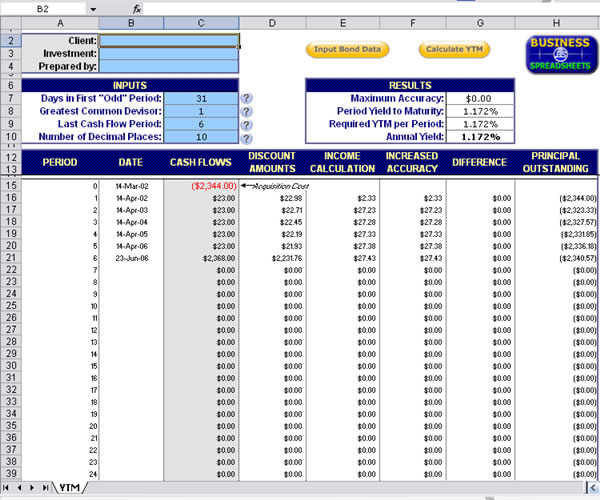
The formula for Bond Pricing calculation by using the following steps:
- Firstly, the face value or par value of the bond issuance is determined as per the funding requirement of the company.
- Now, the coupon rate, which is analogous to the interest rate of the bond and the frequency of the coupon payment, is...
- Now, the total number of periods till maturity is computed by...
Full Answer
How do you compute a bond price?
The basic steps required to determine the issue price are:
- Determine the interest paid by the bond. For example, if a bond pays a 5% interest rate once a year on a face amountof $1,000, the interest payment is $50.
- Find the present value of the bond. …
- Calculate present value of interest payments. …
- Calculate bond price. …
How to compute the effective rate of a bond?
Effective Interest Rate Formula. First, calculate the amount of the discount by subtracting the bond’s price from its face value. Second, divide the result by the number of bond payments remaining before the bond matures. Third, add the interest received per bond payment by the result.
What is the equation for bond price?
Example #1
- Given, F = $100,000
- C = 7% * $100,000 = $7,000
- n = 15
- r = 9%
How do you calculate the market value of a bond?
- IF c = r then the bond should be selling at par value.
- IF c <> r AND Bond price > F then the bond should be selling at a premium.
- IF c <> r AND Bond price < F then the bond should be selling at a discount.

How is a bonds value or price calculated?
Bond price is calculated as the present value of the cash flow generated by the bond, namely the coupon payment throughout the life of the bond and the principal payment, or the balloon payment, at the end of the bond's life.
What is the bond price in relation to stock prices?
Bonds affect the stock market because when bonds go down, stock prices tend to go up. The opposite also happens: when bond prices go up, stock prices tend to go down. Bonds compete with stocks for investors' dollars because bonds are often considered safer than stocks. However, bonds usually offer lower returns.
How do you calculate the selling price of a bond?
Definition of Selling Price of Bond Expressed another way, the current selling price, present value, or market value of a bond = the total of the semiannual interest payments PLUS the amount that will be received when the bond matures both discounted by the current market interest rate.
Is bond value and price the same?
The most important difference between the face value of a bond and its price is that the face value is fixed, while the price varies. Whatever amount is set for face value remains the same until the bond reaches maturity. On the other hand, bond prices can change dramatically.
Why do bond prices go up when stock prices fall?
The reason: stocks and bonds typically don't move in the same direction—when stocks go up, bonds usually go down, and when stocks go down, bonds usually go up—and investing in both typically provides protection for your portfolio.
Do stocks and bonds have inverse relationship?
What's the relationship between stocks and bonds? Bonds and shares have an inverse relationship but are both similarly affected by interest and inflation rates.
How are bonds calculated?
To calculate the value of a bond, add the present value of the interest payments plus the present value of the principal you receive at maturity. To calculate the present value of your interest payments, you calculate the value of a series of equal payments each over time.
How do you calculate the price of a bond using a financial calculator?
N = (Number of payments per period) x (Number of years to maturity) i = (Interest rate or YTM) / (Number of payments per period) FV = The Bond's Face Value. PMT = (FV) x (Coupon Rate) / (Number of payments per period)...Solving the problem using BA II Plus Financial CalculatorN = 18.I/Y = 4.FV = 1000.PMT = 30.
How do you calculate bond value in Excel?
Bond valuation examplerate - C6/C8 = 8%/2 = 4%nper - C7*C8 = 3*2 = 6.pmt - C5/C8*C4 = 7%/2*1000 = 35.fv - 1000.
What happens to bonds when stock market crashes?
While it's always possible to see a company's credit rating fall, blue-chip companies almost never see their rating fall, even in tumultuous economic times. Thus, their bonds remain safe-haven investments even when the market crashes.
What makes bond prices go up?
The most influential factors that affect a bond's price are yield, prevailing interest rates, and the bond's rating. Essentially, a bond's yield is the present value of its cash flows, which are equal to the principal amount plus all the remaining coupons.
What do higher bond yields mean for stock market?
Higher yields mean that bond investors are owed larger interest payments, but may also be a sign of greater risk. The riskier a borrower is, the more yield investors demand to hold their debts. Higher yields are also associated with longer maturity bonds.
How does this bond price calculator work?
This financial calculator approximates the selling price of a bond by considering these variables that should be provided:
Example of a result
Let’s assume that someone holds for a period of 10 years a bond with a face value of $100,000, with a coupon rate of 7% compounded semi-annually, while similar bonds on the market offer a rate of return of 6.5%. Let’s figure out its correct price in case the holder would like to sell it:
What is a bond?
