
Generally, dividend rates are quoted in terms of dollars per share, or they may be quoted in terms of a percentage of the stock's current market price per share, which is known as the dividend yield. Key Takeaways Dividend stock ratios are an indicator of a company's ability to pay dividends to its shareholders in the future.
How often are dividends paid to stockholders?
Dividends are normally paid every quarter. The dividend yield is the annual payout divided by the current stock price. Dividends change when stock prices rise and fall. A corporation may also change the size of a dividend. Corporations do not need to change dividend amounts when the common stock price changes.
What is a stock dividend and how does it work?
As noted above, a stock dividend increases the number of shares while also decreasing the share price. By lowering the share price through a stock dividend, a company’s stock may be more “affordable” to the public.
Are dividends paid per share or per share owned?
Are Dividends Paid per Shares Owned? Dividends are payments from companies to their shareholders, usually either in the form of cash or additional stock. Cash dividends are paid on the basis of the number of shares you own, so if you own 100 shares you will receive 100 times as much from a dividend as someone who owns one share of the stock.
How are dividends paid out?
How Dividends Are Paid Out A dividend is the distribution of some of a company's earnings to a class of its shareholders. Dividends are usually paid in the form of a dividend check. However, they may also be paid in additional shares of stock.
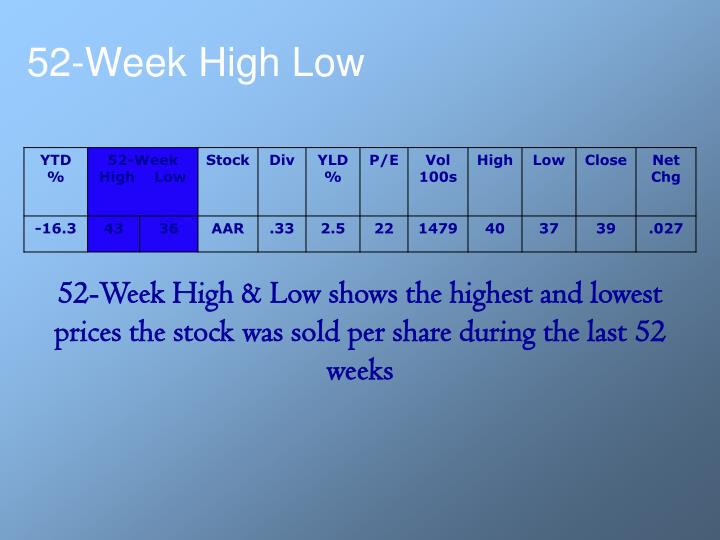
Are dividends a percentage of stock price?
The dividend yield is a financial ratio that tells you the percentage of a company's share price that it pays out in dividends each year. For example, if a company has a $20 share price and pays a dividend of $1 per year, its dividend yield would be 5%.
What price are dividends based on?
Dividends per share (DPS) measures the total amount of profits a company pays out to its shareholders, generally over a year, on a per-share basis. DPS can be calculated by subtracting the special dividends from the sum of all dividends over one year and dividing this figure by the outstanding shares.
Are dividends paid per share or value?
A dividend is paid per share of stock — if you own 30 shares in a company and that company pays $2 in annual cash dividends, you will receive $60 per year.
How are dividends paid on stocks?
The standard practice for the payment of dividends is a check that is mailed to stockholders a few days after the ex-dividend date, which is the date on which the stock starts trading without the previously declared dividend.
How do you calculate a dividend?
To calculate the DPS from the income statement:Figure out the net income of the company. ... Determine the number of shares outstanding. ... Divide net income by the number of shares outstanding. ... Determine the company's typical payout ratio. ... Multiply the payout ratio by the net income per share to get the dividend per share.
Which stock has the highest dividend?
