There is no way to know anything about who has shorted stuff or how concentrated the positions are in a few investors. Short positions are not even reported in 13 (F) institutional filings. I'll take the bonus points, though, and point you to the US Equity Short Interest data source at quandl.
How do I find out if a stock has been shorted?
For general shorting information about a company's stock, you can usually go to any website with a stock quote service. For more specific short-interest info (as shorted stocks are known), you would have to go to the stock exchange where the company is listed.
What is going short in stocks?
Going short, on the other hand, is what some investors do when they believe the stock is about to decrease and think they can take advantage of that. In short selling a stock, the investor doesn't actually own it.
Can You short a stock that you don't own?
Usually, when you short stock, you are trading shares that you do not own. For example, if you think the price of a stock is overvalued, you may decide to borrow 10 shares of ABC stock from your broker. If you sell them at $50 each, you can pocket $500 in cash.
Where can I find short interest in stocks?
However, the specific site you will need to visit will depend on the stock exchange in which the stock that you are seeking information for trades. For example, if the stock in question is traded on the Nasdaq, you would have to use Nasdaq Trader's Trading Data, where you can find Nasdaq's Monthly Short Interest Tool.
How to know if someone has shorted stuff?
There is no way to know anything about who has shorted stuff or how concentrated the positions are in a few investors. Short positions are not even reported in 13 (F) institutional filings.
Can you know how much of each underlying share you're borrowing?
No, except for funds who publicly advertise their investment strategy (2x Short S&P 500 ETF), and even then you don't know from day to day how much of each underlying share they're borrowing, or how many individuals are invested in the fund. And even if you could know the, say, top 10 shorters of some stock, how would you know for sure that, say, 5 of them aren't actually the same entity masquerading as 5 different ones? Or whether one of them is actually a fund with a million investors?
What happens when you short a stock?
When you short a stock, you expose yourself to a large financial risk. One famous example of losing money due to shorting a stock is the Northern Pacific Corner of 1901. Shares of the Northern Pacific Railroad shot up to $1,000.
How does shorting stock work?
How Shorting Stock Works. Usually, when you short stock, you are trading shares that you do not own. For example, if you think the price of a stock is overvalued, you may decide to borrow 10 shares of ABC stock from your broker. If you sell them at $50 each, you can pocket $500 in cash.
How to profit from a stock decline?
Two of the most common ways to profit from a stock's decline without shorting are options and inverse ETFs. Buying a put option gives you the right to sell a stock at a given "strike price," so the buyer hopes the stock goes down and they can make more money by selling at the strike price. Inverse ETFs contain swaps and contracts that effectively replicate a short position. For example, SQQQ is an inverse ETF that moves in the opposite direction of QQQ. If you believe the price of QQQ shares will go down, then shorting QQQ, buying a put option on QQQ, and buying shares in SQQQ will all allow you to profit from a move down.
What happens if you buy 10 shares of a stock for $250?
If the price of the stock goes down to $25 per share, you can buy the 10 shares again for only $250. Your total profit would be $250: the $500 profit you made at first, minus the $250 you spend to buy the shares back. But if the stock goes up above the $50 price, you'll lose money.
What happens if a stock goes up to $50?
But if the stock goes up above the $50 price, you'll lose money. You'll have to pay a higher price to repurchase the shares and return them to the broker's account. For example, if the stock were to go to $250 per share, you'd have to spend $2,500 to buy back the 10 shares you'd owe the brokerage.
What is the opposite of shorting a stock?
The opposite of shorting a stock is " going long ." That's how traders refer to opening a position with a buy order, as opposed to a sell order. In other words, the opposite of shorting a stock is buying it.
What is short selling?
Shorting stock, also known as "short selling," involves the sale of stock that the seller does not own or has taken on loan from a broker. 1 Investors who short stock must be willing to take on the risk that their gamble might not work.
Why do people sell short?
People may also sell short in order to hedge a long position. For instance, if you own call options (which are long positions) you may want to sell short against that position to lock in profits. Or, if you want to limit downside losses without actually exiting a long stock position you can sell short in a stock that is closely related or highly correlated with it.
How does a short sell work?
With short selling, a seller opens a short position by borrowing shares, usually from a broker-dealer, hoping to buy them back for a profit if the price declines . Shares must be borrowed because you can sell shares that do not exist. To close a short position, a trader buys the shares back on the market—hopefully at a price less than what they borrowed the asset—and returns them to the lender or broker. Traders must account for any interest charged by the broker or commissions charged on trades.