In finance bonds are often referred to as fixed-income securities as they are a type of investment in which the holder (usually called as the investor) lends money to a bond issuer (usually governmental e.g: foreign governments, municipalities, states or corporate organizations) for a specific period of time while the borrower understands to pay to the investor a fixed interest rate, compounded by the rule negotiated and paid within certain terms.
What is the formula for bond pricing?
The formula for bond pricing is basically the calculation of the present value of the probable future cash flows, which comprises of the coupon payments and the par value, which is the redemption amount on maturity. The rate of interest which is used to discount the future cash flows is known as the yield to maturity (YTM.)
Why is bond pricing important?
The concept of bond pricing is very important because bonds form an indispensable part of the capital markets, and as such, investors and analysts are required to understand how the different factors of a bond behave in order to calculate its intrinsic value. Similar to stock valuation, the pricing of a bond is helpful in understanding whether it ...
What is a bond price? Understanding the dynamic of the bond price equation
Before we dive into calculating the current bond price with our bond valuation calculator, let's take some time to talk about what a bond is. A bond is one of the most prevalent fixed-income securities. When an entity issues bonds, it is considered as acquiring funding from investors through issuing debt.
How to calculate the bond price? The bond price formula
Bond price is calculated as the present value of the cash flow generated by the bond, namely the coupon payment throughout the life of the bond and the principal payment, or the balloon payment, at the end of the bond's life. You can see how it changes over time in the bond price chart in our calculator.
Bond price calculator's results - some more insights
Now that you understand the meaning of bond price and how to find bond price. Here are a few insights we wish to share with you:
How to find the dollars of interest paid annually?
To determine the dollars of interest paid annually, multiply the par value by the coupon rate. The call date (if a bond is callable) is essential information when evaluating a bond. The issuer of the bond may have the right to 'call' the bond prior to maturity. The date this can happen is the "call date".
What is the settlement date of a bond?
The settlement date is the date that the buyer and seller exchange cash and securities. Generally, the settlement date is one business day after the trade date for bonds of all types. The coupon rate is the rate of interest a bond pays annually. (Coupon interest, however, is most frequently paid semiannually.)
How long does a bond have to be matured?
Any maturity date is legally permissible; however, bonds usually have a maturity of between 10 and 40 years from the issue date. Redemption value or par value is the stated face value of the bond; it is often $1,000.
What is taxable equivalent yield?
Taxable equivalent yield is the yield one would have to earn if the yield-to-maturity is tax-free. (Macaulay) Duration is the weighted average of the time until the bond holder receives all the cash flows. Duration is always less than the time to maturity unless the bond is a zero coupon bond.
What is the dollar price of a bond?
A bond's dollar price represents a percentage of the bond's principal balance, otherwise known as par value. A bond is simply a loan, after all, and the principal balance, or par value, is the loan amount. So, if a bond is quoted at 99-29, and you were to buy a $100,000 two-year Treasury bond, you would pay $99,906.25.
What determines the discount rate of a bond?
That determines the current discount rate that is required to calculate the bond's price. The credit quality, or the likelihood that a bond's issuer will default, is also considered when determining the appropriate discount rate. The lower the credit quality, the higher the yield and the lower the price.
Why is it so hard to calculate the yield on a callable bond?
For example, calculating the yield on a callable bond is difficult because the date at which the bond might be called is unknown. The total coupon payment is unknown. However, for non-callable bonds such as U.S. Treasury bonds, the yield calculation used is a yield to maturity.
Why are bond prices good predictors of future economic activity?
When inflation expectations rise, interest rates rise, bond yields rise, and bond prices fall. That's why bond prices/yields, or the prices/yields of bonds with different maturities, are an excellent predictor of future economic activity.
What is yield in bond?
A yield relates a bond's dollar price to its cash flows. A bond's cash flows consist of coupon payments and return of principal. The principal is returned at the end of a bond's term, known as its maturity date .
What happens to a bond when it matures?
That is, if you buy a bond that pays 1% interest for 3 years, that's exactly what you'll get. And when the bond matures, its face value will be returned to you.
When is the coupon rate on a bond higher than the current interest rate?
In other words, the investor will receive interest payments from a premium-priced bond that are greater than could be found in the current market environment.
What is the value of a bond?
The value of a bond is the present value sum of its discounted cash flows. Bonds have a face value, a coupon rate, a maturity date, and a discount rate. The face value is the amount paid at maturity. The coupon rate is the interest rate paid to the investor.
Why is a bond issued at a premium?
The bond is issued at a premium when the coupon rate is greater than the discount rate. The bond's purchase price is greater than the face value. An investor is willing to pay more than the face value because the expected cash flow from the bond will be greater than the required rate of return.
What is discount rate in bond valuation?
The discount rate of bond valuation is subjective for each investor. It reflects the investor's evaluation of the entity issuing the bond in terms of how likely default might be. For example, a U.S. Treasury security will have a very low discount rate since the U.S. has never defaulted on its debts.
When is a bond discounted?
The bond is discounted when the coupon rate is less than the discount rate. The bond's purchase price is less than the face value. Because the expected cash flow from the bond is below the required rate of return, the investor will only purchase the bond when the price is below the face value.
What happens when the coupon rate is equal to the discount rate?
Again, in the particular case where the coupon rate is equal to the discount rate, then the bond's price is the same as its par value (since the bond cannot command a premium or require a discount).