9 highest dividend-paying stocks in the S&P 500:AT&T Inc. (T)Williams Cos. Inc. (WMB)Devon Energy Corp. (DVN)Oneok Inc. (OKE)Simon Property Group Inc. (SPG)Kinder Morgan Inc. (KMI)Vornado Realty Trust (VNO)Altria Group Inc. (MO)More items...•
Am I taxed on dividends that are reinvested?
Dividends are taxable regardless of whether you take them in cash or reinvest them in the mutual fund that pays them out. You incur the tax liability in the year in which the dividends are reinvested.
Do you pay tax on dividends?
You do not pay tax on any dividend income that falls within your Personal Allowance (the amount of income you can earn each year without paying tax)....Working out tax on dividends.Tax bandTax rate on dividends over the allowanceBasic rate8.75%Higher rate33.75%Additional rate39.35%
What is a good dividend yield?
between 2% and 6%Dividend yield can help investors evaluate the potential profit for every dollar they invest, and judge the risks of investing in a particular company. A good dividend yield varies depending on market conditions, but a yield between 2% and 6% is considered ideal.
Do dividends have to be paid equally?
A company will be unable to pay different rates of dividend to its shareholders unless it is clearly provided for. Failure to do so can result in the dividend being unlawful, resulting in the company's directors being in breach of their legal duties.
Can you get rich from dividend stocks?
Yes, dividends can make you rich. However, it requires regular investment in high-quality dividend stocks, low investment costs, a tax minimization strategy, and a great deal of time in the market.
Does Warren Buffett reinvest dividends?
While Berkshire Hathaway itself does not pay a dividend because it prefers to reinvest all of its earnings for growth, Warren Buffett has certainly not been shy about owning shares of dividend-paying stocks.
How long do you have to hold a stock to get a dividend?
Briefly, in order to be eligible for payment of stock dividends, you must buy the stock (or already own it) at least two days before the date of record and still own the shares at the close of trading one business day before the ex-date.
How often do you get dividends from stocks?
quarterlyDividends are typically paid on a quarterly basis, though some pay annually, and a small few pay monthly. Companies that pay dividends are usually more stable and established, not those still in the rapid growth phase of their life cycles.
How do I know when dividends are paid?
Dividends are paid on the date designated by a company's board of directors as the payment date. The board announces this date on the dividend declaration date. Their decision to issue a payment is based on their review of the company's financial statements, to see if the entity can afford to pay investors.
Can you buy a stock just before the dividend?
Dividend capture specifically calls for buying a stock just prior to the ex-dividend date in order to receive the dividend, then selling it immediately after the dividend is paid. The purpose of the two trades is simply to receive the dividend, as opposed to investing for the longer term.
What is dividend payout?
A dividend is simply a percentage of the profits a company makes that’s paid out to shareholders. Some companies pay out 100% of earnings to investors while others pay less. And some companies don’t offer any type of dividend payout at all. Dividends can be paid in cash or in shares of stock.
How often do dividends come out?
Generally, companies can pay out stock dividends quarterly though some may do so monthly or annually. In terms of when dividends are paid out and who’s eligible to receive them, there are several key dates to know. Many investors have found that working with a financial advisor was a major part of their success.
Why is it important to have a higher dividend yield?
A higher dividend yield could make a stock look more attractive, but it’s important to consider how sustainable it is over time. Dividend per share refers to how much a company distributes in dividends for each of its shares of outstanding stock.
How do dividends work?
How Dividend Payouts Work. If you buy into a dividend-paying stock you might automatically assume that you’ll receive the next dividend payment. But there are some key dates companies use to determine who gets a dividend payment. First, there’s the declaration date.
What is the record date for dividends?
Next is the record date. The record date is the date that you must be on the company’s books as a shareholder to receive a dividend payment. Any shareholders listed in the company records on the date of record are eligible to receive a declared dividend payout.
What is a special dividend?
In some cases, a company can also issue what’s known as a special dividend. This is a one-time payment you receive in addition to regular dividend payouts. Companies may choose to offer a special dividend following a stronger than usual earnings period.
