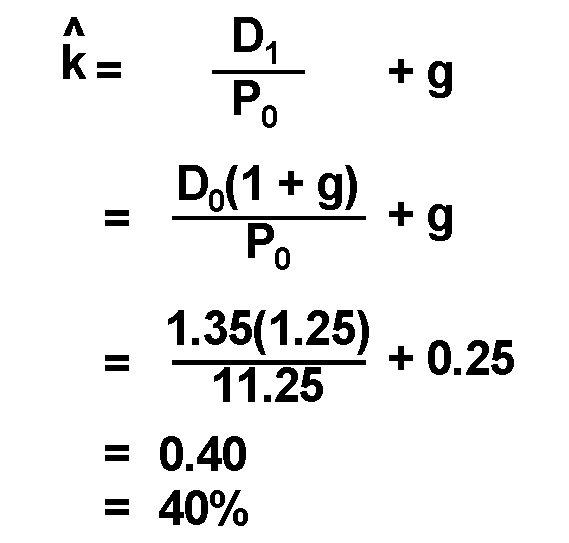The formula looks like this: Fair price = current annual dividend divided by (desired rate of return – expected rate of dividend growth) For example, consider a stock with a $5 annual dividend and an expected dividend growth rate of 4%. The investor’s required rate of return is 10%.
Full Answer
How do you calculate required rate of return on dividends?
Finally, the required rate return is calculated by dividing the expected dividend payment (step 1) by the current stock price (step 2) and then adding the result to the forecasted dividend growth rate (step 3) as shown below, Required rate of return formula = Expected dividend payment / Stock price + Forecasted dividend growth rate
How to calculate dividend growth rate?
1 Firstly, determine the dividend to be paid during the next period. 2 Next, gather the current price of the equity from the stock. 3 Now, try to figure out the expected growth rate of the dividend based on management disclosure, planning, and business forecast. More items...
How do you calculate the value of a stock with a dividend?
We will assume the company’s dividends will grow at 2 percent per year forever. Substitute the values into the dividend discount model: stock value = dividend per share/ (required rate of return - growth rate). In this example, substitute the values to get: stock value = $1.50/ (0.1 - 0.02).
When to use a more advanced formula for dividend growth?
A more advanced formula can be used when the future growth rate of dividends is not expected to be stable. The major weakness of the dividend growth model is that its accuracy is heavily dependent on correctly predicting dividend growth rates. Few companies consistently increase dividends at the same rate for long.

How do you calculate the dividend growth rate?
Mathematically, this dividend growth rate formula can be expressed as : Dividend growth rate= (Dn/D0)1/n-1.
How do you calculate dividend growth rate with roe and payout ratio?
The most basic equation is: Growth = ROE × (1 - payout ratio). E.g. if the company pays 40% of its earnings as dividends and its ROE = 15%, then its growth will be 15% * (1-. 4) = 9%.
How do you find the growth rate of a stock?
Growth rates are computed by dividing the difference between the ending and starting values for the period being analyzed and dividing that by the starting value. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is a variation on the growth rate often used to assess an investment or company's performance.
How do you calculate dividend growth rate in Excel?
0:469:47Calculating the Dividend Growth Rate - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe rate of change. From period to period and then we'll just take an average. So the rate of changeMoreThe rate of change. From period to period and then we'll just take an average. So the rate of change between $1 and $1.00 5 is actually quite easy you can probably just look at it and figure out that
What is dividend growth rate?
The dividend growth rate (DGR) is the percentage growth rate of a company's dividend achieved during a certain period of time. Frequently, the DGR is calculated on an annual basis. However, if necessary, it can also be calculated on a quarterly or monthly basis.
How do you calculate growth rate from payout ratio?
You calculate the sustainable growth rate by taking the company's return on equity times the result of 1 minus the dividend payout ratio. Another way to calculate it is to multiply the retention rate by the return on equity.
Is dividend yield the same as dividend growth rate?
Key Takeaways. A company's dividend or dividend rate is expressed as a dollar figure and is the combined total of dividend payments expected. The dividend yield is expressed as a percentage and represents the ratio of a company's annual dividend compared to its share price.
