not factor in the dilutive effect of shares that could be issued by the company. When the capital structure of a company includes items such as stock options, warrants, or restricted stock units (RSU), these investments—if exercised—could increase the total number of shares outstan…
EPS Excluding Extraordinary Items
- Earnings per share can be distorted, both intentionally and unintentionally, by several factors. Analysts use variations of the basic EPS formula to avoid the most common ways that EPS may be inflated. Imagine a company that owns two factories that make cellphone screens. The land on which one of the factories sits has become very valuable as new developments have surrounde…
EPS from Continuing Operations
- A company started the year with 500 stores and had an EPS of $5.00. However, assume that this company closed 100 stores over that period and ended the year with 400 stores. An analyst will want to know what the EPS was for just the 400 stores the company plans to continue with into the next period. In this example, that could increase the EPS because the 100 closed stores wer…
EPS and Capital
- An important aspect of EPS that is often ignored is the capital that is required to generate the earnings (net income) in the calculation. Two companies could generate the same EPS, but one could do so with fewer net assets; that company would be more efficient at using its capital to generate income and, all other things being equal, would be a "better" company in terms of effici…
EPS and Dividends
- Although EPS is widely used as a way to track a company’s performance, shareholders do not have direct access to those profits. A portion of the earnings may be distributed as a dividend, but all or a portion of the EPS can be retained by the company. Shareholders, through their representatives on the board of directors, would have to change the portion of EPS that is distrib…
EPS and Price-To-Earnings
- Making a comparison of the P/E ratio within an industry group can be helpful, though in unexpected ways. Although it seems like a stock that costs more relative to its EPS when compared to peers might be “overvalued,” the opposite tends to be the rule. Regardless of its historical EPS, investors are willing to pay more for a stock if it is expected to grow or outperfor…