What happens before dividends are paid?
Before dividends can be paid out, the payments have to be approved by the company’s board of directors. Once this happens, the company will announce when the dividends are to be paid out to investors.
What does dividend yield mean?
A stock's dividend yield tells you how much dividend income you receive, compared to the current price of the stock. Buying stocks with a high dividend yield can provide a good source of income, but there are other factors to take into account.
How to find dividend yield?
The formula for finding a dividend yield is simple: Divide the yearly dividend payments by the stock price.
Why do dividend stocks decrease in value?
During a recession or other times of hardship, dividend-paying stocks can quickly decrease in value, because there is a risk that the firm will reduce payouts in the future. If a company says that it's cutting its dividend, the stock price will react right away.
How to find the yield of a stock?
But the company has not announced a change to the dividend payment. So, if you just found the stock, you would use previous dividend payments to figure out the yield. You would divide $0.40 (the yearly dividend payment) by $5 (the new stock price) to get 0.08, or an 8% yield.
What to do if you don't want to study stocks?
If you don't want to study and purchase individual stocks, you can invest in a dividend income fund instead. These funds allow you to diversify your portfolio while letting experts make the hard choices about which stocks to buy and when to buy them.
What is dividends?
A dividend is how a firm returns profits directly to its shareholders. 1 Companies aren't required to issue dividends, so there isn't a set rule about which will and which ones won't. Even if a company has issued dividends in the past, it may stop at any time.
Why do companies pay dividends?
Companies pay dividends as a way to attract investors by sharing profits with them. This approach may not work for smaller companies that don't yet have enough profits to share, but for established companies, it's a way to draw income investors.
How do companies decide on dividend payments?
In general, a company's board of directors is responsible for its dividend policy and determining the size of a dividend payment. Depending on a company's growth goals, industry, and other factors , the board will determine an appropriate dividend payment.
How do stocks pay dividends?
The short answer is that a company pays a dividend out of its earnings. When a company earns a profit, it has essentially three things it can do:
When do stocks make dividend payments?
The vast majority of dividend stocks pay dividends quarterly, although there are some companies that make dividend payments monthly and a very small number that make annual and semiannual dividend payments.
How do you get dividend payments?
While some investors own stocks in company-sponsored direct stock purchase plans and receive the dividend directly from the company, the vast majority own stocks through a broker. In this case, the dividend payments come to your brokerage and are deposited in your brokerage account.
What determines the appropriate dividend payment?
Depending on a company's growth goals, industry, and other factors, the board will determine an appropriate dividend payment . This can vary from one industry to the next and among companies in different growth phases. Industries that are lower growth but generate stable earnings and cash flows, such as utility companies, ...
How long does it take for dividends to show up in checking account?
For this reason, your dividend payment may not appear in your account on the payment date in the company's release declaring it -- it could be a day or two before the money shows up. This is particularly important if you are counting on those dividend payments for income since you may need to allow for a few more days to transfer the cash from your brokerage account into your checking or savings account.
How to determine when a stock will pay dividends?
When a company's board of directors determines the next dividend, it will declare the dividend, typically in a press release or in a filing with the Securities and Exchange Commission , or SEC. This release will disclose the amount of the dividend, the dividend payment date, ...
What Is a Dividend Payout Ratio?
The dividend payout ratio is the ratio of the total amount of dividends paid out to shareholders relative to the net income of the company. It is the percentage of earnings paid to shareholders via dividends. The amount that is not paid to shareholders is retained by the company to pay off debt or to reinvest in core operations. It is sometimes simply referred to as simply the payout ratio.
What does the payout ratio tell you?
The payout ratio is a key financial metric used to determine the sustainability of a company’s dividend payment program. It is the amount of dividends paid to shareholders relative to the total net income of a company.
Is a high dividend payout ratio good?