How is dividend payout ratio calculated?
The dividend payout ratio can be calculated as the yearly dividend per share divided by the earnings per share (EPS), or equivalently, or divided by net income dividend payout ratio on a per share basis. In this case, the formula used is dividends per share divided by earnings per share (EPS).
How do you calculate growth opportunity?
As a proportion of market cap, PVGO can then also be used in relative valuation, i.e. when comparing between two investments (see similar re PEG ratio). PVGO is calculated as follows: PVGO = share price − earnings per share ÷ cost of capital.
What is the Plowback ratio formula?
The plowback ratio is a simple metric showing the ratio of earnings retained by the company (i.e., not paid out as a dividend) to the total earnings. The formula is as follows: Plowback Ratio = 1 - Payout Ratio (Earnings Per Share / Dividends Per Share) For example, a company earns $10 per share.
How is payout ratio calculated?
Payout Ratio = Total Dividends / Net Income The payout ratio formula can also be expressed as dividends per share divided by earnings per share (EPS).
What is the dividend growth rate?
What is Dividend Growth Rate? The dividend growth rate is the rate of growth of dividend over the previous year; if 2018’s dividend is $2 per share and 2019’s dividend is $3 per share, then there is a growth rate of 50% in the dividend. Although it is usually calculated on an annual basis, it can also be calculated on a quarterly ...
What does a strong dividend growth history mean?
For instance, a strong dividend growth history could indicate likely future dividend growth, which is a sign of long-term profitability#N#Profitability Profitability refers to a company's ability to generate revenue and maximize profit above its expenditure and operational costs. It is measured using specific ratios such as gross profit margin, EBITDA, and net profit margin. It aids investors in analyzing the company's performance. read more#N#for the stock. Further, a financial user can use any interval for the dividend growth calculation. This concept is also essential because it is primarily used in the dividend discount model, which finds extensive application in the determination of security pricing.
How to calculate dividend growth rate?
To calculate the annual dividend growth rate, for example, you will need to compare the dividend payment from one year to the next, using the following formula: (year 2 value / year 1 value) - 1.
What is dividend growth model?
One of the most well-known dividend growth models is the Gordon Growth Model, which is based on the assumption that a company’s dividends will experience constant growth.
What does higher dividend yield mean?
A higher yield means the shareholder will receive more money ...
Is dividend growth a good investment?
When dividend growth rates are consistent and trending up, they suggest a good investment to potential shareholders, as well as being indicative of a bright future for the company itself. Looking at dividend growth rates alone, however, can be a trap when looking to invest. If a company’s dividend growth rate fluctuates wildly;
Does Sharesight include dividends?
Because dividends can have a significant impact on returns, Sharesight includes dividends in its performance calculations, along with capital gains and losses, brokerage fees and currency fluctuations, giving investors a more accurate picture of their returns.
Do dividends increase over time?
Dividend growth rates also vary by business cycles and only rarely increase indefinitely over time. Typically, companies will try to increase the rate of dividends they pay to their shareholders year on year in order to return value to investors who own the stock.
What is dividend growth rate?
The dividend growth rate is the annualized percentage rate of growth that a particular stock's dividend undergoes over a period of time. Many mature companies seek to increase the dividends paid to their investors on a regular basis.
What is dividend discount model?
The dividend discount model is based on the idea that a stock is worth the sum of its future payments to shareholders, discounted back to the present day.
How to calculate required rate of return?
For stock paying a dividend, the required rate of return (RRR) formula can be calculated by using the following steps: 1 Firstly, determine the dividend to be paid during the next period. 2 Next, gather the current price of the equity from the stock. 3 Now, try to figure out the expected growth rate of the dividend based on management disclosure, planning, and business forecast. 4 Finally, the required rate return is calculated by dividing the expected dividend payment (step 1) by the current stock price (step 2) and then adding the result to the forecasted dividend growth rate (step 3) as shown below,#N#Required rate of return formula = Expected dividend payment / Stock price + Forecasted dividend growth rate
How to calculate risk premium?