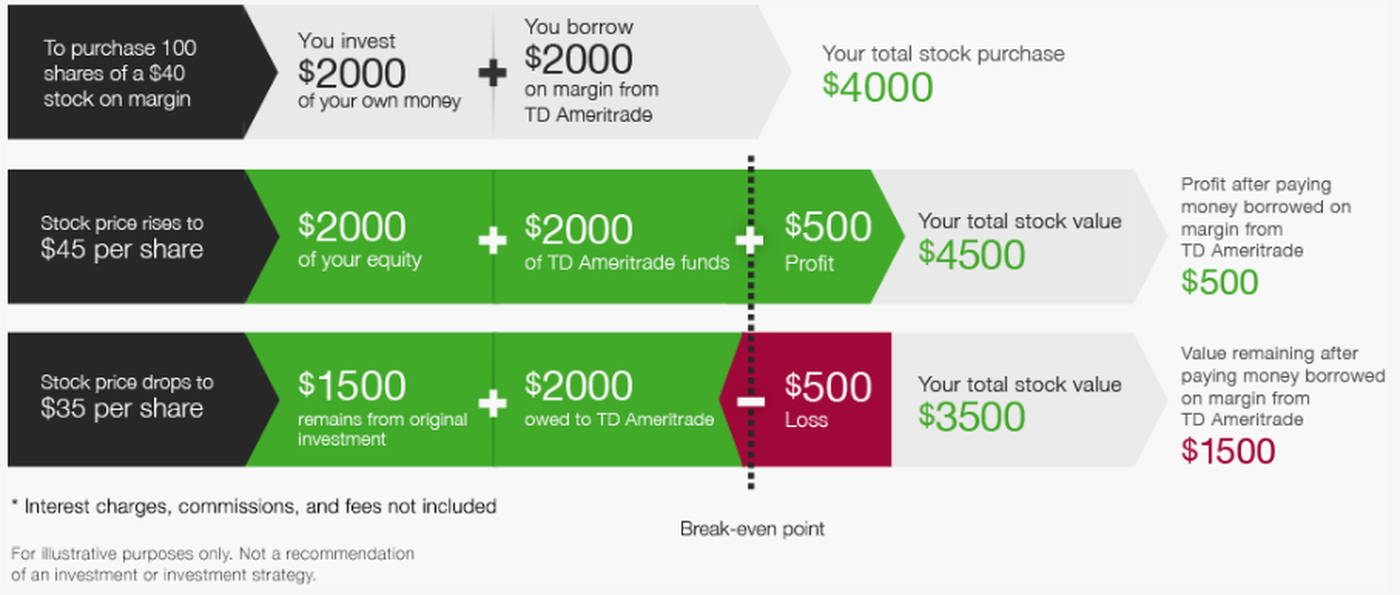
What is shorting margin?
Shorting is known as margin trading . When short selling, you open a margin account, which allows you to borrow money from the brokerage firm using your investment as collateral. Just as when you go long on margin, it's easy for losses to get out of hand because you must meet the minimum maintenance requirement of 25%. If your account slips below this, you'll be subject to a margin call and forced to put in more cash or liquidate your position. 1
How much did GE stock fall in 2019?
By the middle of 2016, GE’s share price had topped out at $33 per share and began to decline. By February 2019, GE had fallen to $10 per share, which would have resulted in a profit of $23 per share to any short sellers lucky enough to short the stock near the top in July 2016. 2.
Why do regulators ban short sales?
Regulators may sometimes impose bans on short sales in a specific sector, or even in the broad market, to avoid panic and unwarranted selling pressure. Such actions can cause a sudden spike in stock prices, forcing the short seller to cover short positions at huge losses.
Why are shares so hard to borrow?
Shares that are difficult to borrow—because of high short interest, limited float, or any other reason—have “ hard-to-borrow ” fees that can be quite substantial. The fee is based on an annualized rate that can range from a small fraction of a percent to more than 100% of the value of the short trade and is pro-rated for the number of days that the short trade is open.
What is short selling?
Short selling occurs when an investor borrows a security and sells it on the open market, planning to buy it back later for less money. Short-sellers bet on, and profit from, a drop in a security's price. This can be contrasted with long investors who want the price to go up.
What does it mean to short a stock?
Shorting a stock means opening a position by borrowing shares that you don't own and then selling them to another investor. Shorting, or selling short, is a bearish stock position -- in other words, you might short a stock if you feel strongly that its share price was going to decline. Short-selling allows investors to profit from stocks ...
What happens if you buy a stock?
When you buy a stock, the most you can lose is what you pay for it. If the stock goes to zero, you'll suffer a complete loss, but you'll never lose more than that. By contrast, if the stock soars, there's no limit to the profits you can enjoy.
What is short selling?
Short-selling allows investors to profit from stocks or other securities when they go down in value. In order to sell short, an investor has to borrow the stock or security through their brokerage company from someone who owns it. The investor then sells the stock, retaining the cash proceeds.
What is an alternative to shorting?
Alternative to shorting. As a final thought, an alternative to shorting that limits your downside exposure is to buy a put option on a stock. Essentially, a put option gives you the right, but not the obligation, to sell a stock at a predetermined price (known as the strike price) at any time before the option contract expires.
Why do investors buy stocks?