A high dividend payout ratio is not always valued by active investors. An unusually high dividend payout ratio can indicate that a company is trying to mask a bad business situation from investors by offering extravagant dividends, or that it simply does not plan to aggressively use working capital to expand.
How to calculate augmented payout ratio?
The augmented payout ratio incorporates share buybacks into the metric; it is calculated by dividing the sum of dividends and buybacks by net income for the same period. If the result is too high, it can indicate an emphasis on short-term boosts to share prices at the expense of reinvestment and long-term growth.
Why is payout ratio important?
The payout ratio is also useful for assessing a dividend's sustainability. Companies are extremely reluctant to cut dividends since it can drive the stock price down and reflect poorly on management's abilities. If a company's payout ratio is over 100%, it is returning more money to shareholders than it is earning and will probably be forced to lower the dividend or stop paying it altogether. That result is not inevitable, however. A company endures a bad year without suspending payouts, and it is often in their interest to do so. It is therefore important to consider future earnings expectations and calculate a forward-looking payout ratio to contextualize the backward-looking one.
What is dividend yield?
The dividend yield shows how much a company has paid out in dividends over the course of a year about the stock price. The yield is presented as a percentage, not as an actual dollar amount. This makes it easier to see how much return per dollar invested the shareholder receives through dividends.
How to calculate dividends per share?
First, if you are given the sum of the dividends over a certain period and the outstanding shares, you can calculate the dividends per share (DPS). Suppose you are invested in a company that paid a total of $5 million last year and it has 5 million shares outstanding. On Microsoft Excel, enter "Dividends per Share" into cell A1. Next, enter "=5000000/5000000" in cell B1; the dividend per share in this company is $1 per share.
How do corporations pay dividends?
Corporations pay dividends out of retained earnings -- the accumulated profits of the company. Dividends are normally paid every quarter. The dividend yield is the annual payout divided by the current stock price. Dividends change when stock prices rise and fall. A corporation may also change the size of a dividend. Corporations do not need to change dividend amounts when the common stock price changes. However, a corporation committed to a particular dividend yield will need to increase the payout if the common stock price rises. When a stock price rises because of increased profits, the corporation might decide to boost dividends to “share the wealth” with stockholders, but it’s optional.
Why are dividend stocks attractive?
Income-oriented investors find such stocks attractive because the dividend yield relative to their purchase price rises over time.
What is a common stock dividend?
They provide current income to investors and help stabilize the stock price. Common stock dividends are optional and can change over time. A corporation fixes preferred stock dividends at the time it issues the stock.
When do dividends change?
Dividends change when stock prices rise and fall. A corporation may also change the size of a dividend. Corporations do not need to change dividend amounts when the common stock price changes. However, a corporation committed to a particular dividend yield will need to increase the payout if the common stock price rises.
Does preferred stock change over time?
Preferred Stock. The dividends on preferred stock do not change over time. This has the effect of divorcing the value of preferred shares from the growth of the company.Traders price preferred shares based on their dividend yield relative to prevailing interest rates. If interest rates rise, preferred share prices fall and the dividend yield rises, ...
Do preferred shares have to be paid before common stock dividends?
“Cumulative” preferred shares also require that any missed dividends be paid before common stock dividends may be paid.
Can a missed dividend be a default?
A missed interest payment can throw a company into default and bankruptcy, but a cut or missed dividend payment does not result in default. For this reason, when a corporation's board of directors evaluates its response to low cash reserves, it will suspend the dividend rather than default on an interest payment. 00:00.
What Are Dividends?
"Money for Nothing" is not only the title of a song by the band Dire Straits from the 1980s, but it is also the feeling many investors get when they receive a dividend. All you have to do is buy shares in the right company, and you'll receive some of its earnings. How exciting is that?
How many shares are issued in 11 to 10 stock split?