Step 1: Firstly, determine the risk-free rate of return, which is basically the return of any government issues bonds such as 10-year G-Sec bonds. Step 2: Next, determine the market rate of return, which is the annual return of an appropriate benchmark index such as the S&P 500 index. Based on this, the market risk premium can be calculated by ...
Why is it important to understand the concept of the required return?
It is important to understand the concept of the required return as it is used by investors to decide on the minimum amount of return required from an investment. Based on the required returns, an investor can decide whether to invest in an asset based on the given risk level.
How to calculate dividend growth?
The formula for the dividend growth model, which is one approach to dividend investing, requires knowing or estimating four figures: 1 The stock’s current price 2 The current annual dividend 3 The investor’s required rate of return 4 The expected rate at which dividends will increase
Why use dividend growth model?
Because of this, investors who use the dividend growth model need to monitor the stocks they are modeling and promptly update their models as new information becomes available. Ultimately, dividend growth modeling is just one way to assess whether a security is trading at a fair price and is an attractive investment.
How does dividend growth work?
Dividend growth modeling uses a mathematical formula to assess the fair value of a security. It uses figures for current trading price, current annual dividend, expected future dividend growth rate and required rate of return. By plugging these figures into the formula an investor can estimate how far a security is from its fair value. Just remember: this model is just one of several ways to evaluate a stock’s price, and the model calls for making a number of assumptions that may not match what eventually happens.
What is the weakness of dividend growth?
The major weakness of the dividend growth model is that its accuracy is heavily dependent on correctly predicting dividend growth rates. Few companies consistently increase dividends at the same rate for long.
How many members are there in Dividend Aristocrats?
These are companies that have increased their dividends annually for at last 25 years. There are approximately 60 members of the Dividend Aristocrats group. Their reliable dividend increases make it easier to forecast their future dividend growth, which can boost the accuracy of dividend growth models.
Is dividend growth easy to perform?
The dividend growth model is relatively easy to perform and can provide a helpful way to decide whether or not to invest in a particular security. Just keep in mind that the assumptions used may not turn out to be accurate. A financial advisor can help you as you develop your dividend investing strategy and tactics.
Is there a guarantee that an investor will achieve this rate of return?
Of course, there is no guarantee an investor will achieve this rate of return. The expected dividend growth requires another significant assumption. Generally, this is arrived at by looking at the historical trend of a company’s dividend growth.
What is supernormal growth?
The purpose of the supernormal growth model is to value a stock that is expected to have higher than normal growth in dividend payments for some period in the future. After this supernormal growth, the dividend is expected to go back to normal with constant growth.
Why is supernormal growth so difficult?
Calculations using the supernormal growth model are difficult because of the assumptions involved, such as the required rate of return, growth or length of higher returns. If this is off it could drastically change the value of the shares. In most cases, such as tests or homework, these numbers will be given. But in the real world, we are left to calculate and estimate each of the metrics and evaluate the current asking price for shares. Supernormal growth is based on a simple idea, but can even give veteran investors trouble.
What is the most important skill an investor can learn?
Updated Jun 25, 2019. One of the most important skills an investor can learn is how to value a stock. It can be a big challenge though, especially when it comes to stocks that have supernormal growth rates. These are stocks that go through rapid growth for an extended period of time, say, for a year or more. Many formulas in investing, though, are ...
What is preferred equity?
Preferred equity will usually pay the stockholder a fixed dividend, unlike common shares. If you take this payment and find the present value of the perpetuity, you will find the implied value of the stock.
Can you use a constant growth rate?
Sometimes when you're presented with a growth company, you can't use a constant growth rate. In these cases, you need to know how to calculate value through both the company's early, high growth years, and its later, lower constant growth years. It can mean the difference between getting the right value or losing your shirt .
What does discount rate mean in stock market?
It uses a discount rate to convert all of the stock’s expected future dividend payments into a single, theoretical stock price, which you can compare to the actual market price. If the market price is greater than the model’s price, the market may be overvaluing the stock.
What is the difference between a stock with less risk and a stock with more risk?
A stock with more risk has a higher required rate of return, while a stock with less risk has a lower required rate of return. In this example, assume you require a 10 percent rate of return on the stock. Estimate the stable rate at which you expect the company and its dividend payments to grow per year forever.