One reason for that is general market behavior . Most investors own stocks, funds, and other investments that they want to see rise in value. The stock market can fluctuate dramatically over short time periods, but over the long term it has a clear upward bias. For long-term investors, owning stocks has been a much better bet than short-selling the entire stock market. Shorting, if used at all, is best suited as a short-term profit strategy.
Is short selling a stock profitable?
Short-selling can be profitable when you make the right call, but it carries greater risks than what ordinary stock investors experience. Specifically, when you short a stock, you have unlimited downside risk but limited profit potential.
Can you buy a put option with a strike price of $100?
For example, if you buy a put option in a stock with a strike price of $100 and the stock drops to $60, you can then buy shares for $60 and exercise your option to sell them for $100, thereby profiting from the decline in the stock. So, the idea behind buying a put option is similar to shorting, although the most you can possibly lose is ...
What does it mean to go short on a stock?
Going short, on the other hand, is what some investors do when they believe the stock is about to decrease and think they can take advantage of that. In short selling a stock, the investor doesn't actually own it.
What are the pros and cons of shorting a stock?
A lot can happen. What if you short-sell a fledgling company that is suddenly bought out by a larger company and the shares rise? What if a company you view as overvalued doesn't come back down to earth as quickly as you thought it would? Your investment is not only at a loss, but your margin increases too.
Why do short sellers sell?
Many short-sellers are hedge funds, trying to protect themselves during a bearish market or worse. Short-selling is done at times, not just to possibly make a profit, but try to avoid any more disastrous losses. When the market is in a downturn, it can be difficult to find a stock you can profit from while buying.
Why is short selling a stock important?
Short-selling a stock gives investors the option to make money in environments where it has become harder to do so. It is also done to mitigate losses from a declining stock in your portfolio.
What is short selling a stock?
Short-selling a stock is how some investors try to take advantage of a declining company stock price. But it's risky, to say the least. Here's what you need to know. Short-selling a stock is how some investors try to take advantage of a declining company stock price. But it's risky, to say the least.
What happens if a short seller is wrong?
If the short-seller was wrong and the share value goes up, though, the margin requirement will increase as well, and he will need to put more money into the account.
How much can you lose on a short sale?
There's no limit to how much you could lose on an attempted short-sale. Waiting too long to stop a failed short-sale could devastate an investor financially, especially if they made too large an investment in it.
What happens if you short a stock?
But if you're shorting, there's no limit to how high a stock can go, so it makes your risk of loss infinite. Jones: That's really the scary part, when it comes to shorting.
What happens when you sell stock you don't own?
Your hope is that the price of the stock will go down so that you can buy them back and give those shares back to whoever you borrowed from at a cheaper price than you sold it for , profiting from the difference. For example, say I wanted to short Apple.
Why is short selling important?
Frankel: Yeah. Like you said, short-selling definitely adds to the efficiency of the market by allowing people to bet in both directions. It helps control bubbles if an asset gets too highly priced. Short sellers can come in and keep that in check. And, it provides investors with a hedging mechanism. If I own a portfolio of ten stocks and it's gone through the roof, I could short an ETF, like we're about to talk about, to try to mitigate my risk.
Is shorting important for long term investors?
It's really important to have a plan going into a shorting position. Like you said, generally, long-term investors are better off just buying stocks and holding them and not worrying about shorting. Jones: Exactly. We certainly don't knock shorting as an important component of our markets.
Is shorting a good move?
While shorting is a part of any healthy market, that doesn't mean it's the best move for you. If you think a stock is a little too expensive, it could seem like a smart idea to bet against it with a short position. However, the risk of unlimited losses can be quite scary, especially from a long-term point of view.
Is shorting a good investment strategy?
If done correctly, it could be a healthy investment strategy. But you really need to be careful. You need to have a clearly defined exit strategy if you initiate a short position. In my Amazon example, if you don't have an exit strategy, it could have gone on forever and ever. It's really important to have a plan going into a shorting position. Like you said, generally, long-term investors are better off just buying stocks and holding them and not worrying about shorting.
What does it mean when a stock is shorted?
So if a stock has a very high percentage of its shares being shorted, it means that there are more investors who need to buy shares at some point, whether the stock goes up or down.
What would happen if the percentage of shorts in a stock were to hit 100%?
If the percentage of shorts in a stock were to hit 100% that would mean that every single available share of a stock had been sold and would have to be bought back before being available to be sold again. (Note: In reality, 100% would be effectively impossible to see, but it is useful to explain this concept.)
Why are blue chip stocks so low short?
This is due to a number of factors, including the sheer amount of stock that is being held my mutual funds and other institutions, as well as the simple fact that anyone looking for a stock that could go down significantly will generally not be interested in these stocks, which are safer and significantly correlated to the broad economy.
What is Ask TheStreet?
Editor's Note: Ask TheStreet is designed to answer questions about the market, terms, strategies and investment methods. Please email us to ask a question, but keep in mind that we cannot offer specific investment- or stock-related advice.