For instance, if instead of a 10% stock dividend, the above company declares an 11-to-10 stock split, the 100 million shares are called in, and 110 million new shares are issued, each with a par value of $0.227. This leaves the common stock at par value account's total unchanged. The retained earnings account is not reduced either.
How does a dividend reduce retained earnings?
Dividend payments, whether cash or stock, reduce retained earnings by the total amount of the dividend. In the case of a cash dividend, the money is transferred to a liability account called dividends payable. This liability is removed when the company makes the payment on the dividend payment date, usually a few weeks after the ex-dividend date.
Why does the stock market adjust to limit orders?
Because the downward adjustment of the stock price might trigger the limit order, the exchange also adjusts outstanding limit orders. The investor can prevent this if his or her broker permits a do not reduce (DNR) limit order. Note, however, that not all exchanges make this adjustment. The U.S. exchanges do, but the Toronto Stock Exchange, for example, does not.
Why is the dividend adjustment made?
The reason for the adjustment is that the amount paid out in dividends no longer belongs to the company, and this is reflected by a reduction in the company's market cap. Instead, it belongs to the individual shareholders.
How much will retained earnings be reduced if 100 million shares are outstanding?
For instance, if the dividend was $0.025 per share, and 100 million shares are outstanding, retained earnings will be reduced by $2.5 million, and that money eventually makes its way to the shareholders.
What is the basis of a stock split?
The basis is also adjusted in the case of stock splits and stock dividends. For the investor, these are treated the same way. Taking our 10% stock dividend example, assume you hold 100 shares of the company with a basis of $11. After the payment of the dividend, you would own 110 shares with a basis of $10. The same would hold true if the company had an 11-to-10 split instead of that stock dividend.
How do dividends work?
Dividends are payments from companies to their shareholders, usually either in the form of cash or additional stock. Cash dividends are paid on the basis of the number of shares you own, so if you own 100 shares you will receive 100 times as much from a dividend as someone who owns one share of the stock. You must own the stock before ...
What is the ratio of dividends paid out per share?
The ratio of the total dividend amount paid out per share in a year to the share price is called the dividend yield, and it's usually written as a percentage. For instance, a company with a share price of $10 per share paying 30 cents per share in dividends over a year would have a 3 percent dividend yield.
How much do dividends depend on?
How much you get from a dividend payment depends on how many shares of the company's stock you own , and whether you receive any dividend payment at all depends on when you own the stock.
Why is dividend yield per share important?
For a stock with a relatively stable share price, looking at dividend yield per share can be a good, simple way to compare an investment to other opportunities like interest-paying bonds or bank accounts. It can also be useful to compare per-share dividend yields between similar stocks, such as stocks in the same industry, to decide which is worth investing in.
What is dividend in stock?
A dividend is the term for a company returning a share of its profits to investors. A cash dividend is paid based on how many shares of the company you own, so a company might declare a dividend of some amount like 10 cents per share. Some companies have different classes of stock, such as preferred stock and common stock, ...
Why do companies split their stock?
Stock splits are often done to increase or reduce the stock price to make the stock desirable and affordable to a larger group of potential investors. Stock splits can also lead to investors owning fractional shares in a company.
Why do people buy stocks?
Some of that may come from selling the stock at a higher price in the future, but in many cases some of the reward comes from a dividend paid by the stock-issuing company.
How are dividends paid?
A dividend is the distribution of some of a company's earnings to a class of its shareholders. Dividends are usually paid in the form of a dividend check. However, they may also be paid in additional shares of stock. The standard practice for the payment of dividends is a check that is mailed to stockholders ...
What is dividend distribution?
A dividend is the distribution of some of a company's earnings to a class of its shareholders. If a company elects to distribute dividends, usually, both the date and the amount is determined on a quarterly basis, after a company finalizes its income statement and the board of directors meets to review the company's financials.
What happens if you pay dividends?
If dividends are paid, a company will declare the amount of the dividend, and all holders of the stock (by the ex-date) will be paid accordingly on the subsequent payment date. Investors who receive dividends may decide to keep them as cash or reinvest them in order to accumulate more shares.
How do you know if a company has declared dividends?
If a dividend is declared, all qualified shareholders of the company are notified via a press release; the information is usually reported through major stock quoting services for easy reference. The key dates that an investor should look for are:
What is the ex-date on a stock?
The day preceding the record date is called the ex-date, or the date the stock begins trading ex-dividend. This means that a buyer on ex-date is purchasing shares that are not entitled to receive the most recent dividend payment. The payment date is usually about one month after the record date.
How long after record date is a payment due?
The payment date is usually about one month after the record date.
When is a dividend declared?
If a company has excess earnings and decides to pay a dividend to common shareholders, then an amount is declared, in addition to the date when this amount will be paid out to the shareholders. Usually, both the date and the amount is determined on a quarterly basis, after a company finalizes its income statement and the board of directors meets to review the company's financials.
What is a high yield stock?
Some stocks have higher yields, which may be very attractive to income investors. Under normal market conditions, a stock that offers a dividend yield greater than that of the U.S. 10-year Treasury yield is considered a high-yielding stock. As of June 5, 2020, the U.S. 10-year Treasury yield was 0.91%. 1 Therefore, any company that had a trailing 12-month dividend yield or forward dividend yield greater than 0.91% was considered a high-yielding stock. However, prior to investing in stocks that offer high dividend yields, investors should analyze whether the dividends are sustainable for a long period. Investors who are focused on dividend-paying stocks should evaluate the quality of the dividends by analyzing the dividend payout ratio, dividend coverage ratio, free cash flow to equity (FCFE), and net debt to earnings before interest taxes depreciation and amortization (EBITDA) ratio.
What are the four most common ratios?
The four most popular ratios are the dividend payout ratio, dividend coverage ratio, free cash flow to equity, and Net Debt to EBITDA. Mature companies no longer in the growth stage may choose to pay dividends to their shareholders. A dividend is a cash distribution of a company's earnings to its shareholders, which is declared by ...
How to calculate dividend payout ratio?
The dividend payout ratio may be calculated as annual dividends per share (DPS) divided by earnings per share (EPS) or total dividends divided by net income. The dividend payout ratio indicates the portion of a company's annual earnings per share that the organization is paying in the form of cash dividends per share. Cash dividends per share may also be interpreted as the percentage of net income that is being paid out in the form of cash dividends. Generally, a company that pays out less than 50% of its earnings in the form of dividends is considered stable, and the company has the potential to raise its earnings over the long term. However, a company that pays out greater than 50% may not raise its dividends as much as a company with a lower dividend payout ratio. Additionally, companies with high dividend payout ratios may have trouble maintaining their dividends over the long term. When evaluating a company's dividend payout ratio, investors should only compare a company's dividend payout ratio with its industry average or similar companies.
What is dividend ratio?
Dividend Ratios. Dividend stock ratios are used by investors and analysts to evaluate the dividends a company might pay out in the future. Dividend payouts depend on many factors such as a company's debt load, its cash flow, its earnings, its strategic plans and the capital needed for them, its dividend payout history, and its dividend policy.
Why is a low dividend payout ratio considered preferable to a high dividend ratio?
A low dividend payout ratio is considered preferable to a high dividend ratio because the latter may indicate that a company could struggle to maintain dividend payouts over the long term. Investors should use a combination of ratios to evaluate dividend stocks.
What is dividend in business?
A dividend is a cash distribution of a company's earnings to its shareholders, which is declared by the company's board of directors. A company may also issue dividends in the form of stock or other assets.
How is FCFE calculated?
The FCFE is calculated by subtracting net capital expenditures, debt repayment, and change in net working capital from net income and adding net debt. Investors typically want to see that a company's dividend payments are paid in full by FCFE.
